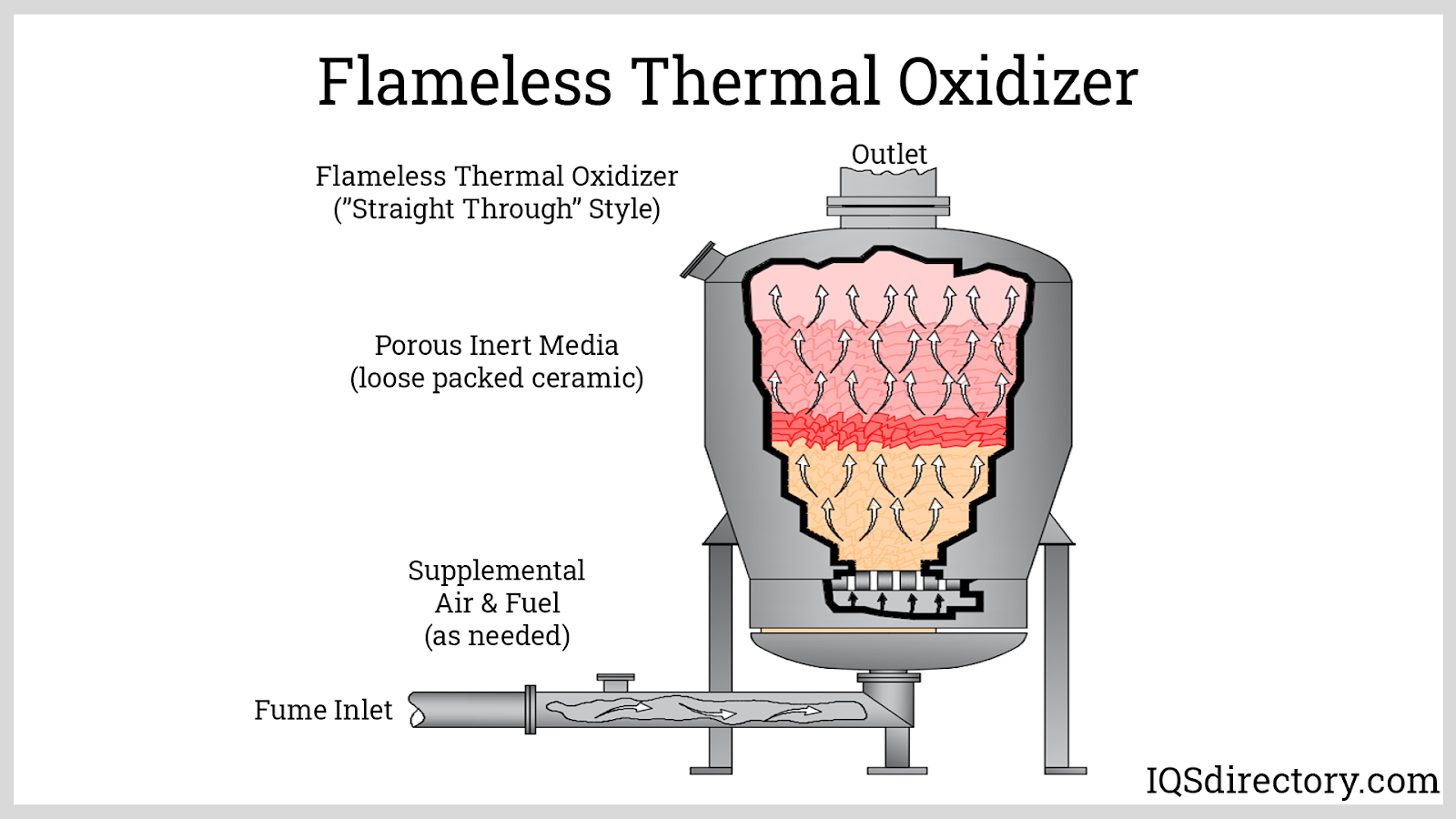
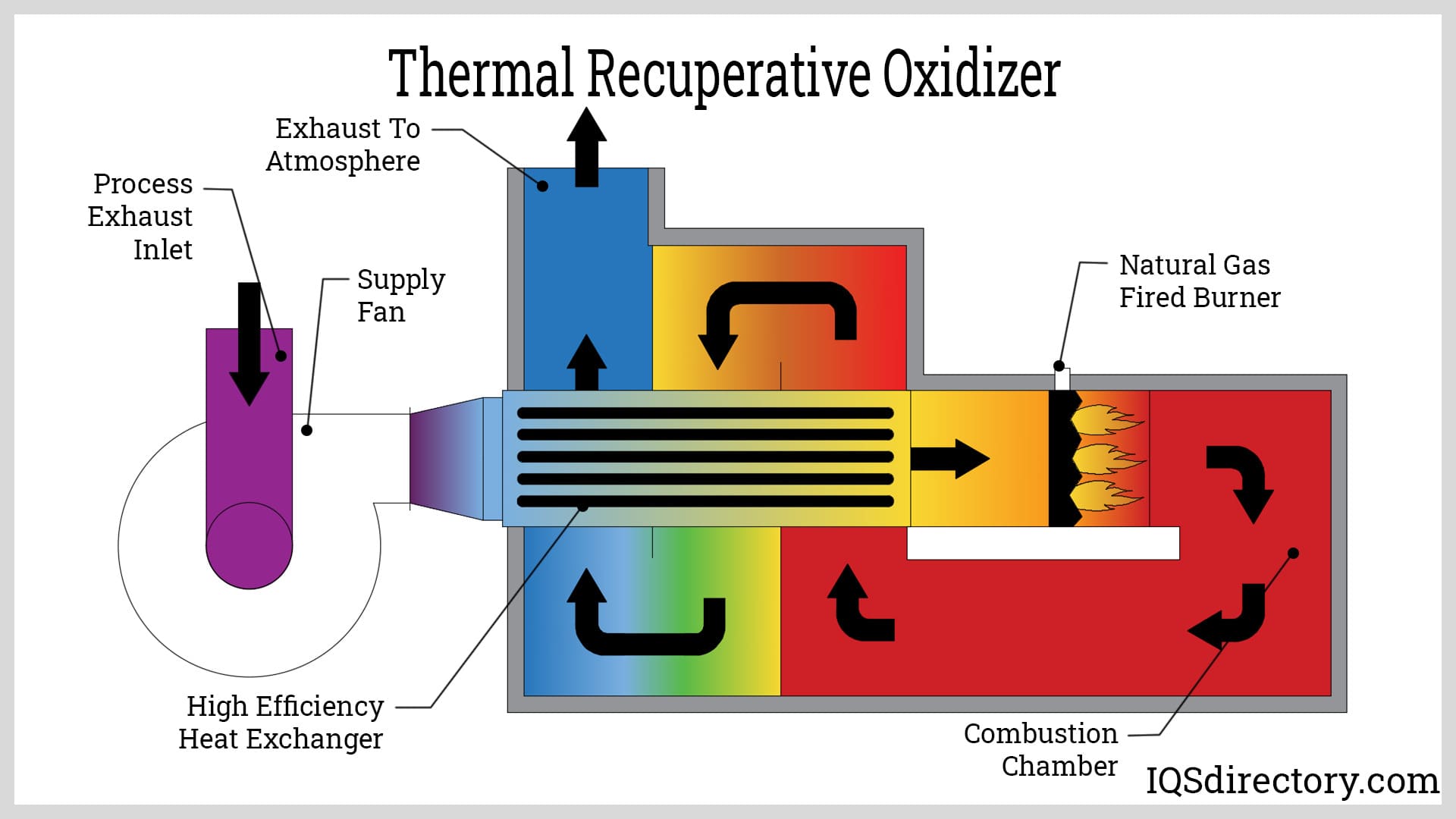
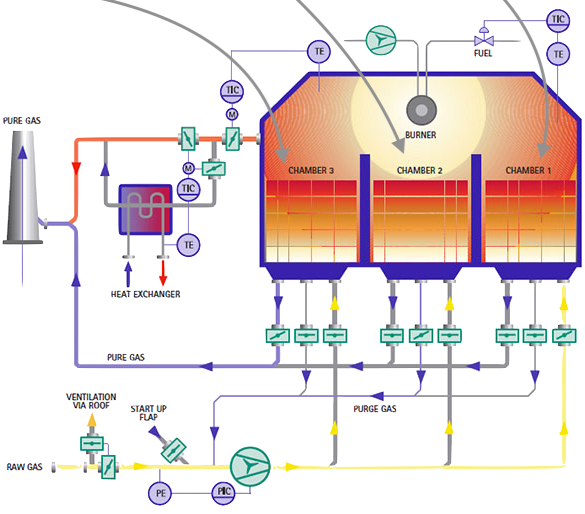
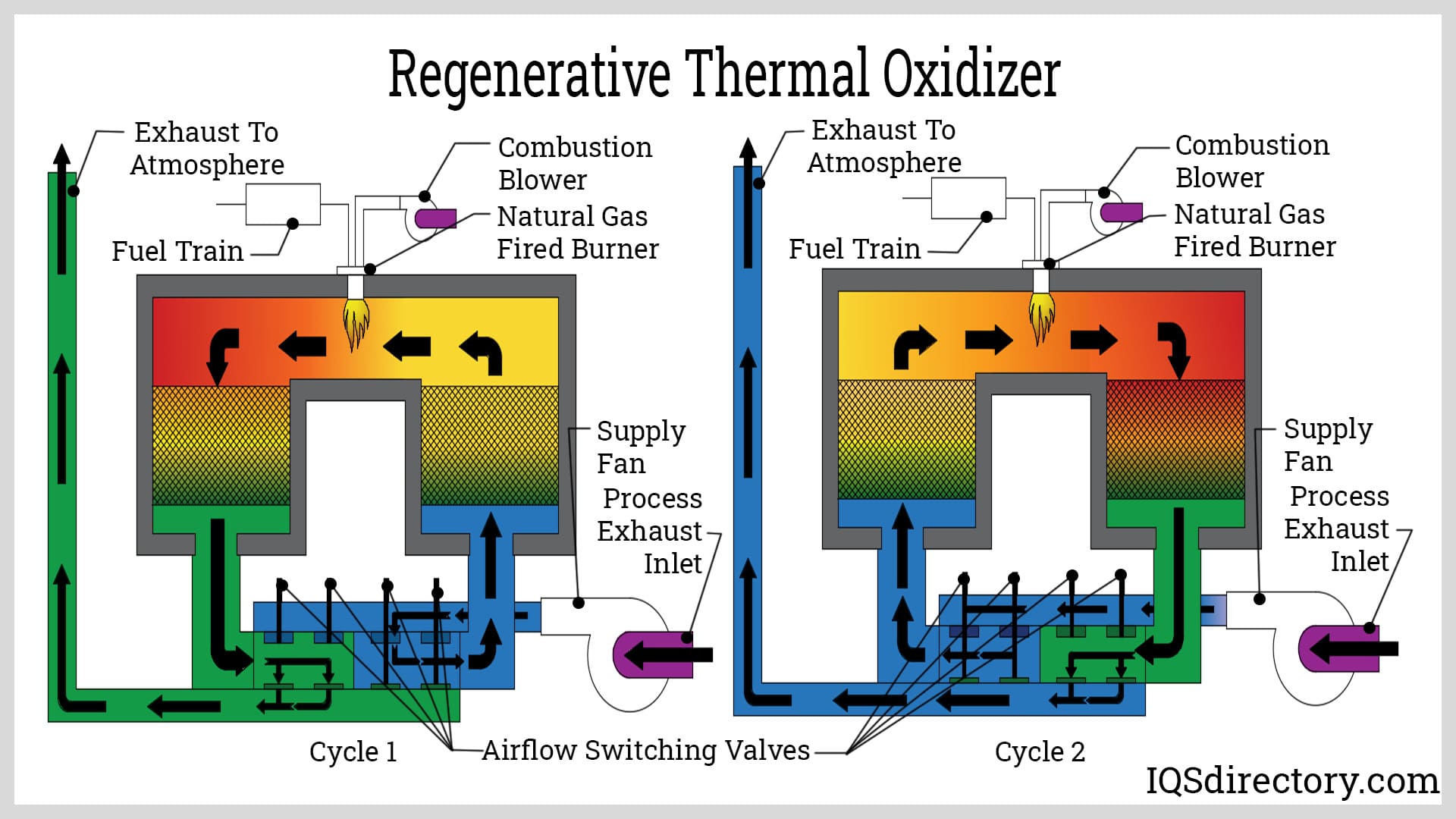
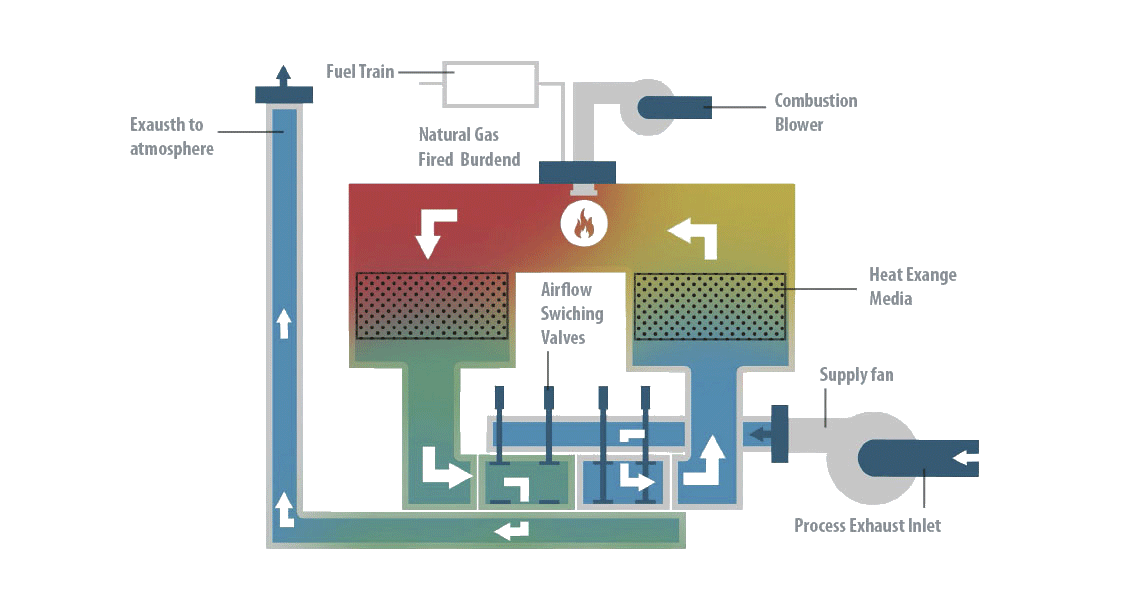
How Does A Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer Work

Imagine a factory billowing gentle plumes into the sky. But instead of harmful pollutants, these are the ghosts of yesterday's production, now harmless, clean, and reborn as energy. This isn't science fiction, but a reality thanks to a technology called a Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer, or RTO.
At its heart, the RTO is a pollution control device. It tackles harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) released from industrial processes. It does this by using intense heat and a clever energy recovery system, transforming these pollutants into harmless carbon dioxide and water vapor, while also minimizing energy consumption.
The Problem: Air Pollution from Industry
Industrial processes, from painting and coating to chemical manufacturing, inevitably release pollutants into the air. These pollutants, often VOCs and HAPs, contribute to smog, respiratory problems, and other environmental and health issues.
