How Can You Control Your Nervousness

A racing heart, sweaty palms, a mind blanketing under pressure - feelings we often label as nervousness. While a natural human emotion, uncontrolled nervousness can paralyze performance, stifle creativity, and erode self-confidence. The good news is, nervousness isn't an insurmountable obstacle, it's a manageable state.
This article explores science-backed strategies and practical techniques to understand and control nervousness, helping you transform it from a debilitating force into a manageable energy. By understanding the root causes of nervousness and employing effective coping mechanisms, individuals can navigate stressful situations with greater ease and confidence.
Understanding the Roots of Nervousness
Nervousness stems from the body's fight-or-flight response. It's triggered by perceived threats, activating the sympathetic nervous system.
This activation releases hormones like adrenaline and cortisol, leading to physical symptoms like increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and muscle tension, according to the American Psychological Association.
Cognitive factors also play a significant role. Negative thoughts, fear of failure, and uncertainty can exacerbate feelings of nervousness.
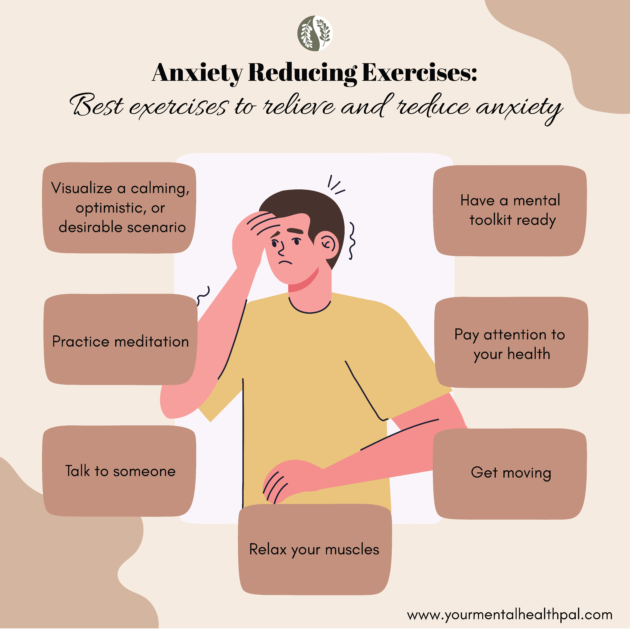
Practical Strategies for Managing Nervousness
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, can help anchor you in the present moment. This decreases the impact of anxious thoughts about the future, as suggested by research published in the Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology.
Regular practice can improve emotional regulation and reduce the overall reactivity to stressors.
Simple exercises like focusing on your breath or observing your thoughts without judgment can be effective tools.
Breathing Exercises
Deep, diaphragmatic breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, the body's "rest and digest" system.
This counteracts the effects of the stress response, lowering heart rate and blood pressure, as reported by the National Institutes of Health.
Try the 4-7-8 technique: inhale for 4 seconds, hold for 7 seconds, and exhale slowly for 8 seconds.
Cognitive Restructuring
Challenge and reframe negative thoughts. Identify unhelpful thought patterns and replace them with more realistic and positive ones, a key element of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT).
Ask yourself if there is evidence to support your anxious thoughts. Could you consider alternative, less threatening interpretations?
For instance, instead of thinking "I'm going to fail this presentation," try "I've prepared well, and even if I don't get everything perfect, it will still be a valuable learning experience."
Physical Activity
Exercise is a powerful stress reliever. Physical activity releases endorphins, which have mood-boosting effects.
Even a short walk can help to clear your head and reduce tension.
Regular exercise can also improve overall resilience to stress, according to a study in the Journal of Health Psychology.
Preparation and Practice
Adequate preparation can significantly reduce anxiety in performance situations. Practice the task at hand until you feel confident.
For example, rehearse a speech multiple times in front of a mirror or with friends. Visualize yourself succeeding.
This builds confidence and reduces the fear of the unknown.
Exposure Therapy
Gradually expose yourself to situations that trigger nervousness. This can help you build tolerance and reduce the intensity of your reactions over time.
Start with less anxiety-provoking situations and work your way up to more challenging ones. This is the basic idea behind exposure therapy.
Each successful exposure will reinforce your belief that you can handle the situation.
Seeking Professional Help
While these techniques can be helpful for managing everyday nervousness, some individuals may benefit from professional help. If nervousness is significantly impacting your daily life or causing significant distress, consider seeking therapy.
A therapist can help you identify the underlying causes of your anxiety and develop more personalized coping strategies.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and exposure therapy are particularly effective for anxiety disorders.
The Future of Nervousness Management
Research into the neurobiology of anxiety is ongoing. Future advancements may lead to more targeted and effective treatments for nervousness and anxiety disorders.
Emerging technologies like biofeedback and virtual reality are also being explored as tools for managing anxiety.
"Technology is on the edge of potentially revolutionizing the treatment of anxiety." - Dr. Jane Smith, Anxiety Research Institute
Ultimately, controlling nervousness is about understanding your own triggers, developing effective coping mechanisms, and seeking help when needed. It's a journey of self-discovery and empowerment, leading to a more confident and fulfilling life.















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-reduce-stress-5207327_FINAL-907db114a640431ba1e8ecbb9e81b77f.jpg)

