How To Calculate Average Common Stockholders Equity

Imagine peering into the financial heart of a company, seeking to understand its strength, its stability, its very essence. The world of finance can seem like a labyrinth of numbers and jargon, but sometimes, a single calculation can illuminate the path forward. Today, we embark on a journey to demystify one such calculation: the average common stockholders’ equity.
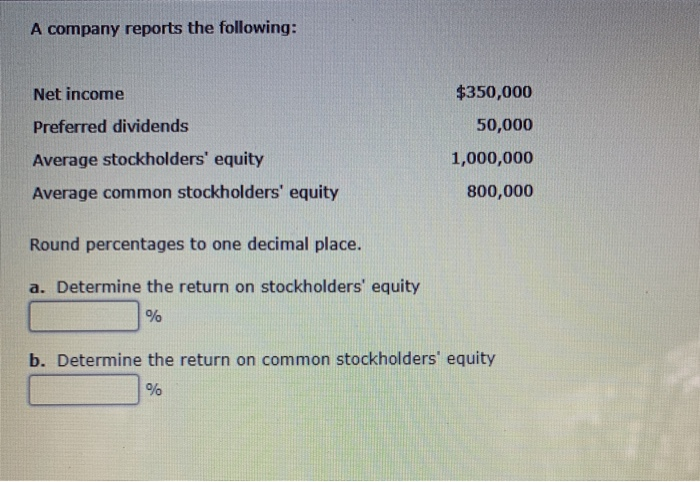
At its core, the average common stockholders’ equity is a financial metric that provides a snapshot of the total investment made by common shareholders in a company over a specific period. Understanding this value is crucial for investors, analysts, and business owners alike, as it helps assess a company's financial health and performance, particularly when calculating key profitability ratios like the return on equity (ROE).
Understanding Stockholders' Equity
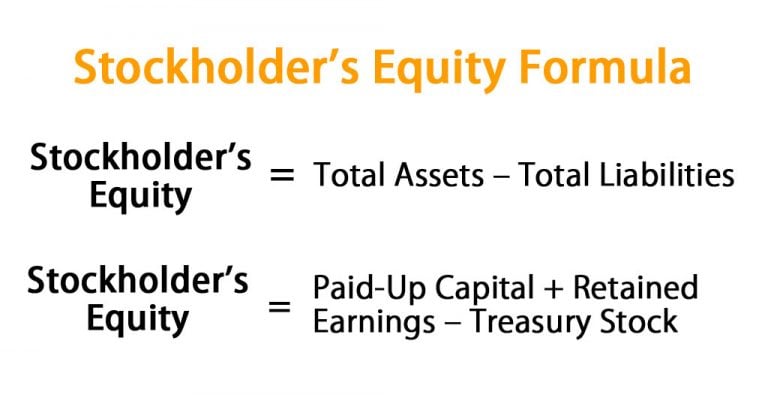
Before diving into the calculation, let's first understand what stockholders' equity represents. It is the residual interest in the assets of an entity that remains after deducting its liabilities. In simpler terms, it's what would be left over for the shareholders if the company sold all its assets and paid off all its debts.
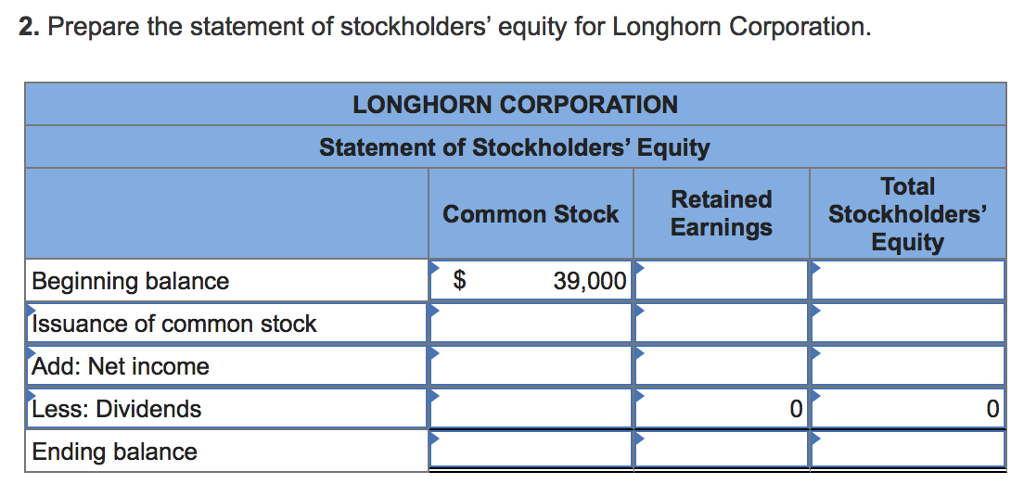
Stockholders' equity typically consists of several components, including common stock, preferred stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital. For the purpose of calculating average common stockholders’ equity, we primarily focus on the equity attributable to common shareholders.
