How Much Do You Make Being In The Army

The U.S. Army offers a complex compensation structure that extends beyond a simple paycheck. Understanding the financial realities of military service requires a closer look at base pay, allowances, and potential bonuses. These factors all determine a soldier’s financial well-being.
This article breaks down the various components of Army compensation. It provides a clear picture of what soldiers earn. This information is based on publicly available pay scales and official Army resources.
Base Pay: The Foundation
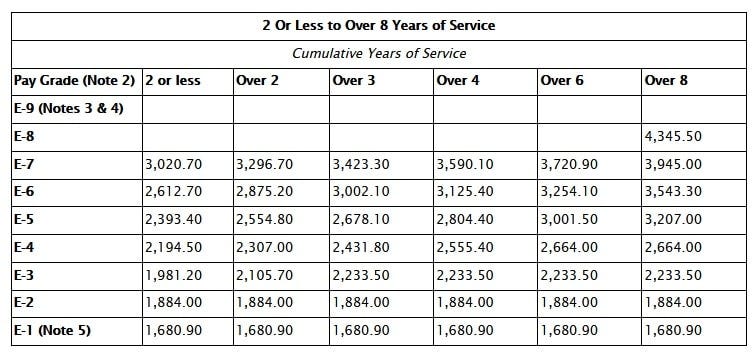
Base pay is the fundamental component of an Army soldier’s earnings. This is determined by their rank and years of service. A brand new, entry-level Private (E-1) with less than four months of service earns a starting base pay of approximately $20,172 per year, as of 2023 pay scales.
As soldiers advance in rank and accumulate years of service, their base pay increases. A Sergeant (E-5) with four years of service can expect to earn significantly more. This reflects their increased responsibility and experience.
Allowances: Covering Basic Needs
In addition to base pay, soldiers receive allowances to cover essential living expenses. Two primary allowances are Basic Allowance for Housing (BAH) and Basic Allowance for Subsistence (BAS). These significantly boost their overall compensation.
BAH is designed to offset the cost of housing. Its amount varies depending on the soldier's rank, location, and whether they have dependents. Soldiers living on base typically do not receive BAH, as housing is provided.
BAS is intended to cover the cost of food. In 2023, the monthly BAS rate for enlisted personnel is $452.56.
Special Pay and Bonuses: Incentives for Specialized Skills
The Army offers various special pays and bonuses to incentivize service in specific roles or locations. These can substantially increase a soldier's earnings.
Hazardous duty pay, for example, is awarded to soldiers who perform tasks that involve a high risk of injury or death. Enlistment bonuses are also offered to attract qualified individuals to join the Army, particularly in high-demand career fields like cyber security or special operations.
Recruiting bonuses are also often available, especially for difficult-to-fill positions. These incentives can add a substantial sum to a soldier's overall compensation package.
Healthcare and Other Benefits: Beyond the Paycheck
Beyond direct monetary compensation, soldiers receive a comprehensive package of benefits. This includes healthcare, retirement plans, and educational opportunities. These benefits can represent significant long-term value.
Military healthcare, known as TRICARE, provides comprehensive medical and dental coverage for soldiers and their families. This is a significant benefit, as it eliminates the need for private health insurance premiums.
Soldiers are also eligible for retirement benefits after a certain number of years of service. They also gain access to the GI Bill, which provides funding for education and training after leaving the Army.
Financial Planning and Resources
The Army provides soldiers with resources to help them manage their finances effectively. This includes financial counseling services and educational programs.
These resources can help soldiers develop budgeting skills, manage debt, and plan for their financial future. They are tools that can greatly improve soldiers' financial well-being.
Understanding the components of Army pay requires considering base pay, allowances, bonuses, and benefits. This information can help prospective recruits and current soldiers make informed financial decisions.





/GettyImages-177279569-5aec6e7aff1b780036231270.jpg)








/enlisted-promotions-made-simple-3332773_FINAL-5bbd0ee8c9e77c00513a439f.png)