How Big Is 500 000 Square Feet

Five hundred thousand square feet: a seemingly abstract measurement that’s increasingly relevant in today's world of sprawling logistics centers, gargantuan data farms, and ambitious real estate developments. But what does that actually look like? Grasping the magnitude of such a vast space is crucial for comprehending the scale of modern infrastructure and its impact on our lives.
This article aims to translate the abstract concept of 500,000 square feet into relatable terms, offering concrete comparisons to familiar landmarks and structures. We'll explore how this measurement manifests across various sectors, from commercial real estate to industrial complexes, and what it signifies for economic growth and resource allocation.
Visualizing the Scale
The challenge in understanding 500,000 square feet lies in its sheer size. To put it into perspective, consider this: it's roughly equivalent to 11.5 acres. This figure alone begins to paint a picture, but further comparisons are needed for true comprehension.
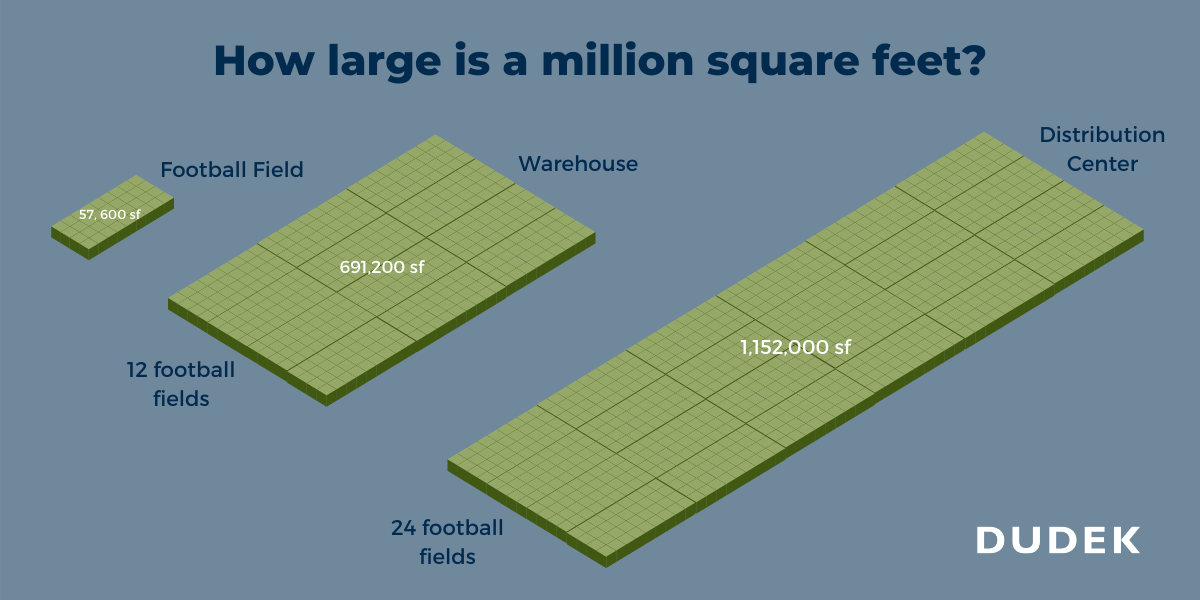
Think of a typical American football field, including the end zones. Its area is approximately 57,600 square feet. Therefore, 500,000 square feet is roughly the area of 8.7 football fields. Imagine trying to fit nearly nine football fields into a single contiguous space – a truly vast expanse.
Another readily understandable comparison is to well-known buildings. The Pentagon, one of the world's largest office buildings, has approximately 6.5 million square feet of floor space. This means our 500,000 square feet represents about 7.7% of the Pentagon's total area.
Consider a standard Walmart Supercenter, which typically occupies around 180,000 square feet. A 500,000 square foot space could house almost three Walmart Supercenters. These comparisons offer a tangible understanding of the scale.
Applications in Real Estate and Industry
The size of 500,000 square feet is frequently encountered in large-scale commercial and industrial projects. This measurement is significant in the logistics and distribution sector, where massive warehouses are essential for storing and processing goods.
According to a 2023 report by Cushman & Wakefield, a leading commercial real estate services firm, the demand for industrial space exceeding 500,000 square feet is steadily increasing, driven by the growth of e-commerce and the need for efficient supply chains.
These warehouses often serve as regional distribution hubs, facilitating the movement of products from manufacturers to retailers and consumers. The rise of online shopping has fueled the demand for larger and more sophisticated distribution centers.
Beyond logistics, 500,000 square feet can also represent the footprint of a large manufacturing plant. Automobile factories, food processing plants, and technology manufacturing facilities can easily occupy this amount of space.
Data centers are another significant application. These facilities, which house the servers and infrastructure that power the internet and cloud computing, require massive amounts of space. A 500,000 square foot data center can house thousands of servers, consuming vast amounts of electricity and generating substantial heat.
The Economic and Environmental Impact
Developments encompassing 500,000 square feet have significant economic implications for the surrounding communities. These projects create jobs during construction and operation, boosting local economies and generating tax revenue.
However, these large-scale developments also raise environmental concerns. The construction process can disrupt ecosystems and contribute to deforestation. The operational phase can lead to increased energy consumption, water usage, and waste generation.
Sustainability is becoming increasingly important in the design and construction of these large facilities. Developers are incorporating green building practices, such as using recycled materials, installing energy-efficient lighting, and implementing water conservation measures.
The impact on traffic patterns is also a consideration. A 500,000 square foot warehouse or manufacturing plant can generate significant truck traffic, potentially leading to congestion and air pollution. Careful planning and infrastructure improvements are crucial to mitigate these impacts.
Future Trends and Considerations
As technology continues to advance, the demand for large-scale facilities is likely to increase further. The growth of artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and other emerging technologies will drive the need for more data centers and specialized manufacturing facilities.
The use of automation and robotics will also influence the design and operation of these facilities. Automated warehouses, for example, require less human intervention, allowing for more efficient storage and retrieval of goods.
Looking ahead, the challenge will be to balance economic growth with environmental sustainability. Developers, governments, and communities must work together to ensure that these large-scale projects are developed responsibly and in a way that minimizes their impact on the planet.
Smart planning and technological advancements are essential to achieve this balance. Using technology to optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and improve transportation efficiency is critical. Public dialogue and transparent decision-making are equally important.
In conclusion, 500,000 square feet is not just a number, it's a representation of the scale of modern infrastructure. Understanding its implications is crucial for informed decision-making about economic development, environmental protection, and the future of our communities.