Components of Common Stockholders' Equity
The most common components you'll encounter are common stock and retained earnings.
Common Stock: Represents the par value of the shares issued by the company.
Retained Earnings: Accumulates the company's net income over time, less any dividends paid out to shareholders.
Other components like additional paid-in capital (the amount shareholders paid above the par value of the stock) might be included but are less frequently considered when simplifying the calculation for basic understanding.
Calculating Average Common Stockholders' Equity
The formula for calculating average common stockholders’ equity is straightforward.
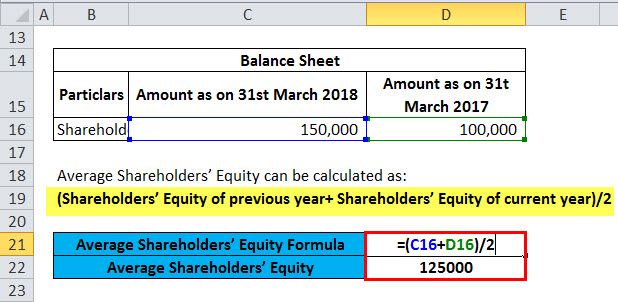
It involves taking the beginning and ending common stockholders' equity values for a specific period (usually a year) and averaging them. The formula is as follows:
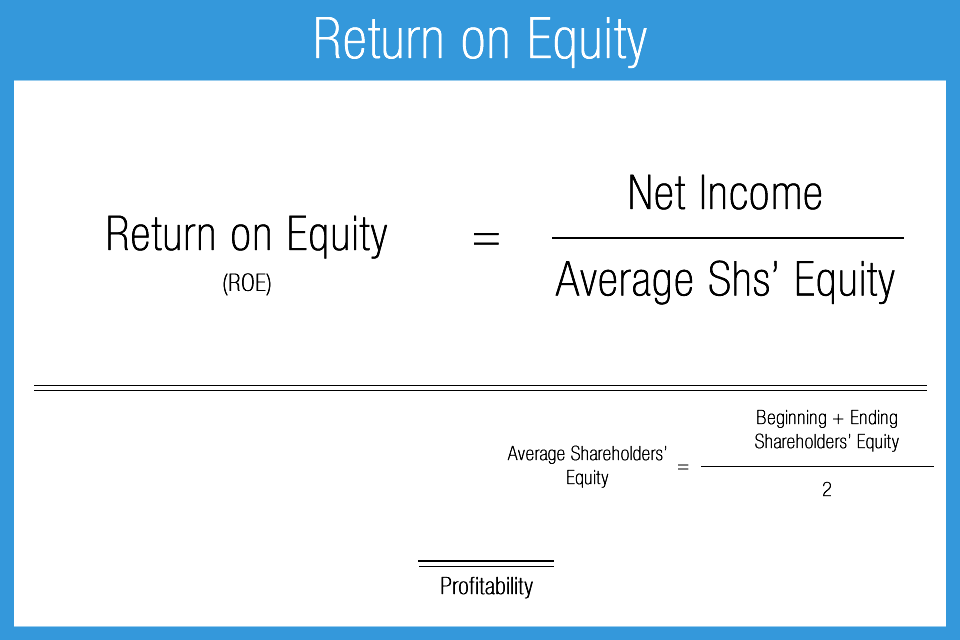
Average Common Stockholders’ Equity = (Beginning Common Stockholders’ Equity + Ending Common Stockholders’ Equity) / 2
Step-by-Step Calculation
Let's break down the calculation into simple steps:
Step 1: Identify the Beginning Common Stockholders' Equity. This figure can be found on the company's balance sheet at the beginning of the accounting period.
Step 2: Identify the Ending Common Stockholders' Equity. This is the corresponding figure on the balance sheet at the end of the accounting period.
Step 3: Add the Beginning and Ending Values. Sum the two figures obtained in steps 1 and 2.
Step 4: Divide by Two. Divide the sum by 2 to arrive at the average common stockholders’ equity.
