How Many Therms Of Gas Per Month

Imagine stepping inside on a chilly evening, the comforting warmth of your home enveloping you like a gentle hug. The thermostat clicks softly, the furnace hums to life, and the aroma of dinner simmering on the stove fills the air. We often take for granted the invisible energy that powers these simple comforts, but have you ever stopped to wonder just how much natural gas, measured in therms, it takes to keep our homes running smoothly each month?
Understanding your natural gas consumption is more than just a matter of curiosity; it's key to budgeting, conserving energy, and making informed decisions about your household's energy footprint. The average household in the United States uses approximately 50 to 75 therms of natural gas per month, but this figure can fluctuate significantly based on several factors.
Understanding Therms: The Basics
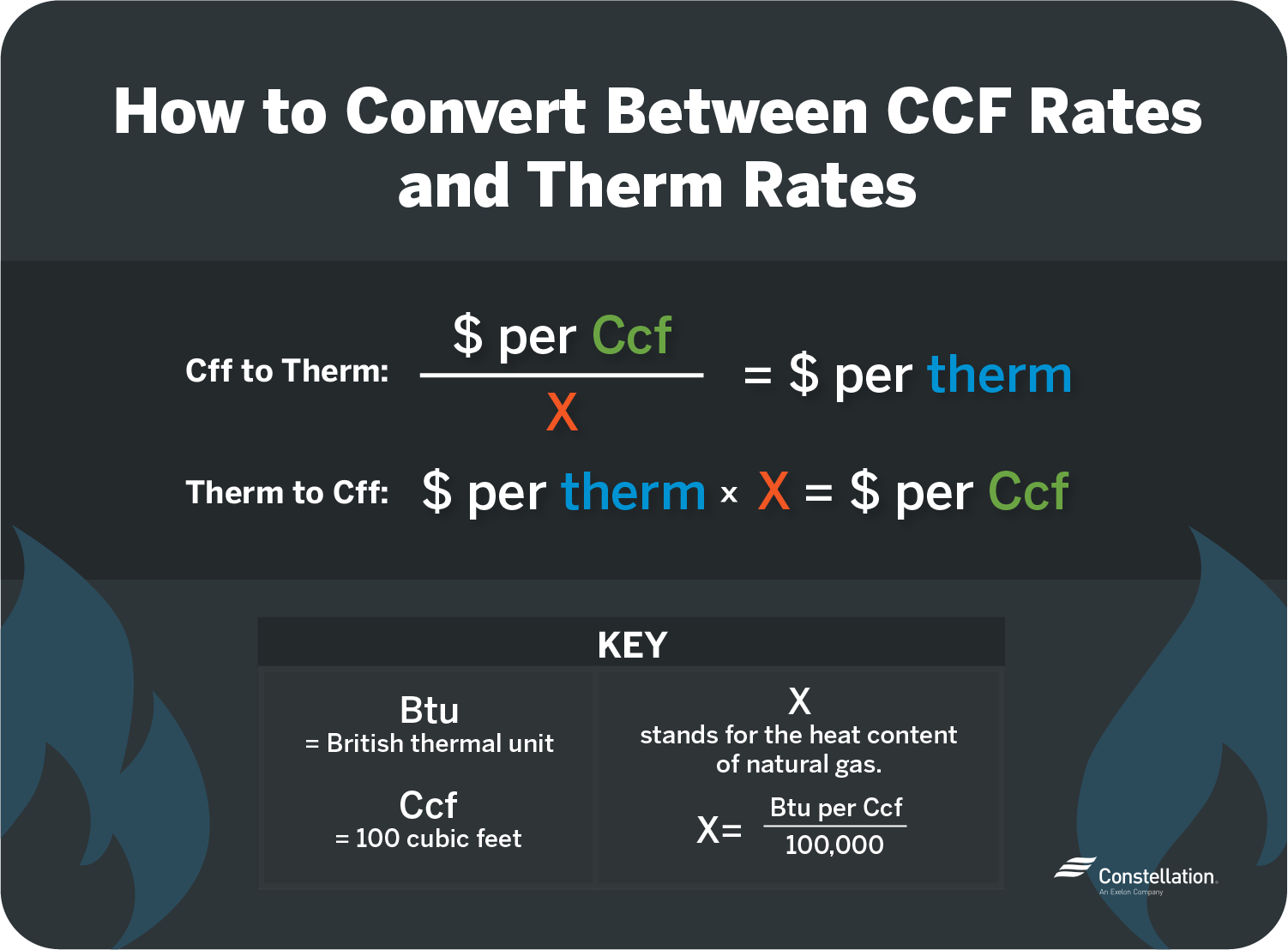
Before diving into the specifics of monthly gas usage, let's clarify what a therm actually is. A therm is a unit of heat energy equivalent to 100,000 British thermal units (BTUs).
