How To Get Rid Of Echo In Ear
A persistent echo in your ear, often described as autophony, can be more than just a minor annoyance. For some, it's a disconcerting disruption that interferes with daily life, affecting communication, concentration, and overall well-being. Understanding the causes and potential solutions is crucial for regaining auditory comfort and clarity.
This article delves into the multifaceted world of autophony, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding its potential causes, exploring various diagnostic approaches, and outlining a range of treatment options, from simple home remedies to advanced medical interventions. This will help individuals experiencing this frustrating symptom to navigate the path towards relief and improved quality of life.
Understanding Autophony: What Causes the Echo?
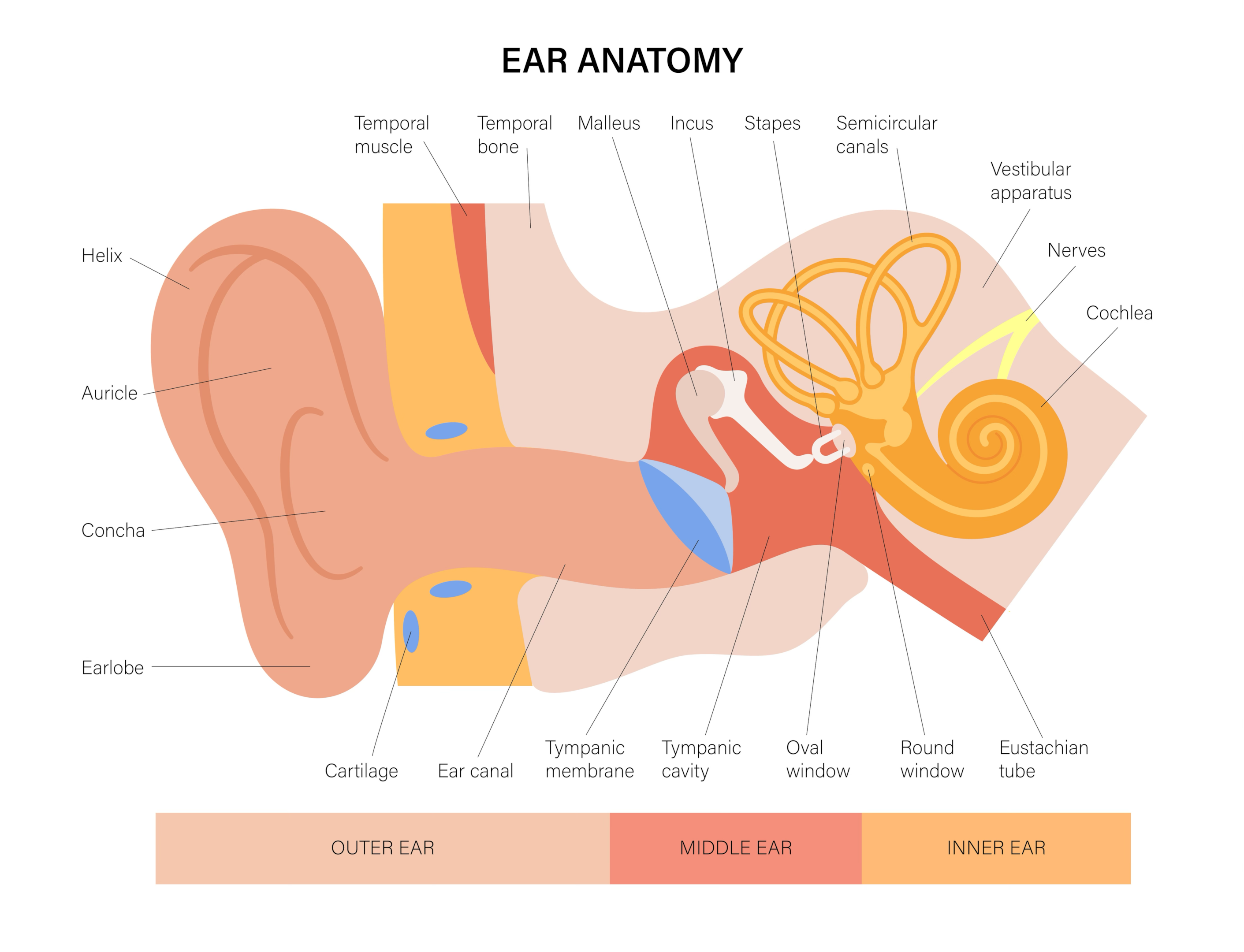
Autophony, the sensation of hearing your own voice or other internal sounds louder than normal, often accompanied by an echo, arises from disruptions in the way sound is conducted and processed within the ear.
The root cause often lies in issues affecting the middle ear, the area responsible for transmitting sound vibrations to the inner ear.
