How Long Do Caffeine Jitters Last

Caffeine jitters got you wired and wondering when relief will come? The uncomfortable side effects of too much caffeine typically last between 30 minutes and several hours, depending on individual factors.
This article breaks down the science behind caffeine jitters, exploring the factors that influence their duration and offering practical strategies to mitigate their effects. Understanding how your body processes caffeine is key to managing these unwanted side effects.
The Caffeine Culprit: How It Works
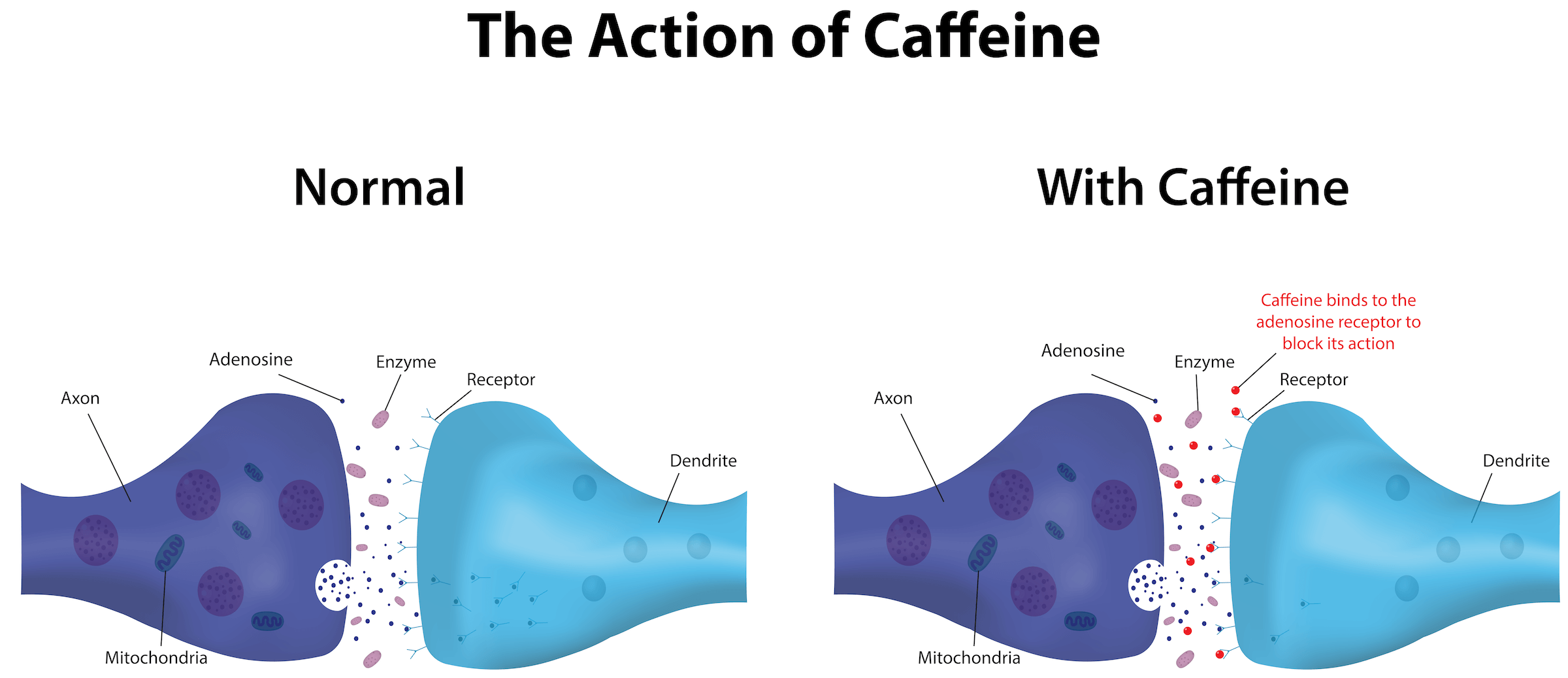
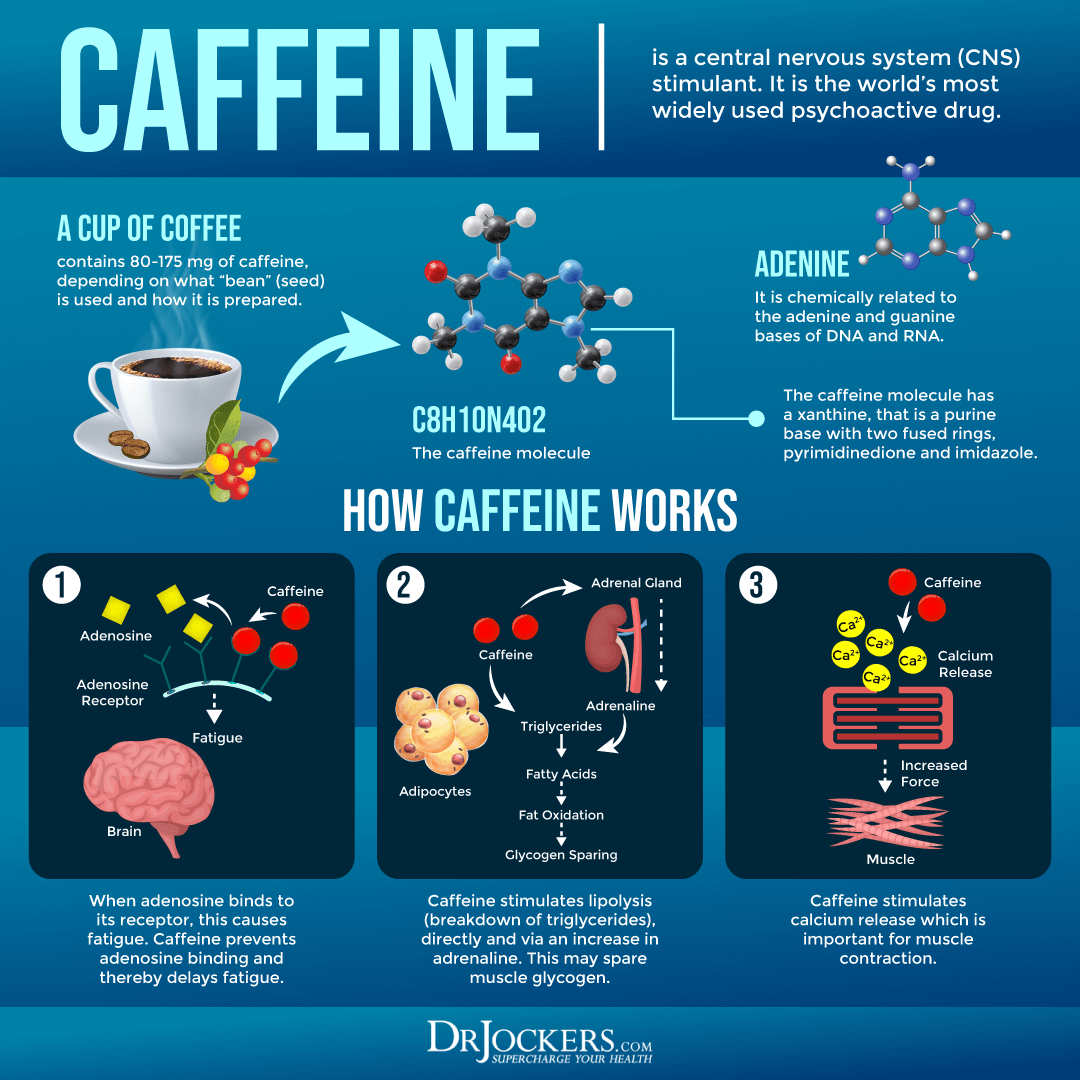
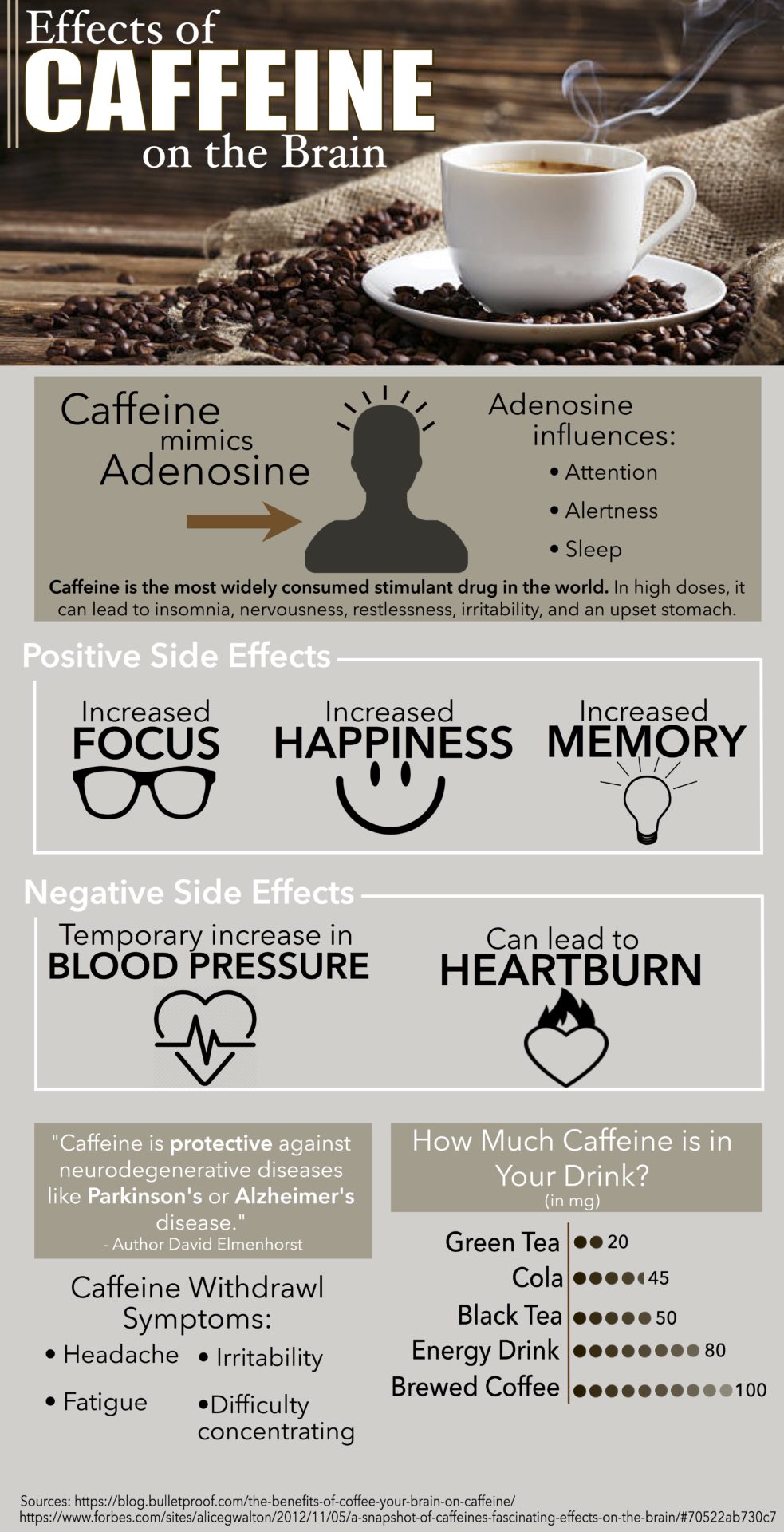
Caffeine, a stimulant found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and chocolate, works by blocking adenosine, a neurotransmitter that promotes relaxation and sleepiness. This blockage leads to increased neuronal activity, resulting in alertness and heightened energy.
However, excessive caffeine intake can overstimulate the central nervous system, causing the infamous jitters: anxiety, nervousness, rapid heartbeat, and even gastrointestinal distress.
Factors Influencing Jitter Duration
Several elements determine how long caffeine jitters persist. Individual metabolism plays a crucial role; some people process caffeine much faster than others.
