How Can Malicious Code Spread Select All That Apply

Urgent cybersecurity alert: A surge in malicious code infections is threatening both individual users and enterprise networks. Understanding the pathways of these threats is now critical to bolstering defenses.
This article provides a concise overview of the most common methods used to spread malicious code, empowering readers to take immediate action and minimize risk. Recognizing these attack vectors is the first line of defense against a growing digital threat landscape.
Common Infection Vectors
Email Attachments and Links
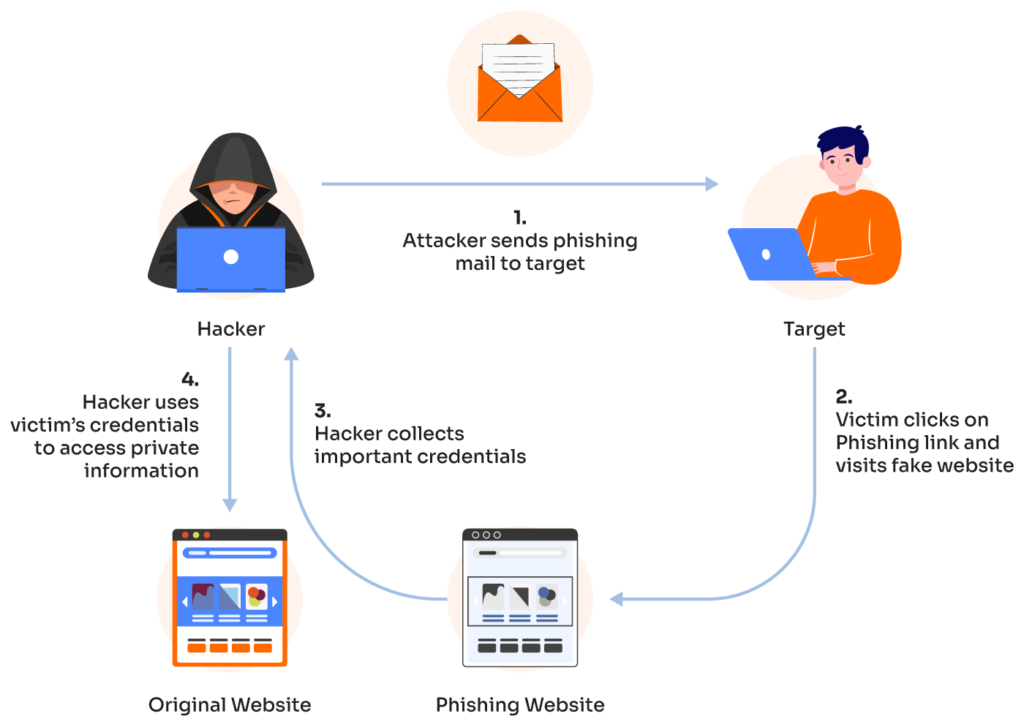
Phishing remains a dominant method. Malicious actors send emails disguised as legitimate communication, often containing infected attachments or links.