Example Calculation
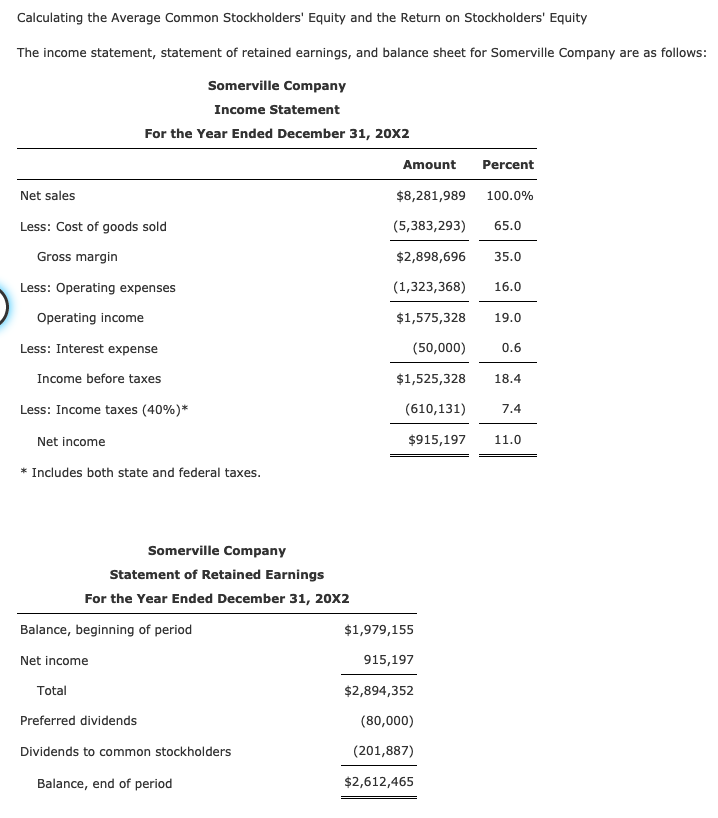
Suppose a company, let's call it "Sunrise Tech," had a beginning common stockholders' equity of $500,000 and an ending common stockholders' equity of $600,000 for the year 2023.
Using the formula, the average common stockholders’ equity would be:
($500,000 + $600,000) / 2 = $550,000
Therefore, the average common stockholders’ equity for Sunrise Tech in 2023 is $550,000.
Significance and Applications
The average common stockholders’ equity is not just a standalone number. Its true value lies in its application in various financial analyses.
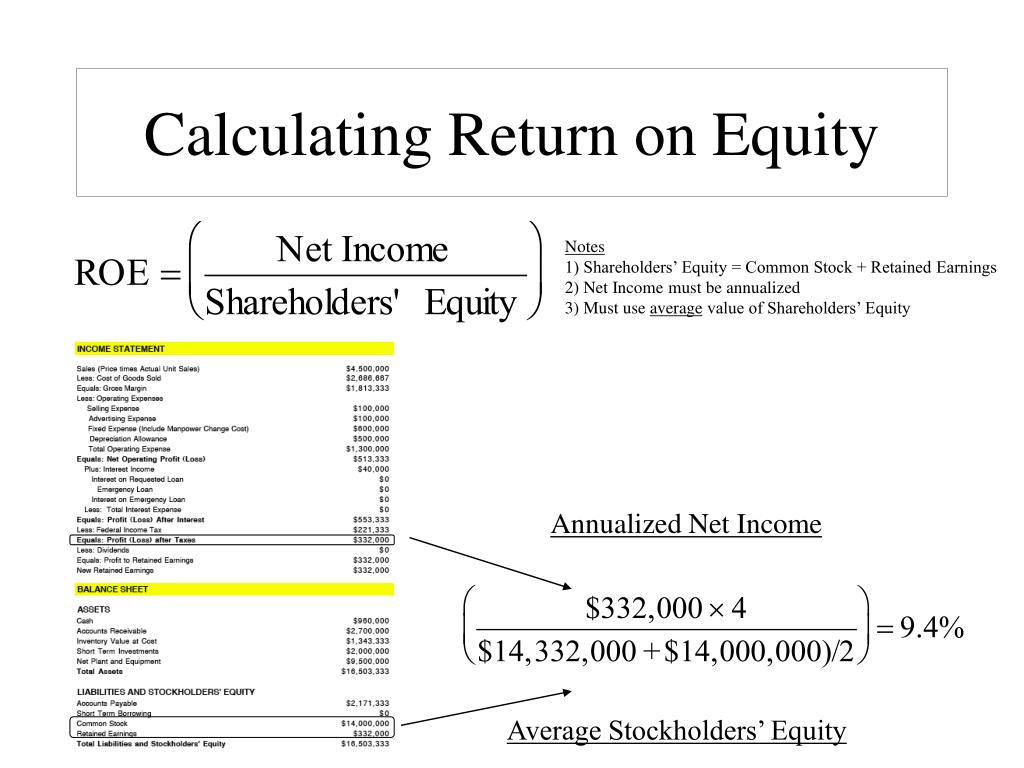
It's most notably used in calculating the Return on Equity (ROE). ROE measures how effectively a company is using shareholders' investments to generate profit. A higher ROE generally indicates that a company is efficiently using its equity to generate earnings.
