How Is Delta 9 Different From Thc

The landscape of cannabis consumption is rapidly evolving, leaving many consumers, and even regulators, struggling to keep pace. With the proliferation of hemp-derived products containing psychoactive compounds, a key question arises: What exactly is the difference between Delta 9 THC and the seemingly endless array of other THC variants now available? The answer, while rooted in chemistry, has significant implications for legality, accessibility, and the consumer experience.
At the heart of this debate lies a nuanced understanding of chemical structures. This impacts potency, legal status, and ultimately, how the substance interacts with the human body. Understanding the specific distinctions between Delta 9 THC and other THC isomers like Delta 8 or Delta 10 is critical for navigating the complexities of the modern cannabis market, and is the primary focus of this report.
The Core Difference: Chemical Structure
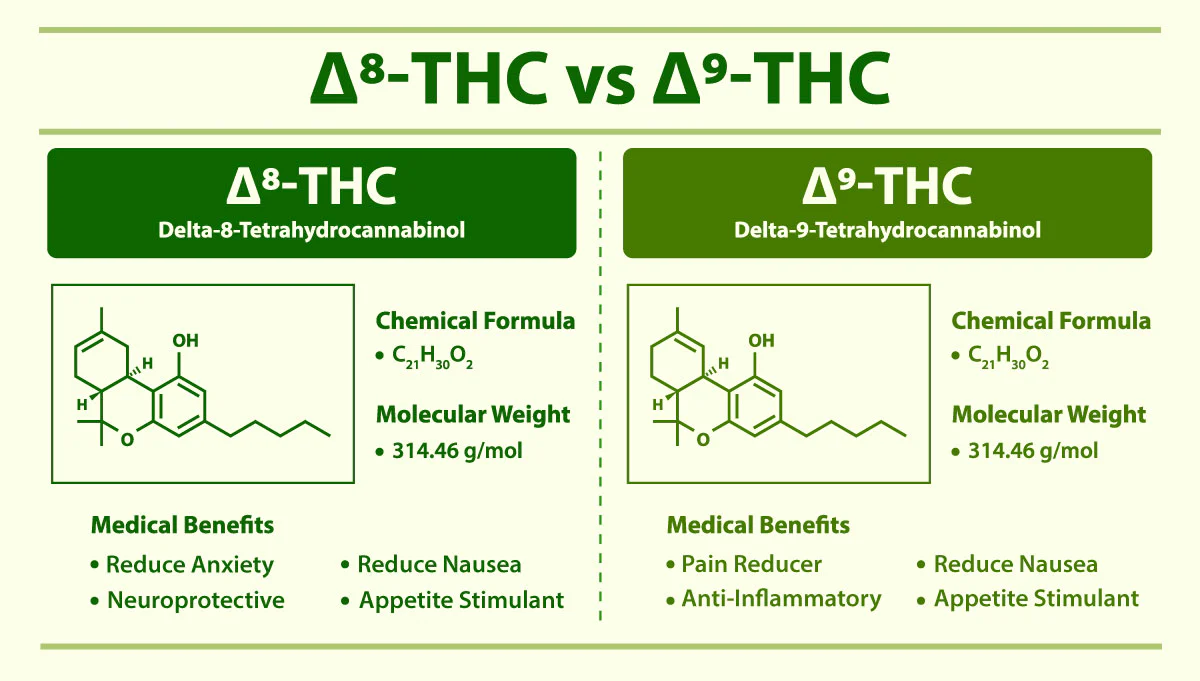
Delta 9 THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive component found in cannabis.
Its chemical structure features a double bond on the ninth carbon atom, hence the name "Delta 9."
This seemingly minor detail dictates how the molecule binds to the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS), producing the familiar effects associated with cannabis use.
Delta 8 and Delta 10: Isomers of Delta 9
Delta 8 THC and Delta 10 THC are isomers of Delta 9 THC, meaning they share the same chemical formula but differ in the position of the double bond. In Delta 8, the double bond is located on the eighth carbon atom, and in Delta 10, it’s on the tenth.
This structural difference might seem insignificant, but it results in varying affinities for the CB1 receptors in the ECS, leading to different psychoactive effects.
Consumers often report that Delta 8 produces a milder, more relaxing high compared to Delta 9, while Delta 10 is sometimes described as more energizing and less anxiety-inducing.
Legality: A Shifting Landscape
The legal status of these THC variants is complex and constantly evolving.
Under the 2018 Farm Bill, hemp-derived products containing less than 0.3% Delta 9 THC are federally legal.
This provision has created a loophole, allowing manufacturers to produce and sell Delta 8 and Delta 10 products, often derived from hemp, as long as they meet the Delta 9 THC threshold.
However, many states have explicitly banned or restricted the sale of Delta 8 and other THC isomers.
Some states view these products as synthetic cannabinoids, subject to stricter regulations, while others are still grappling with how to classify them.
The legal ambiguity surrounding these compounds has led to a patchwork of regulations across the country, creating confusion for consumers and businesses alike.
Potency and Effects: Understanding the Differences
While all three compounds interact with the ECS, their potency and effects differ significantly.
Delta 9 THC is generally considered the most potent, producing a strong psychoactive experience with potential side effects such as anxiety, paranoia, and impaired cognitive function.
Delta 8 is estimated to be about half as potent as Delta 9, offering a milder high with reduced anxiety and cognitive impairment.
Delta 10 is considered the least potent of the three, with effects often described as more subtle and uplifting.
However, it is important to note that individual responses to these compounds can vary depending on factors such as dosage, tolerance, and individual physiology.
Furthermore, the lack of rigorous scientific research on Delta 8 and Delta 10 means that their long-term effects and potential risks are still largely unknown.
Manufacturing and Safety Concerns
Another critical difference lies in the manufacturing processes used to produce these compounds.
While Delta 9 THC is naturally abundant in cannabis plants, Delta 8 and Delta 10 are typically produced through chemical conversion processes, often involving the use of solvents and other potentially harmful chemicals.
This raises significant safety concerns, as the final product may contain residual solvents or other contaminants if not properly purified.
The lack of regulation and standardization in the manufacturing of these products further exacerbates these concerns.
Consumers may unknowingly be purchasing products that are mislabeled, contain inaccurate dosages, or are contaminated with harmful substances.
Increased oversight and testing are necessary to ensure the safety and quality of these products.
Consumer Awareness and Education
Given the complexities surrounding these compounds, consumer education is crucial.
Consumers should be aware of the potential risks associated with using Delta 8 and Delta 10 products, particularly the lack of regulation and potential for contamination.
It is important to purchase products from reputable sources that provide third-party lab testing results to verify the potency and purity of the product.
Furthermore, consumers should start with low doses and gradually increase their intake to assess their individual tolerance.
It is also essential to be aware of the legal status of these compounds in their jurisdiction before purchasing or using them.
Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications.
The Future of THC Variants
The market for THC variants is likely to continue to evolve as new compounds are discovered and regulations change.
Increased research is needed to fully understand the effects and potential risks associated with these compounds.
Standardized testing and labeling requirements are also necessary to ensure consumer safety and transparency.
Ultimately, a balanced approach that considers both the potential benefits and risks of these compounds is needed to develop responsible regulations and protect public health.
As the cannabis industry continues to mature, a greater emphasis on scientific research, regulatory oversight, and consumer education will be essential to navigating the complexities of this rapidly evolving landscape.
Only through informed decision-making can consumers safely and responsibly explore the potential of these novel compounds.