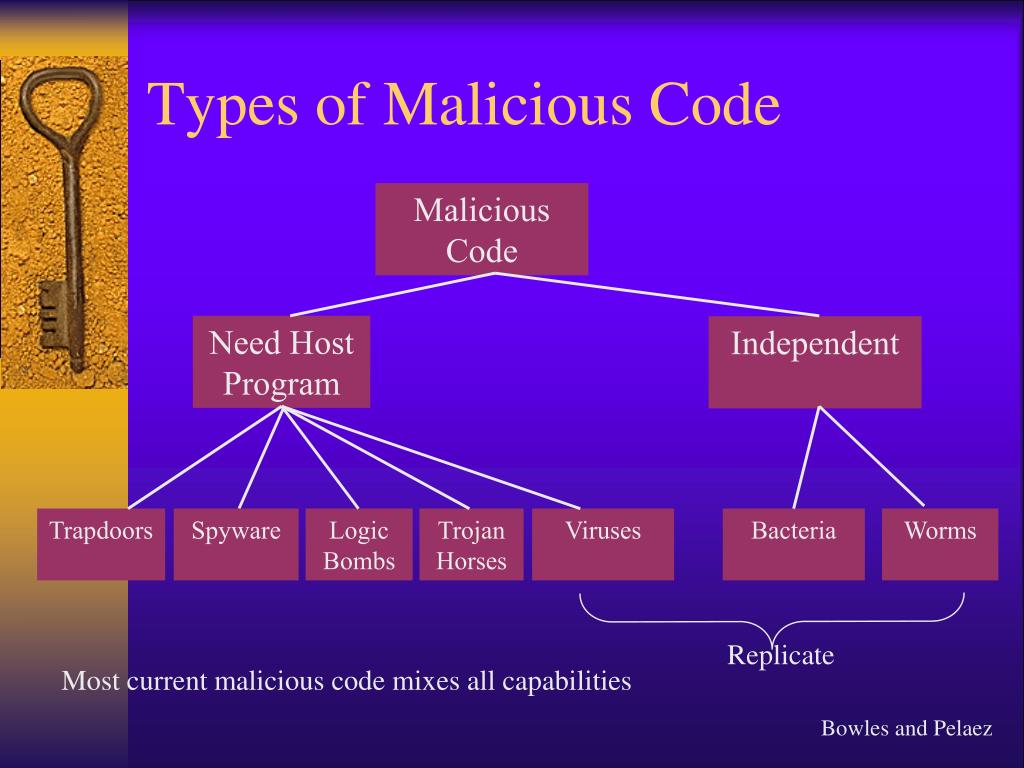
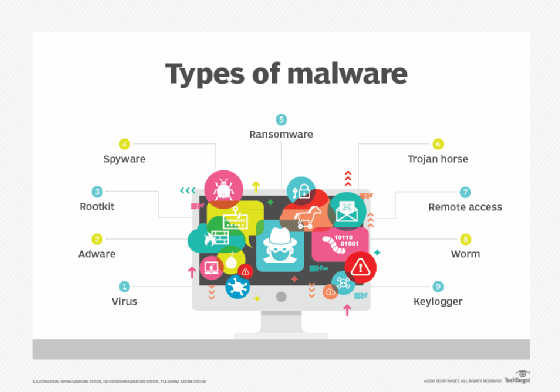
These attachments may contain viruses, worms, or Trojan horses. Clicking on malicious links redirects users to fake websites that download malware or steal credentials.
Users should always verify the sender's address and carefully examine links before clicking.
Drive-by Downloads
Unsuspecting users can become infected simply by visiting a compromised website. This is known as a drive-by download.
Attackers exploit vulnerabilities in website software to inject malicious code. This code automatically downloads and installs malware onto the visitor's computer without their explicit consent.
Keeping web browsers and plugins up to date is crucial for mitigating this risk.
Software Vulnerabilities
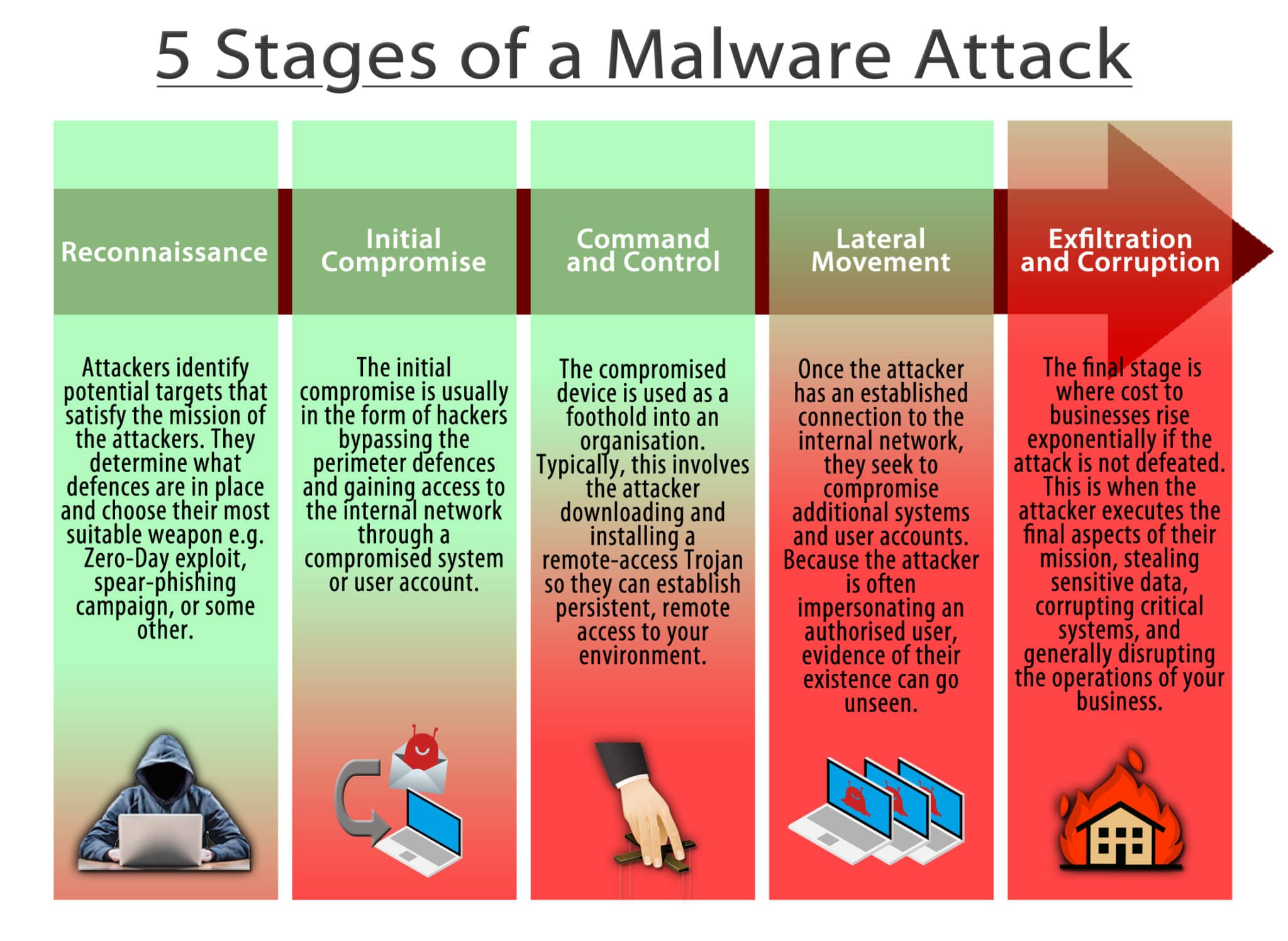
Exploiting software flaws is a primary tactic. Vulnerabilities in operating systems, applications, and even firmware allow attackers to execute malicious code.
Attackers scan for systems running vulnerable software. Once a vulnerability is identified, they can remotely install malware.
Regularly patching and updating software is paramount to closing these security holes.
Removable Media
USB drives and other removable media can also serve as infection vectors. A seemingly innocuous USB drive can harbor malicious code.
When inserted into a computer, the malware automatically executes. This can spread quickly across networks.
Exercise caution when using removable media from unknown sources. Scan all external devices before opening any files.
Malvertising
Malvertising involves embedding malicious code within online advertisements. This method allows attackers to reach a broad audience through legitimate websites.
When users click on these ads, they are redirected to malicious websites or unknowingly download malware. Ad blockers and reputable antivirus software can help to defend against this.
This sophisticated technique makes it difficult for even experienced users to avoid infection.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) File Sharing
P2P networks are often used to share pirated software and media. These files frequently contain malware.
Downloading files from untrusted sources exposes users to significant risk. The lack of quality control on P2P networks makes them a prime distribution channel for malware.
Avoid using P2P file sharing services to minimize the risk of infection.
Social Engineering
Attackers manipulate individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. Social engineering can be coupled with other methods.
For example, an attacker might impersonate a trusted colleague to trick a user into opening an infected attachment. Recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts is crucial.
Raising awareness about social engineering tactics is essential for protecting individuals and organizations.
Protecting Yourself and Your Organization
Implementing a multi-layered security approach is essential. This includes using strong passwords, enabling multi-factor authentication, and keeping software up to date.
Regular security audits and employee training programs are also crucial. Stay informed about the latest threats and vulnerabilities by consulting reputable security resources like the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Ongoing vigilance and proactive security measures are critical in the fight against malicious code. Be proactive with security measures and make it a priority for everyone.