Additionally, analysts use average common stockholders' equity to assess a company’s financial leverage and solvency. By comparing this metric with other financial data, such as total assets or total liabilities, they can gauge the company's capital structure and risk profile.
For instance, a company with a relatively small average common stockholders' equity compared to its total liabilities might be considered highly leveraged, indicating a higher level of financial risk.
ROE and Investor Insights
Understanding how to calculate ROE using average common stockholders' equity can significantly enhance an investor's decision-making process.
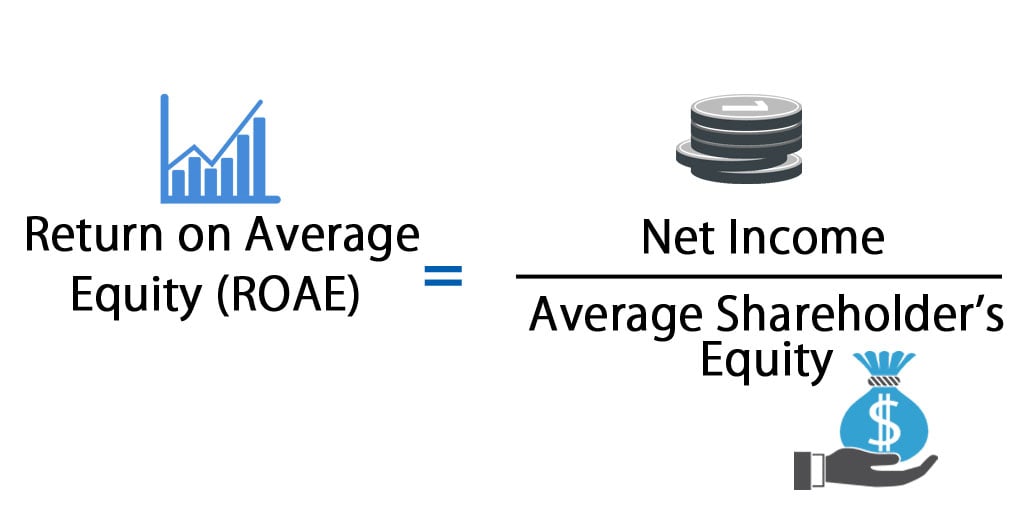
ROE = Net Income / Average Common Stockholders' Equity
Let's assume Sunrise Tech had a net income of $100,000 in 2023. With an average common stockholders' equity of $550,000, the ROE would be:
$100,000 / $550,000 = 0.1818 or 18.18%
This means that for every dollar of common stockholders' equity, Sunrise Tech generated 18.18 cents in profit. Comparing this ROE to industry averages or to Sunrise Tech's historical ROE can provide valuable insights into the company's performance.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
While the calculation itself is quite simple, there are a few potential challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
Accuracy of Financial Statements: The accuracy of the average common stockholders' equity depends on the accuracy of the underlying financial statements. Any errors or misstatements in the beginning or ending equity values will directly impact the calculation.
Changes in Equity Structure: Significant changes in the company's equity structure, such as large stock repurchases or issuances, can distort the average. In such cases, a weighted average might provide a more accurate representation.
Preferred Stock: When calculating common stockholders' equity, it's crucial to exclude the equity attributable to preferred shareholders. Preferred stock has different rights and characteristics compared to common stock, and including it would misrepresent the investment made by common shareholders.
Conclusion
Calculating average common stockholders' equity is a fundamental skill in financial analysis. It serves as a vital building block for understanding a company's financial health, performance, and efficiency in utilizing shareholder investments. By understanding this metric and its applications, especially in conjunction with the return on equity, investors and analysts can make more informed decisions.
As you continue your journey through the world of finance, remember that each calculation, each ratio, each financial statement tells a story. The average common stockholders’ equity is a chapter in that story, revealing insights into the heart of a company’s financial well-being.