How Much Does Clomid Increase Testosterone

Clomiphene citrate, commonly known as Clomid, is a medication primarily prescribed to women to induce ovulation. However, its off-label use in men to increase testosterone levels has become increasingly prevalent. Understanding the extent to which Clomid can influence testosterone production is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers considering this treatment option.
This article explores the science behind Clomid's effect on testosterone, the typical range of increase one can expect, and the potential benefits and risks associated with its use in men.
Clomid and Testosterone: The Mechanism
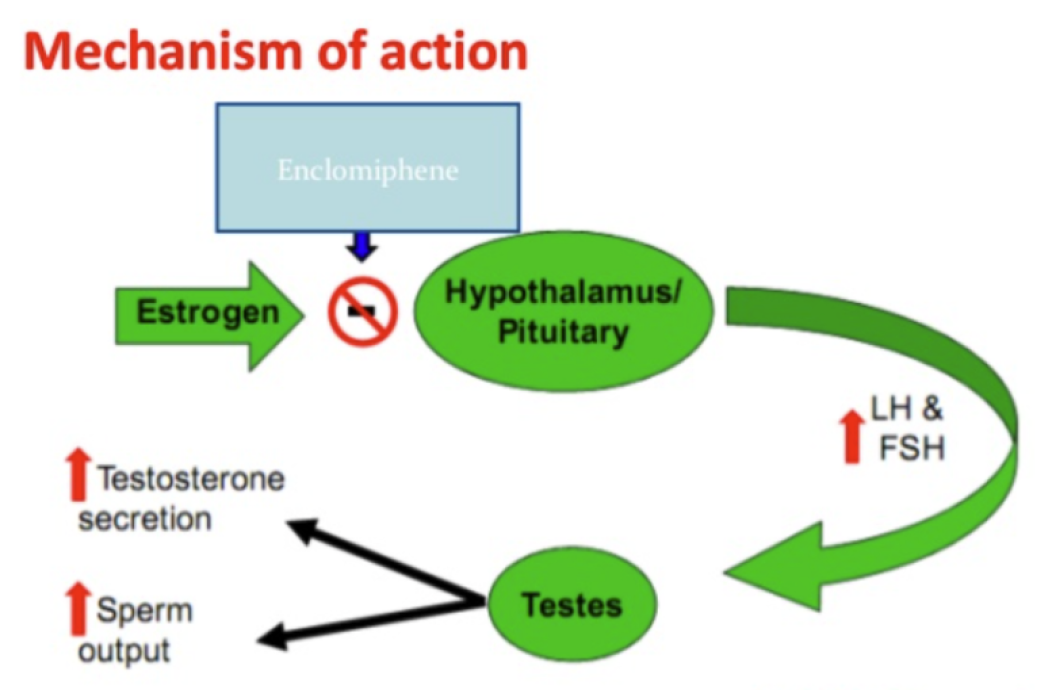
Clomid functions as a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, a region of the brain responsible for regulating hormone production.
By blocking estrogen, Clomid tricks the hypothalamus into thinking the body has low estrogen levels. This stimulates the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
GnRH then prompts the pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones, in turn, stimulate the testes to produce more testosterone.
Expected Testosterone Increase: The Numbers
The degree to which Clomid increases testosterone levels varies from person to person. It depends on individual factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and the initial testosterone level.
Studies generally show that Clomid can increase testosterone levels by an average of 50 to 250 ng/dL in men with low to normal testosterone. A 2013 study published in the journal "Fertility and Sterility" showed a mean increase of 136 ng/dL in hypogonadal men treated with Clomid.
It's crucial to remember that these are average increases. Some men may experience a more significant boost, while others may see a minimal change. Baseline testosterone levels significantly influence the magnitude of the increase. Men with very low baseline testosterone are likely to see a larger percentage increase than those with levels already in the low-normal range.
Benefits of Increased Testosterone
Raising testosterone levels, even moderately, can have several beneficial effects. These can include improved energy levels, increased libido, and enhanced mood.
