How Many Volts To Charge A Laptop

The question of how many volts are needed to charge a laptop often leads to confusion, as the voltage supplied to the laptop is not the same as the voltage of the battery inside. Understanding the power requirements and adapter specifications is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient charging.
This article breaks down the intricacies of laptop charging voltages, exploring the roles of adapters, batteries, and the implications of using incorrect power supplies. It aims to clarify the technical specifications involved in laptop charging and offer practical guidance for users.
Understanding Laptop Charging Voltages
Laptop charging involves a complex interplay of voltages. The AC voltage from a wall outlet is converted by the laptop's power adapter into a DC voltage suitable for charging the internal battery and powering the laptop.
The voltage required to charge a laptop is not a fixed number. It depends on the laptop model and its battery specifications.
The Role of the Power Adapter
The power adapter, often referred to as a charger, plays a critical role in laptop charging. It transforms the high-voltage AC power from a wall outlet (typically 120V in North America or 230V in Europe) into a lower-voltage DC power.
The output voltage of the adapter is specifically designed to match the charging requirements of the laptop's battery and internal components. Using an incorrect adapter can damage the laptop or battery.
Laptop adapters typically output DC voltages ranging from 15V to 20V. However, the specific voltage and amperage (current) required are clearly labeled on the adapter itself.
Laptop Battery Voltage
While the adapter provides a voltage in the 15-20V range, the internal battery operates at a different voltage. Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in laptops, usually have a nominal voltage of 3.7V per cell.
Laptops typically use battery packs consisting of multiple cells connected in series. This increases the overall voltage of the battery pack, commonly falling between 10.8V and 14.8V.
The charging circuitry within the laptop manages the charging process. It ensures that the battery receives the correct voltage and current to charge safely and efficiently.
Key Specifications: Volts, Amps, and Watts
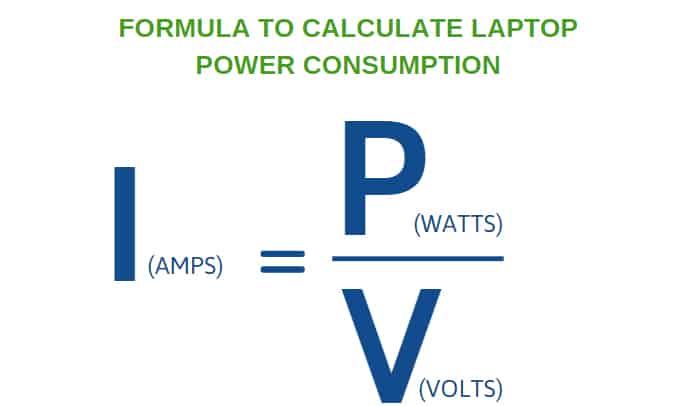
Understanding the relationship between volts, amps, and watts is essential for comprehending laptop power requirements. Voltage (V) represents the electrical potential difference, current (amps or A) represents the flow of electrical charge, and power (watts or W) is the rate at which energy is transferred.
The formula connecting these three is: Watts (W) = Volts (V) x Amps (A). Laptop adapters display both voltage and amperage. Multiplying these two values yields the adapter's power output in watts.
For instance, an adapter labeled 19V and 3.42A delivers approximately 65W of power. It is crucial to match the voltage and wattage requirements of the laptop when selecting a replacement adapter.
Using the Wrong Voltage: Potential Risks
Using an adapter with the wrong voltage can have serious consequences. If the voltage is too high, it can overheat and damage the laptop's internal components, including the motherboard and battery.
This can lead to permanent damage, rendering the laptop unusable. Conversely, if the voltage is too low, the laptop may not charge properly or at all.
It might also cause the adapter to overheat as it struggles to deliver the required power. While using an adapter with a slightly higher amperage than required is generally safe (the laptop will only draw the current it needs), using an adapter with a lower amperage can also lead to overheating and potential damage.
How to Find the Correct Voltage for Your Laptop
The easiest way to determine the correct voltage for your laptop is to check the original power adapter. The voltage and amperage are typically printed on a label on the adapter itself. Look for the "Output" section of the label.
You can also consult your laptop's user manual or the manufacturer's website. The specifications section should provide the required voltage and amperage for the power adapter.
If you're purchasing a replacement adapter, ensure that it matches the voltage and is equal to or greater than the amperage of the original adapter.
Third-Party Adapters: Proceed with Caution
While third-party laptop adapters can be a more affordable option, it is crucial to exercise caution. Not all third-party adapters are created equal, and some may not meet the required safety standards.
Opt for reputable brands that have been tested and certified to meet safety and performance requirements. Avoid purchasing cheap, unbranded adapters, as they may pose a fire hazard or damage your laptop.
Always check the reviews and ratings of third-party adapters before purchasing them. Look for adapters with safety certifications, such as UL or CE markings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the voltage required to charge a laptop is determined by the laptop's specific design and battery specifications. The power adapter plays a critical role in converting AC power to the appropriate DC voltage for charging.
Using the correct voltage is essential for ensuring safe and efficient charging. An incorrect voltage can damage the laptop and battery.
Always check the original adapter or the manufacturer's specifications to determine the correct voltage and amperage before purchasing a replacement.