How Long Does It Take For Glucose Tablets To Work
For individuals managing diabetes, understanding how quickly to respond to a hypoglycemic episode is crucial. One of the most common and readily available treatments for low blood sugar is glucose tablets. But how long does it take for these tablets to effectively raise blood glucose levels, and what factors influence that timeframe?
This article delves into the typical response time of glucose tablets, exploring the variables that can affect their absorption rate and offering guidance on how to use them effectively. Accurate information and timely action are essential for preventing serious complications associated with hypoglycemia.
Understanding Glucose Tablets and Hypoglycemia
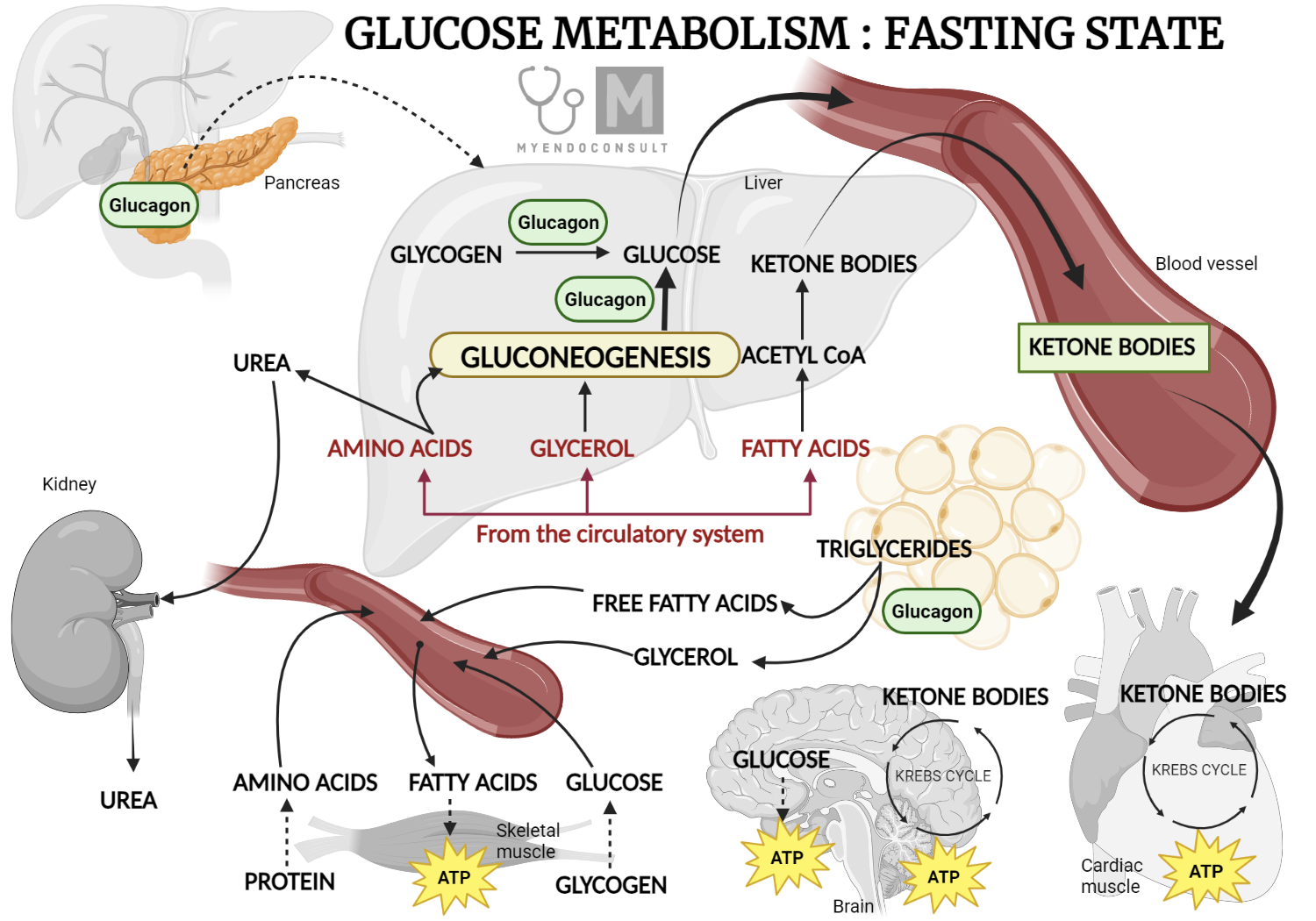
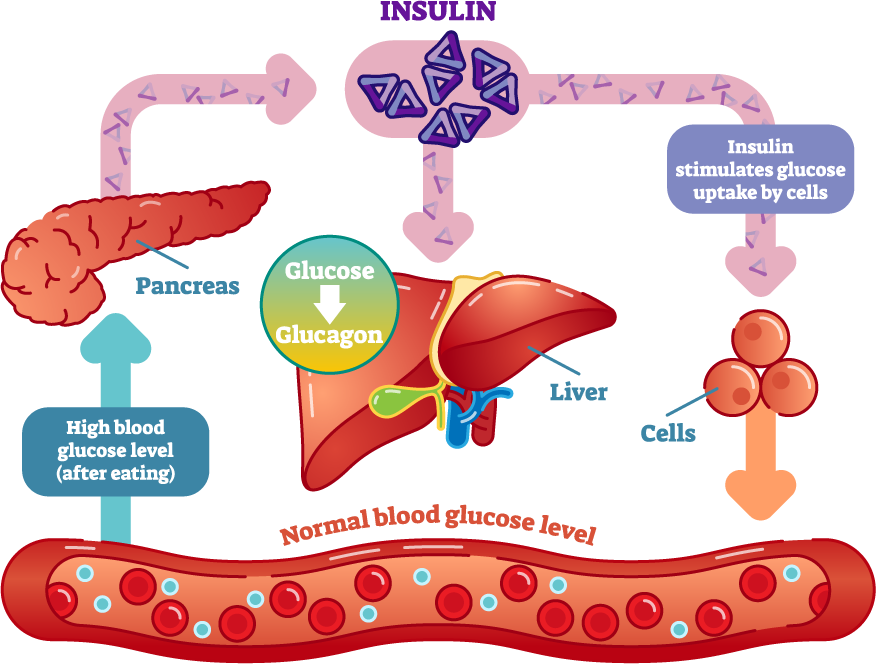
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, occurs when the level of glucose in the blood drops below normal. This can happen for various reasons, including taking too much insulin, skipping meals, or engaging in intense physical activity without adequate carbohydrate intake. Early symptoms can include shakiness, sweating, dizziness, and confusion.
Glucose tablets are specifically designed to provide a rapid source of glucose to quickly raise blood sugar levels. They are usually made of pure glucose (dextrose), allowing for faster absorption compared to other carbohydrates that require more digestion.
The Typical Response Time
The general consensus among healthcare professionals is that glucose tablets typically begin to raise blood sugar levels within 5 to 15 minutes. However, this is just an average, and individual experiences can vary.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends checking blood glucose levels 15 minutes after taking glucose tablets and, if still low, consuming another dose. This "15-15 rule" is a widely accepted guideline for managing mild to moderate hypoglycemia.
