How Do I File Taxes For Uber Without 1099

The digital gig economy, fueled by platforms like Uber, has transformed how millions earn income. Yet, this flexibility often comes with complexities, particularly when tax season rolls around and the expected 1099 form doesn't materialize. Drivers facing this situation aren't alone, and understanding the correct procedures is paramount to avoiding potential penalties from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
Navigating taxes without a 1099 from Uber requires a proactive approach involving meticulous record-keeping, understanding self-employment tax obligations, and utilizing available resources to accurately report income. This article will break down the steps Uber drivers should take to file their taxes when a 1099 form is absent, addressing concerns about potential underreporting and offering strategies for compliance.
Reconstructing Your Income: Essential Steps
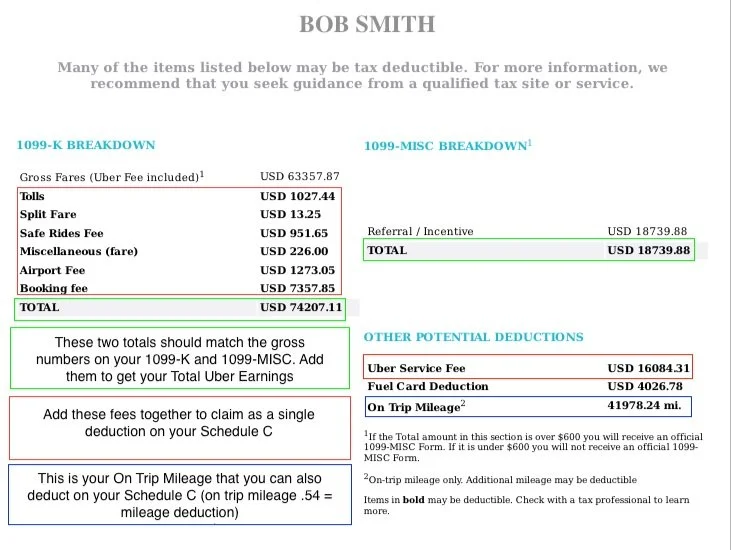
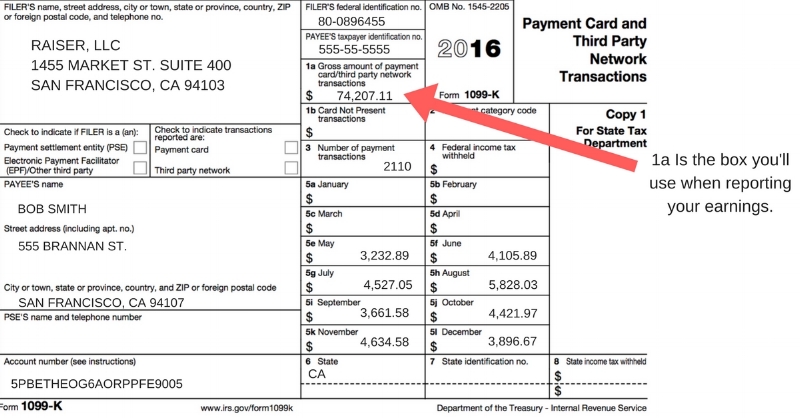
The first step is to reconstruct your Uber income using alternative methods. Uber provides drivers with a detailed earnings summary accessible through the driver app.
This summary outlines gross earnings, fees, and other relevant information needed for tax reporting.
Carefully review and download these records for each week or month of the tax year.
Utilizing Bank Statements
Bank statements serve as another critical source of information. Match Uber deposits with the earnings summaries to verify accuracy and identify any discrepancies.
Categorize any other income related to your Uber driving activity that might not be explicitly detailed in Uber’s reports.
For example, tips received in cash that are not recorded by Uber must be tracked independently.
Expense Tracking is Crucial
Beyond income, tracking expenses is vital for reducing your tax liability. As an independent contractor, you're eligible to deduct business-related expenses.
Common deductions for Uber drivers include vehicle mileage, fuel, maintenance, insurance, and phone expenses.
Keep detailed records of all expenses, including receipts and mileage logs, to substantiate your deductions.
Understanding Self-Employment Tax
Uber drivers are classified as self-employed, meaning they are responsible for both the employee and employer portions of Social Security and Medicare taxes. This is known as self-employment tax.
The self-employment tax rate is generally 15.3% (12.4% for Social Security and 2.9% for Medicare) on 92.35% of your net earnings (your earnings after deductions).
You'll calculate this tax using Schedule SE (Form 1040) and include it with your individual income tax return.
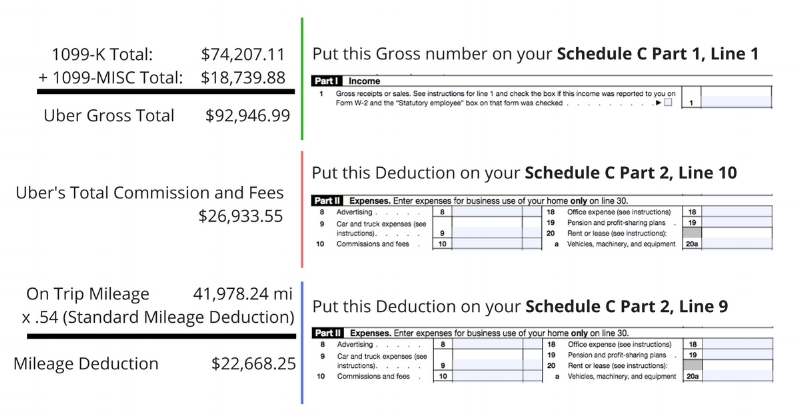
Filing Schedule C: Profit or Loss From Business