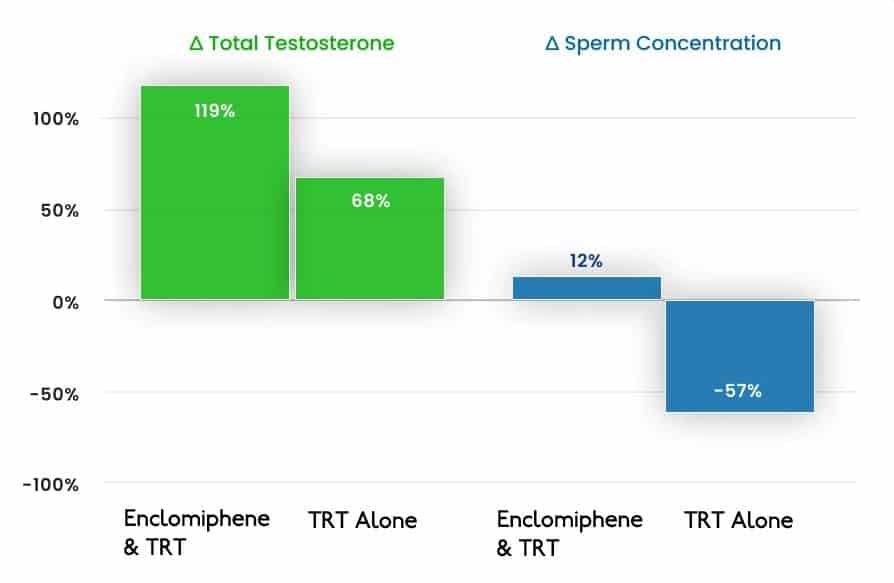
Some men may also experience improved muscle mass and bone density. Clomid can be a viable alternative to testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) in certain cases. It can help preserve fertility, as TRT can sometimes suppress sperm production.
Risks and Side Effects
Like all medications, Clomid carries potential risks and side effects. Common side effects include mood swings, visual disturbances, and breast tenderness (gynecomastia).
Less common but more serious side effects can include blood clots and allergic reactions. It is essential to note that Clomid is an off-label use for men and long-term safety data is still being gathered.
Men considering Clomid should undergo a thorough medical evaluation. This should include a hormone panel and a discussion of potential risks and benefits with their physician. Individuals with pre-existing liver disease or uncontrolled hypertension should generally avoid Clomid.
Who Benefits Most from Clomid?
Clomid is often considered for men with secondary hypogonadism. This is a condition where the testes are functioning correctly. But the pituitary gland is not signaling them to produce enough testosterone.
Men experiencing symptoms of low testosterone, such as fatigue, low libido, and erectile dysfunction, may benefit. Clomid is also frequently considered for men who are concerned about fertility and wish to avoid the potential sperm-suppressing effects of traditional testosterone replacement therapy.
It is not typically recommended for men with primary hypogonadism. This is a condition where the testes themselves are not functioning properly, as Clomid will not be effective in stimulating testosterone production in these cases.
Alternatives to Clomid
Several alternatives to Clomid exist for treating low testosterone. These include testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) in various forms such as injections, gels, and patches. Lifestyle modifications, such as diet and exercise, can also play a role in naturally boosting testosterone levels.
Other medications, such as aromatase inhibitors, may be used in certain cases to manage estrogen levels. The best treatment option depends on the individual's specific circumstances and medical history.
The Importance of Medical Supervision
It is crucial to emphasize that Clomid should only be used under the direct supervision of a qualified healthcare professional. Self-treating with Clomid can be dangerous and may lead to adverse health outcomes.
A doctor can properly assess a patient's medical history, perform necessary blood tests, and monitor for potential side effects. They can adjust the dosage as needed to achieve the desired testosterone levels. Regular monitoring is essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Conclusion
Clomid can be an effective option for increasing testosterone levels in certain men. It typically raises testosterone by 50 to 250 ng/dL. However, its use comes with potential risks and side effects.
Men considering Clomid should thoroughly discuss the benefits and risks with their physician. They must ensure that it is the appropriate treatment option for their specific condition. With proper medical supervision, Clomid can improve testosterone levels and enhance quality of life for select individuals.
The decision to use Clomid should always be a collaborative one between patient and doctor. It should be based on a careful evaluation of individual needs and circumstances.













![How Much Does Clomid Increase Testosterone How Much Does Testosterone Cost Per Month? | HFS Clinic [HGH & TRT]](https://hghfor-sale.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/testosterone-injections-cost-750x500.jpg)
![How Much Does Clomid Increase Testosterone How Much Does Testosterone Cost Per Month? | HFS Clinic [HGH & TRT]](https://hghfor-sale.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/testosterone-pills-cost.jpg)