Gas companies use therms to measure and bill for natural gas consumption because it provides a standardized way to account for the energy content of the gas, which can vary slightly.
Factors Influencing Monthly Gas Consumption
Several key factors contribute to the variability in monthly therm usage.
Climate and Location
Geographic location and the prevailing climate are perhaps the most significant determinants of gas consumption. Homes in colder regions naturally require more heating during the winter months, leading to a substantial increase in therm usage.
For example, a household in Maine will likely consume far more gas in January than a comparable household in Southern California.
Home Size and Insulation
The size of your home directly impacts the amount of energy needed to heat it. Larger homes have a greater volume of space to warm, requiring more gas.
Similarly, the quality of insulation plays a crucial role; well-insulated homes retain heat more effectively, reducing the need for constant heating and lowering gas consumption.
Appliance Efficiency and Usage
The efficiency of your gas-powered appliances, such as furnaces, water heaters, and stoves, can significantly affect your monthly therm usage. Older, less efficient appliances consume more gas to perform the same tasks as newer, high-efficiency models.
Consider, for instance, an old furnace with an Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) of 60% versus a modern furnace with an AFUE of 95%. The newer model will use significantly less gas to produce the same amount of heat.
Also, the frequency and duration of appliance use matters.
Household Size and Habits
The number of people living in a household and their energy consumption habits also play a role. Larger households typically use more hot water, resulting in higher gas consumption for water heating.
Similarly, habits like setting the thermostat to a higher temperature or taking long, hot showers can increase gas usage.
Average Monthly Therm Usage: A Closer Look
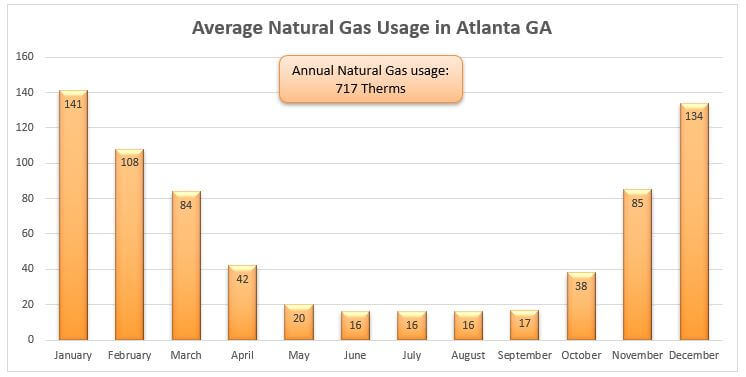
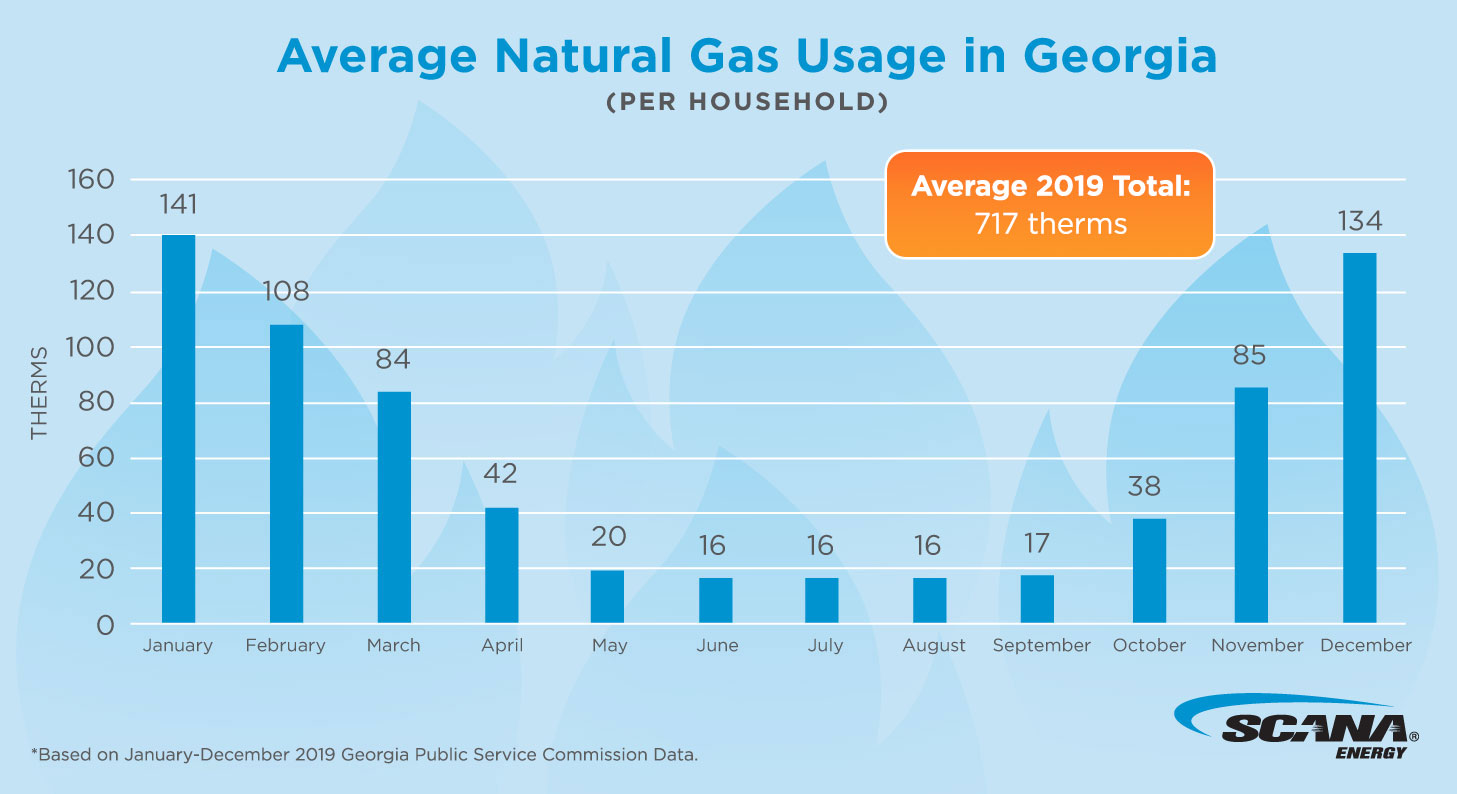
While the national average hovers around 50 to 75 therms per month, it's important to consider regional variations.
Regional Averages
According to data from the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), states in the Northeast and Midwest, which experience harsh winters, tend to have the highest average monthly gas consumption. The EIA provides detailed data on energy consumption by state and sector, offering valuable insights into regional trends.
For instance, states like Massachusetts and Michigan often see average monthly usage exceeding 100 therms during the peak winter months.
Seasonal Variations
Gas consumption typically peaks during the winter months due to heating demands. In contrast, usage is generally lower during the spring and fall when heating needs are minimal.
During the summer, gas consumption may increase slightly due to the use of gas stoves for cooking and potentially gas-powered water heaters, but it remains significantly lower than winter levels.
Tips for Reducing Gas Consumption
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to reduce your monthly gas consumption and lower your energy bills.