Genetics, liver function, and enzyme activity all contribute to metabolic rate variability. Body weight also matters; a larger person generally requires more caffeine to experience the same effects, and the effects may last longer.
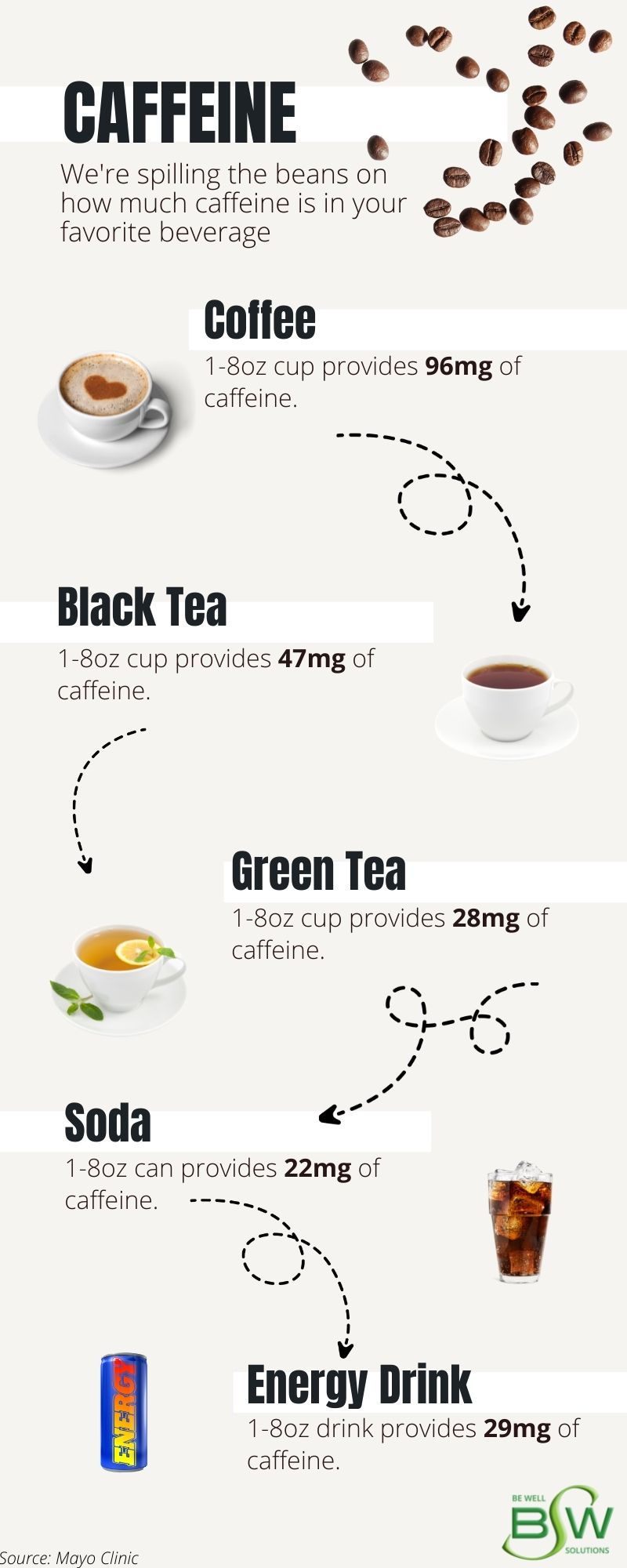
Caffeine dosage is a direct determinant. The more caffeine consumed, the more pronounced and prolonged the jitters are likely to be. A single espresso will typically have a shorter effect compared to a large energy drink.
Tolerance developed through regular caffeine consumption can lessen the intensity of jitters over time. Regular coffee drinkers may experience milder side effects compared to infrequent consumers, even at similar doses.
Food intake can affect caffeine absorption. Consuming caffeine on an empty stomach leads to faster absorption and potentially stronger jitters. Eating food, especially those rich in fiber, can slow absorption and reduce jitter intensity.
Quantifying the Jitter Timeline: Data & Estimates
Research indicates that caffeine has a half-life of approximately 5 hours in most adults. This means that after 5 hours, half of the caffeine consumed is still present in the body.
It takes roughly 5 half-lives for a substance to be almost completely eliminated. Therefore, caffeine can linger in your system for up to 25 hours, though the most intense effects usually subside within a few hours.