For decades, industries grappled with the challenge of reducing these emissions without crippling their operations. Early solutions were often inefficient, costly, or both. This is where the RTO steps in, providing a more sustainable and effective solution.
Enter the Regenerative Thermal Oxidizer
The RTO emerged as a leading technology for air pollution control because of its high efficiency and ability to recover energy. It represents a significant advancement over earlier pollution control methods, offering a win-win scenario for both industry and the environment.
How it Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
The RTO's operation relies on a cycle of heat absorption and release, enabling the efficient oxidation of pollutants.
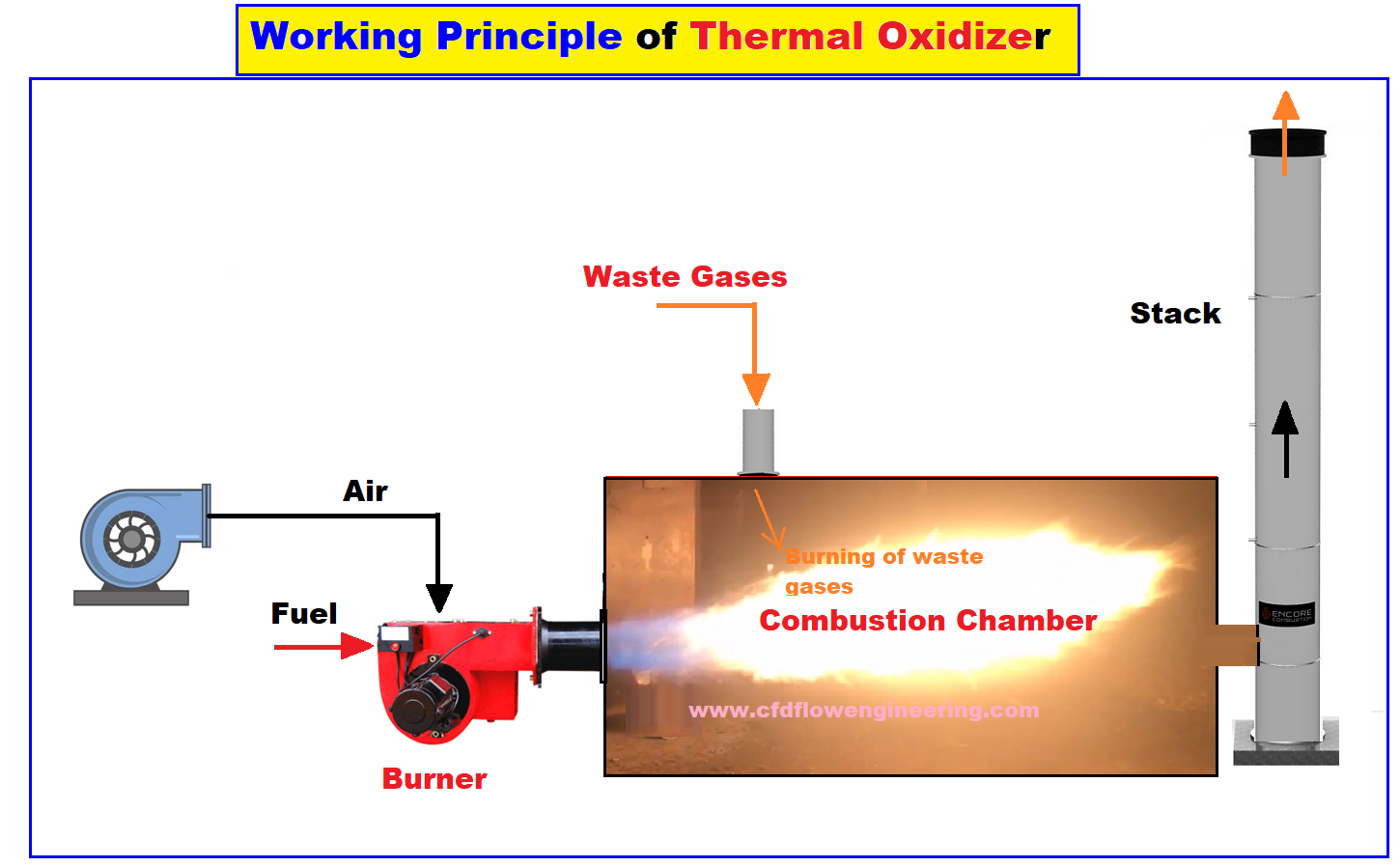
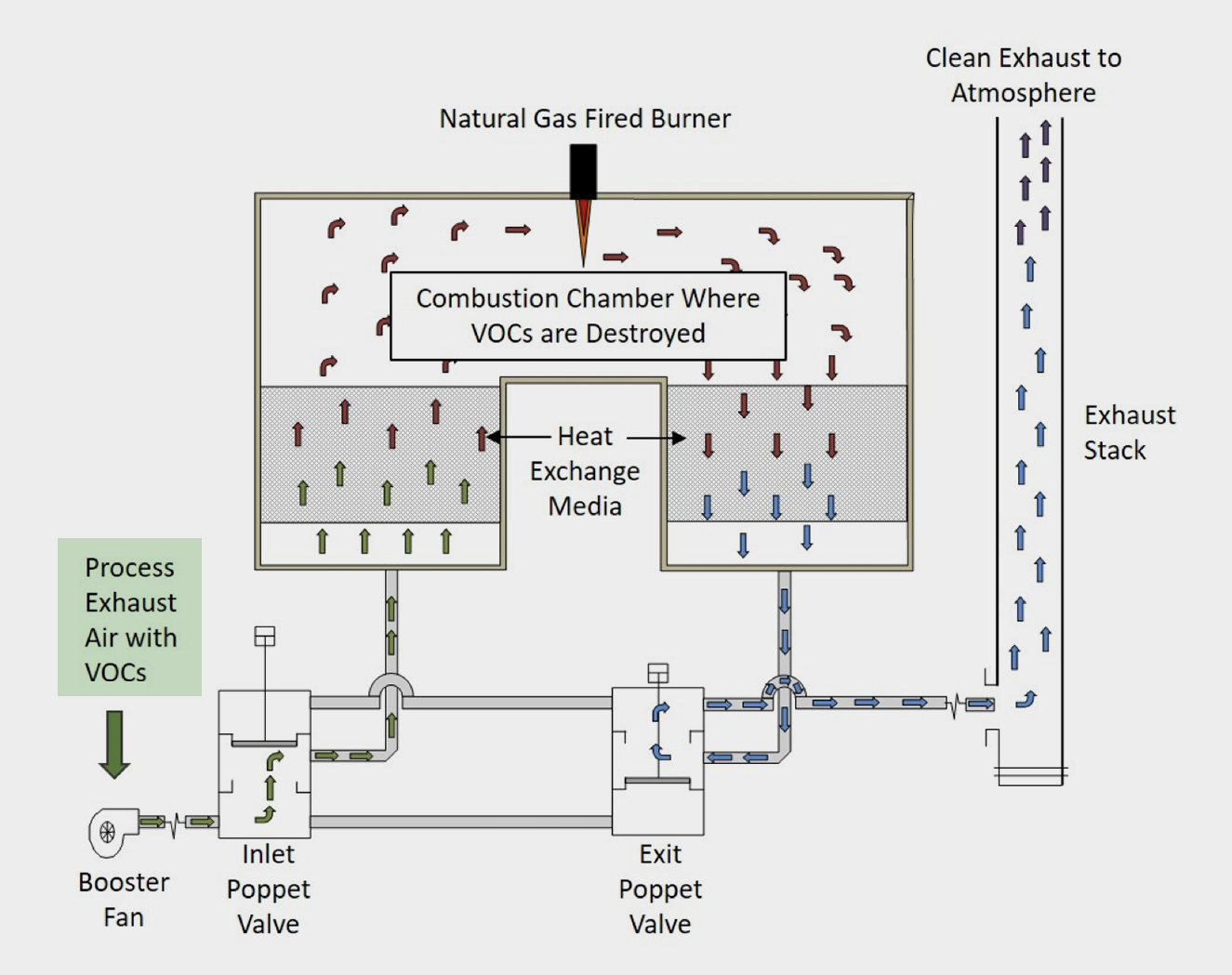
Step 1: Pollutant-Laden Air Intake: The process begins with the pollutant-laden air stream, drawn from the industrial process, entering the RTO system.