Upgrade to Energy-Efficient Appliances
Investing in high-efficiency furnaces, water heaters, and other gas-powered appliances can lead to significant savings over time. Look for appliances with the Energy Star label, indicating that they meet strict energy efficiency guidelines.
While the initial cost may be higher, the long-term savings on gas bills can more than offset the investment.
Improve Insulation
Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature and reducing heat loss. Insulating walls, attics, and basements can significantly decrease the amount of gas needed for heating.
Consider adding weather stripping around windows and doors to seal any drafts and prevent heat from escaping.
Adjust Thermostat Settings
Lowering your thermostat by a few degrees, especially when you're away from home or asleep, can make a noticeable difference in your gas consumption. Programmable thermostats can automate these adjustments, ensuring that you're only heating your home when necessary.
The Department of Energy recommends setting your thermostat to 68°F (20°C) while you're awake and lowering it while you're asleep or away from home.
Conserve Hot Water
Reducing your hot water usage can also help lower your gas bills. Take shorter showers, repair any leaky faucets, and wash clothes in cold water whenever possible.
Installing low-flow showerheads and faucets can further reduce water consumption without sacrificing water pressure.
Regular Maintenance
Regularly maintaining your gas-powered appliances can ensure they operate efficiently. Schedule annual tune-ups for your furnace and water heater to keep them running smoothly and prevent potential problems.
Also, be sure to clean or replace air filters regularly to maintain proper airflow.
Beyond the Numbers: The Broader Impact
Understanding and managing your natural gas consumption extends beyond personal savings. It's also about contributing to a more sustainable future.
Environmental Considerations
Natural gas is a fossil fuel, and its combustion contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, which are a major driver of climate change. By reducing your gas consumption, you can help lower your carbon footprint and mitigate the environmental impacts of energy production.
Consider exploring alternative energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to further reduce your reliance on fossil fuels.
Economic Implications
Lowering your gas bills not only saves you money but also reduces the overall demand for natural gas, potentially stabilizing energy prices for everyone. Energy conservation efforts can also create jobs in the renewable energy sector and promote economic growth.
Conclusion
While the average monthly therm usage of 50 to 75 provides a useful benchmark, it's essential to recognize that your individual consumption will vary depending on a multitude of factors. By understanding these factors and implementing energy-saving strategies, you can take control of your gas usage, lower your bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future. It's about finding a balance between comfort and conservation, ensuring that the warmth in our homes doesn't come at the expense of the planet.