Several factors can contribute to this imbalance, altering the normal auditory experience.
Common Culprits in the Middle Ear
One of the most frequent culprits is a patent Eustachian tube (PET). This condition occurs when the Eustachian tube, which normally opens briefly to equalize pressure in the middle ear, remains persistently open.
This abnormal openness creates a direct pathway for sound to travel from the nasopharynx (the upper part of the throat) to the middle ear, bypassing the usual attenuation mechanisms. Consequently, individuals may hear their own breathing, speech, or heartbeat amplified in their ear.
Another potential cause is middle ear effusion, a build-up of fluid behind the eardrum. This fluid can alter the way sound vibrates the eardrum, leading to altered auditory perception.
Beyond the Middle Ear: Other Contributing Factors
While middle ear issues are the most common source of autophony, other factors can also play a role. Superior canal dehiscence (SCD), a rare condition, involves a small hole or thinning in the bone overlying the superior semicircular canal in the inner ear.
This defect creates an abnormal window, allowing sound and pressure changes to directly stimulate the inner ear, resulting in autophony and other vestibular symptoms.
In some cases, temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, affecting the jaw joint, can also manifest as ear-related symptoms, including a feeling of fullness or echoing.
Diagnosing the Source of the Echo
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management of autophony. A comprehensive audiological evaluation, conducted by an audiologist or ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist, is typically the first step.
This evaluation often includes a detailed medical history, a physical examination of the ear, and a series of hearing tests.
These tests help assess the type and extent of any hearing loss, identify abnormalities in middle ear function, and rule out other potential causes of the symptoms.
Key Diagnostic Procedures
Tympanometry is a key test to evaluate the function of the middle ear. This measures the eardrum's movement in response to changes in air pressure.
Abnormal tympanometry results can suggest the presence of middle ear effusion, Eustachian tube dysfunction, or other middle ear pathologies.
The Valsalva maneuver, where the patient attempts to exhale against a closed nose and mouth, can be used to assess Eustachian tube function.
Advanced Imaging and Further Investigations
In certain cases, imaging studies may be necessary to further investigate the cause of autophony. A high-resolution computed tomography (CT) scan of the temporal bones can help identify structural abnormalities, such as superior canal dehiscence or other bony defects.
Additionally, vestibular testing, including tests like videonystagmography (VNG), may be performed to assess the function of the inner ear's balance system and rule out vestibular disorders.
Depending on the suspected cause, a referral to a neurologist or other specialist may be necessary for further evaluation.
Navigating Treatment Options: From Simple Solutions to Medical Interventions
The treatment approach for autophony varies depending on the underlying cause. In many cases, conservative measures and lifestyle modifications can provide significant relief.
For individuals with patent Eustachian tube (PET), strategies to temporarily close the Eustachian tube, such as lying down or tilting the head forward, may help alleviate symptoms.
Staying well-hydrated and avoiding decongestants (which can dry out the nasal passages) can also be beneficial.
Addressing Middle Ear Issues
If middle ear effusion is the culprit, treatment may involve antibiotics for bacterial infections, decongestants to reduce swelling, or, in some cases, a myringotomy (a small incision in the eardrum) to drain the fluid.
For chronic or recurrent middle ear effusions, placement of pressure equalization (PE) tubes may be considered to ventilate the middle ear and prevent fluid build-up.
In cases of Eustachian tube dysfunction, nasal sprays containing corticosteroids or decongestants may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and improve tube function.
Surgical Interventions and Advanced Therapies
For superior canal dehiscence, surgical repair is often the definitive treatment. This typically involves plugging or resurfacing the dehiscence to restore normal inner ear function.
The specific surgical technique used depends on the location and size of the dehiscence.
For TMJ-related autophony, treatment focuses on addressing the underlying jaw joint dysfunction, which may involve physical therapy, medications, or dental appliances.
Looking Ahead: Managing and Living with Autophony
While autophony can be a challenging condition, understanding its causes and exploring available treatment options can significantly improve the quality of life for affected individuals. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are key to achieving optimal outcomes.
Ongoing research continues to advance our understanding of autophony and its various subtypes, leading to the development of new and improved diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
By working closely with healthcare professionals and adopting proactive self-management strategies, individuals can effectively navigate the challenges of autophony and regain a sense of auditory normalcy.






![How To Get Rid Of Echo In Ear How to Get Water Out of Your Ears [Infographic] Home Remedies For](https://i.pinimg.com/originals/52/44/9d/52449d8e268270298d786763502841fe.jpg)
/how-to-drain-fluid-from-middle-ear-5189742_FINAL-dacf6231a5d3472a9d030388770f4d97.jpg)