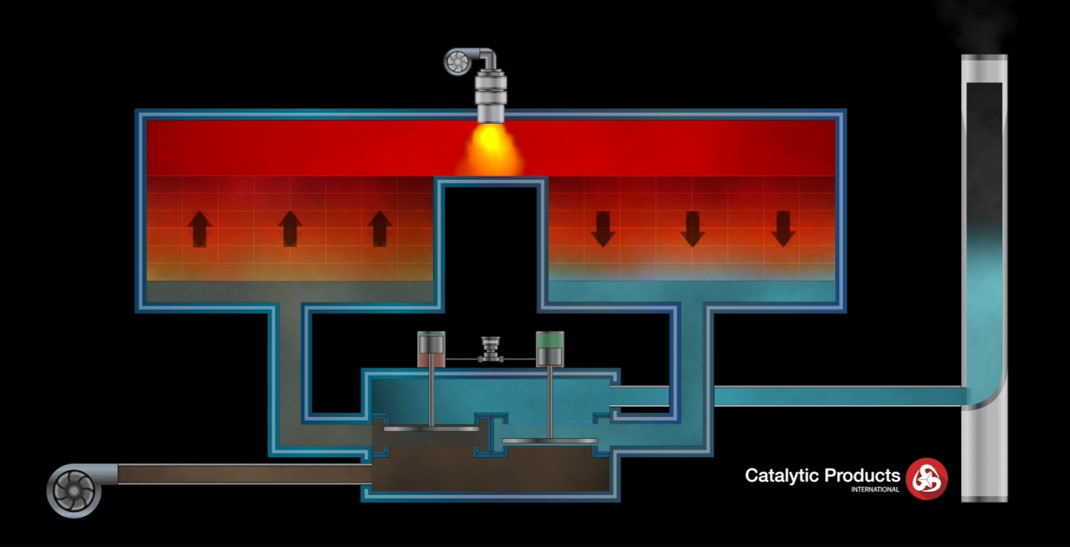
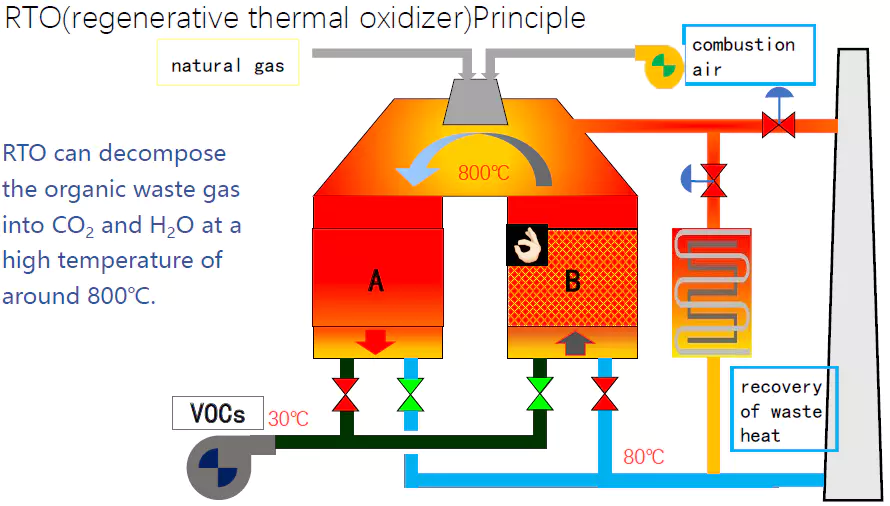
Step 2: Preheating: The air is then directed through one of the RTO's ceramic beds. These beds, preheated from a previous cycle, absorb the heat from the incoming air, raising its temperature significantly.