According to the FDA, 400 milligrams of caffeine per day (about four or five cups of coffee) is generally considered safe for healthy adults. Exceeding this amount increases the risk of experiencing jitters and other adverse effects.
A study published in the Journal of Caffeine Research showed that individuals who consumed caffeine doses exceeding their typical intake experienced jitter-like symptoms for an average of 3 to 5 hours.
Mitigating the Jitters: Practical Solutions
If you find yourself experiencing caffeine jitters, several strategies can help alleviate the discomfort. Hydration is essential; water helps flush caffeine out of your system.
Consuming foods rich in potassium and magnesium, such as bananas and leafy greens, can help counteract the electrolyte imbalances caused by caffeine. Gentle exercise, like a walk, can help burn off excess energy and reduce anxiety.
Deep breathing exercises or meditation can calm the nervous system and reduce feelings of panic or anxiety. Avoid consuming more caffeine or other stimulants while experiencing jitters.
Consider taking L-theanine, an amino acid found in tea, which promotes relaxation without drowsiness and can counteract the stimulating effects of caffeine. Consult with a healthcare professional if you experience severe or persistent jitters, especially if accompanied by chest pain or irregular heartbeat.
Long-Term Management: Prevention is Key
The most effective way to avoid caffeine jitters is to manage your caffeine intake. Monitor your daily consumption and be mindful of caffeine sources beyond coffee, such as tea, soda, energy drinks, and even some medications.
Gradually reduce your caffeine intake to minimize withdrawal symptoms if you're a heavy consumer. Switch to decaffeinated alternatives or herbal teas to reduce your reliance on caffeine.
Pay attention to your body's signals and adjust your caffeine intake accordingly. Dr. Emily Carter, a leading nutritionist, advises, "Understanding your personal caffeine sensitivity and tailoring your consumption is crucial for avoiding unwanted side effects."
Ongoing Research & Future Directions
Researchers are continually exploring the complexities of caffeine metabolism and its effects on the body. Further studies are investigating the role of specific genes and gut microbiota in caffeine sensitivity.
The development of personalized nutrition plans that consider individual caffeine metabolism could lead to more targeted recommendations for caffeine consumption. Mobile apps and wearable devices that track caffeine intake and provide real-time feedback are also emerging as valuable tools for managing caffeine consumption.
Ultimately, understanding how caffeine affects your body and adopting mindful consumption habits are key to enjoying its benefits without the jitters. Seek professional advice if needed.