Factors Influencing Absorption Rate
Several factors can affect how quickly glucose tablets work. One of the most significant is whether the stomach is empty.
When the stomach is empty, the glucose can be absorbed more rapidly into the bloodstream. If food is present, particularly fats and proteins, the absorption rate can be significantly slowed down.
Another factor is the form of glucose taken. Glucose tablets, being pure glucose, are absorbed faster than complex carbohydrates found in foods like bread or fruit. Similarly, glucose gels or liquids might be absorbed slightly faster than solid tablets, though the difference is often negligible.
Individual metabolic rates also play a role. People with faster metabolisms may experience a quicker response, while those with slower metabolisms may see a delayed effect. Moreover, certain medical conditions, such as gastroparesis (delayed stomach emptying), can significantly slow down glucose absorption.
Physical activity can influence glucose absorption as well. While exercise can initially lower blood sugar, the increased blood flow associated with activity might, in some cases, slightly speed up the absorption of glucose taken to correct hypoglycemia.
Proper Usage of Glucose Tablets
Knowing how to use glucose tablets correctly is just as important as understanding their response time. Healthcare providers generally recommend carrying glucose tablets at all times if you're prone to hypoglycemia.
The ADA typically advises consuming 15-20 grams of glucose for a mild to moderate hypoglycemic episode. The packaging of glucose tablets usually indicates the amount of glucose per tablet, making it easy to calculate the correct dosage.