Step 3: Combustion Chamber: The preheated air then enters the combustion chamber, where it is heated to a very high temperature, typically between 1400°F and 1800°F. At this temperature, the VOCs and HAPs oxidize, reacting with oxygen to form harmless carbon dioxide and water vapor.
Step 4: Heat Recovery: The hot, clean air then passes through another ceramic bed, transferring its heat to the bed before being exhausted to the atmosphere. This is the key to the RTO's energy efficiency. The heated ceramic bed is now ready for the next cycle.
Step 5: Cycling: The flow direction is reversed periodically, typically every few minutes. This ensures that the heat is efficiently recovered and that the RTO operates continuously. One bed heats the incoming air, while the other cools the outgoing air, constantly exchanging heat.
Key Components of an RTO System
Several key components work together to ensure the efficient operation of an RTO system.
Ceramic Beds: These are the heart of the RTO's heat recovery system. Constructed of ceramic materials with high thermal conductivity, they efficiently absorb and release heat.
Combustion Chamber: This is where the oxidation of VOCs and HAPs occurs. It is designed to maintain a uniform temperature and provide sufficient residence time for the reaction to complete.
Valves and Dampers: These control the flow of air through the RTO system, directing it to the appropriate ceramic beds and combustion chamber. They are crucial for the cycling process.
Control System: The control system monitors and regulates the RTO's operation, ensuring that the temperature, flow rates, and other parameters are within the optimal range. It also provides alarms and shutdown functions in case of malfunctions.
Advantages of Using an RTO
The advantages of using an RTO are numerous.
High Destruction Efficiency: RTOs can achieve destruction efficiencies of up to 99.5%, significantly reducing emissions of VOCs and HAPs.
Energy Efficiency: By recovering and reusing heat, RTOs minimize energy consumption, reducing operating costs and carbon footprint.
Fuel Savings: The recovered heat reduces the need for auxiliary fuel, further decreasing operating costs.
Versatility: RTOs can handle a wide range of VOCs and HAPs, making them suitable for various industrial applications.
Applications of RTO Technology
RTO technology is widely used in various industries where air pollution control is essential.
Painting and Coating: RTOs are used to control emissions from painting and coating operations, such as automotive manufacturing and furniture finishing.
Chemical Processing: The chemical industry utilizes RTOs to reduce emissions from chemical reactions and manufacturing processes.
Printing and Packaging: RTOs are employed to control emissions from printing presses and packaging equipment.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: The pharmaceutical industry uses RTOs to reduce emissions from drug production and solvent recovery processes.
The Future of RTO Technology
The future of RTO technology looks promising, with ongoing advancements aimed at improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Improved Materials: Research is underway to develop ceramic materials with even higher thermal conductivity and durability, further enhancing heat recovery and reducing maintenance requirements.
Advanced Control Systems: Advanced control systems are being developed to optimize RTO operation based on real-time data, improving efficiency and reducing emissions.
Integration with Other Technologies: RTO technology is being integrated with other pollution control technologies, such as scrubbers and filters, to achieve even greater emission reductions.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recognizes RTOs as a Best Available Control Technology (BACT) for many industries. This designation underscores the effectiveness and importance of RTO technology in achieving air quality standards.
A Breath of Fresh Air
The RTO stands as a testament to human ingenuity and our commitment to protecting the environment. Its ability to transform pollutants into harmless substances while conserving energy embodies the principles of sustainable development.
As we continue to strive for a cleaner and healthier future, technologies like the RTO will play a crucial role in helping industries minimize their environmental impact. The gentle plumes rising from these factories are not a sign of pollution, but a symbol of progress, innovation, and a breath of fresh air for generations to come. It's a powerful reminder that technology, when used responsibly, can be a force for good.