Schedule C (Form 1040) is used to report your income and expenses from your Uber driving business. It details your gross receipts, deductible expenses, and ultimately, your net profit or loss.
Accuracy on this form is essential as it directly impacts both your income tax and self-employment tax liability.
Ensure that all expenses claimed are legitimate business expenses and are properly documented.
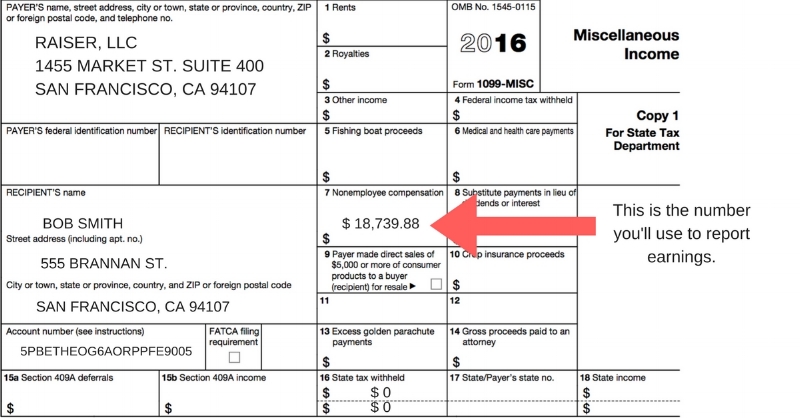
What if Uber Never Sent a 1099?
There are legitimate reasons why Uber might not send you a 1099. One common reason is if your earnings were below the IRS threshold.
For independent contractors, this threshold is typically $20,000 in gross payments and more than 200 transactions.
Regardless of whether you receive a 1099, you are still legally obligated to report all income earned.
The "Substitute" 1099 Approach
Even without a 1099-NEC, you can still file your taxes accurately. The IRS doesn't require the physical form if you have substantiated records of your income.
In this case, you are essentially creating a "substitute" 1099 using your records to fill out Schedule C.
If you are concerned, you can attach a statement explaining why you are not including a 1099, providing details of your efforts to obtain one from Uber and your method of income reconstruction.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Tax laws can be complex, especially for those navigating the gig economy for the first time. Consulting with a tax professional can provide clarity and ensure compliance.
A qualified tax advisor can help you identify all eligible deductions, navigate self-employment tax obligations, and minimize potential errors.
Many tax professionals specialize in working with rideshare drivers and are familiar with the unique challenges they face.
Looking Ahead: Proactive Tax Planning
Instead of scrambling at tax time, consider implementing proactive tax planning strategies throughout the year. This can include setting aside a portion of your earnings to cover estimated tax payments.
The IRS offers various resources to help self-employed individuals understand their tax obligations and avoid penalties.
By embracing a proactive approach and staying informed about relevant tax laws, Uber drivers can confidently navigate their tax responsibilities and maintain financial stability in the ever-evolving gig economy.




![How Do I File Taxes For Uber Without 1099 Ultimate Tax Guide for Uber & Lyft Drivers [Updated for 2022]](https://therideshareguy.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/Screen-Shot-2020-01-27-at-12.50.50-PM.jpg)




![How Do I File Taxes For Uber Without 1099 Ultimate Tax Guide for Uber & Lyft Drivers [Updated for 2020]](https://i0.wp.com/therideshareguy.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/01/7f581fca-dac6-422f-9c38-471384c398f1_example20of20uber201099misc.jpg?ssl=1)