It's crucial to check blood glucose levels with a glucose meter before taking glucose tablets to confirm hypoglycemia. Treating perceived symptoms without confirmation could lead to hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), which can also have negative health consequences.
After taking glucose tablets, recheck blood glucose levels after 15 minutes. If blood sugar is still below the target range (usually around 70 mg/dL), take another dose of 15-20 grams of glucose and recheck again in 15 minutes. Repeat this process until blood sugar reaches the target range.
Once blood sugar is within the target range, it’s important to consume a longer-acting carbohydrate source, such as a piece of fruit or a small serving of crackers and cheese, to prevent another drop. This helps stabilize blood sugar levels and provides sustained energy.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While glucose tablets are effective for treating mild to moderate hypoglycemia, severe cases may require immediate medical attention. Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia include loss of consciousness, seizures, or an inability to swallow.
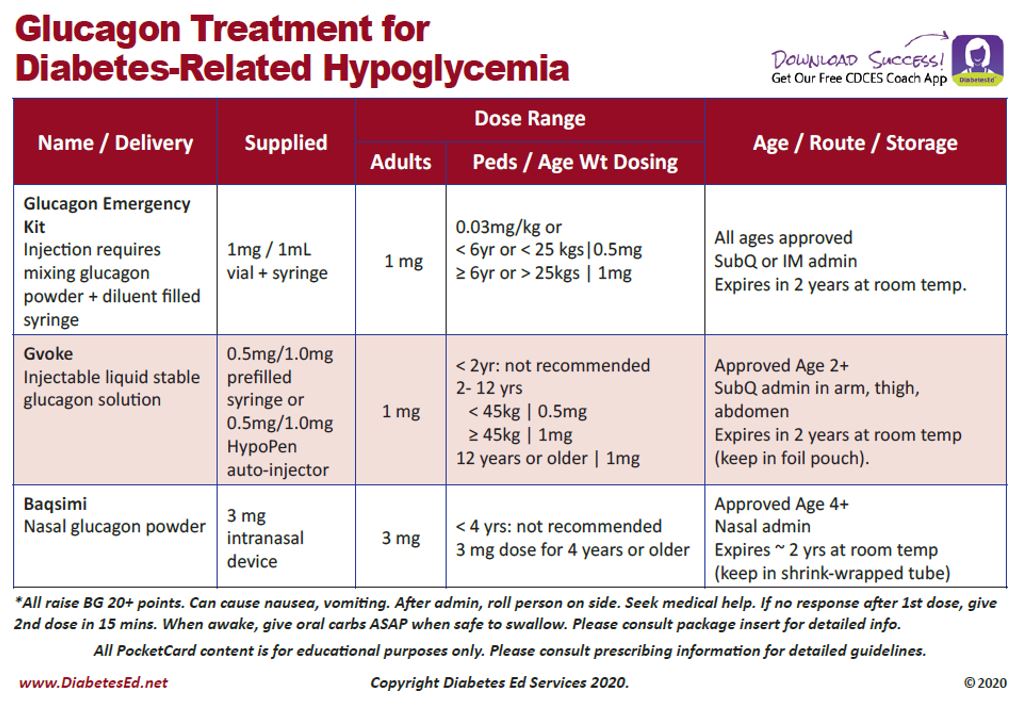
In these situations, a glucagon injection may be necessary. Glucagon is a hormone that stimulates the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream. Family members or caregivers should be trained on how to administer glucagon in case of an emergency.
If a person with diabetes becomes unconscious and glucagon is not available, call emergency services immediately. Time is of the essence in preventing serious complications, such as brain damage or death.
The Importance of Individualized Management Plans
Diabetes management is highly individualized, and the specific recommendations for treating hypoglycemia can vary depending on the person's age, overall health, medication regimen, and lifestyle. Consulting with a healthcare provider or certified diabetes educator is crucial for developing a personalized management plan.
This plan should include clear guidelines on how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia, including the appropriate dosage of glucose tablets, frequency of blood glucose monitoring, and when to seek medical assistance. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the plan with a healthcare professional is essential to ensure its effectiveness and safety.
By understanding how quickly glucose tablets work, what factors influence their absorption, and how to use them correctly, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage hypoglycemic episodes and maintain stable blood sugar levels. This proactive approach can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term complications.