How Many Watts Does A Upright Freezer Use

Urgent alert: Your energy bill could be skyrocketing! Upright freezers, essential appliances for many, consume varying amounts of electricity, directly impacting your household expenses.
Understanding the wattage consumption of your upright freezer is crucial for effective energy management and budgeting. This article breaks down the average wattage usage, factors influencing energy consumption, and practical tips to minimize your freezer's impact on your electricity bill.
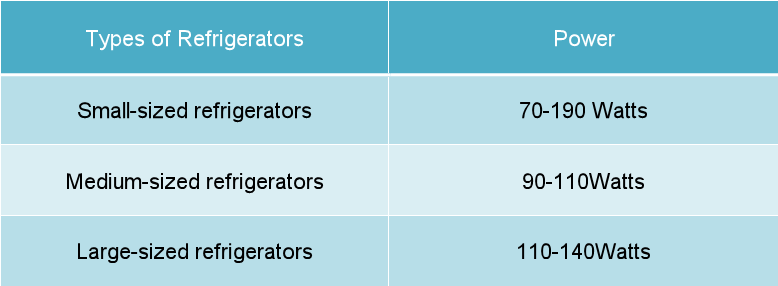
Average Wattage of Upright Freezers
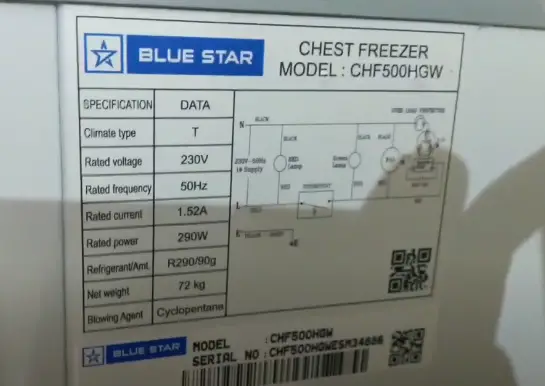
The average upright freezer uses between 100 and 400 watts. This range depends heavily on the freezer's size, age, and energy efficiency rating.
Smaller, more efficient models typically consume closer to 100 watts, while larger, older models can easily draw 400 watts or more.
Knowing your freezer's wattage is the first step toward controlling your energy costs.
Factors Influencing Wattage Consumption
Several factors directly impact how much electricity your upright freezer uses.
Size: Larger freezers require more energy to maintain their internal temperature. Age: Older models are generally less energy-efficient than newer ones due to outdated technology and insulation. Energy Efficiency Rating: Look for the Energy Star label. Usage Habits: Frequent opening of the door lets cold air escape, forcing the freezer to work harder to cool down.
Consider these factors to optimize energy usage and minimize costs.
Calculating Energy Consumption and Cost
To calculate the estimated daily energy consumption, multiply the wattage by the number of hours the freezer runs per day (typically around 8-12 hours) and divide by 1000 to get kilowatt-hours (kWh).
For example, a 200-watt freezer running for 10 hours uses (200 * 10) / 1000 = 2 kWh per day.
Multiply the daily kWh usage by your electricity rate (found on your bill) to determine the daily cost. Further, multiply the daily cost by 30 to estimate the monthly cost.
Practical Tips to Reduce Energy Consumption
Simple changes can significantly reduce your freezer's energy consumption. Regular Defrosting: Frost buildup reduces efficiency. Proper Loading: Don't overfill, but also keep it adequately stocked to maintain temperature. Optimal Temperature Setting: Aim for 0°F (-18°C) for best preservation and energy efficiency. Seal Check: Ensure the door seal is tight to prevent cold air leakage.
These measures can lead to noticeable savings on your energy bill.
Consider upgrading to an Energy Star certified model for long-term savings.
The Impact of "Phantom Load"
Even when not actively cooling, some freezers consume a small amount of power known as "phantom load."
This can be minimized by ensuring the freezer is properly maintained and not drawing unnecessary power when idle.
Unplugging the freezer when not in use for extended periods is another option to eliminate phantom load.
Next Steps: Monitor your freezer's energy consumption using a smart meter or energy monitoring device. Compare your usage with similar households and implement the tips outlined above to optimize efficiency. Consult with an appliance repair professional if you suspect any malfunctions or inefficiencies. Stay informed about energy-saving technologies and government rebates for energy-efficient appliances.