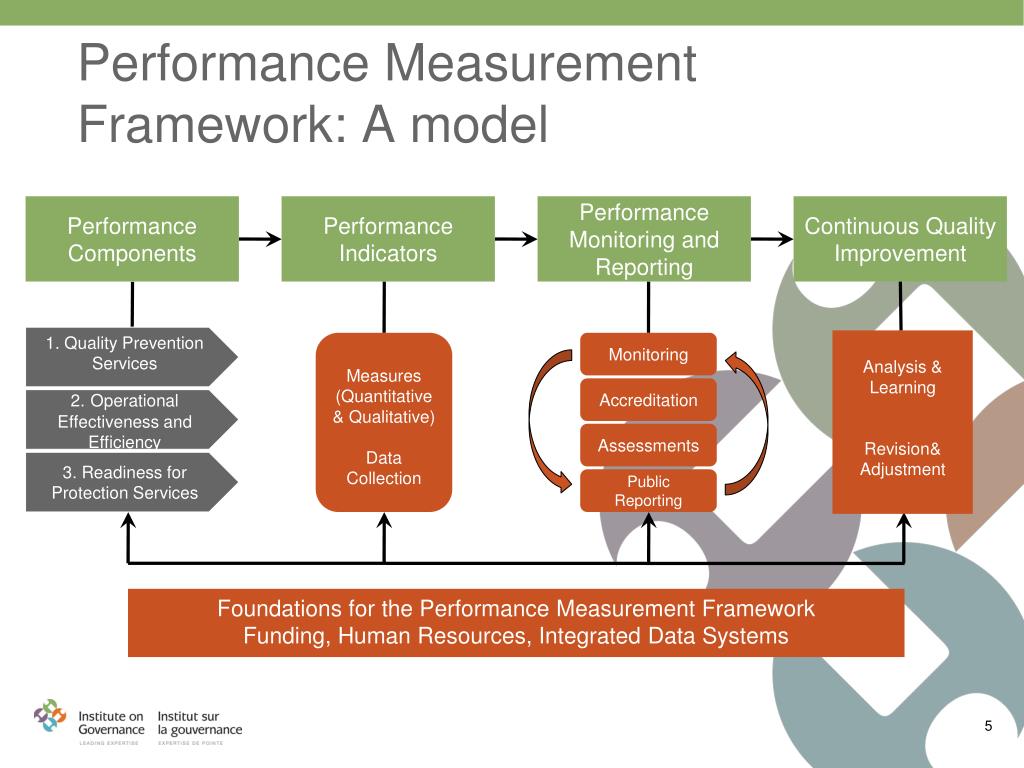
How To Measure Your Performance At Work

In today's dynamic work environment, understanding and measuring individual performance is crucial for career growth and organizational success. But how do employees accurately assess their contributions and identify areas for improvement? This article explores various methods and strategies for effectively measuring your performance at work.
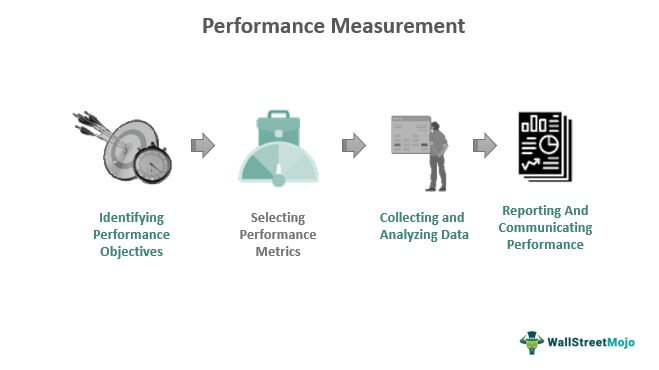
At its core, measuring performance involves tracking progress against defined goals and objectives. This isn't just about ticking boxes; it's about gaining insights into your strengths, weaknesses, and overall impact on the company.
Setting the Foundation: Defining Goals and Objectives
The first step in measuring performance is establishing clear and measurable goals. These goals should align with both your individual responsibilities and the broader organizational strategy.
According to the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM), using the SMART framework – Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound – is essential for crafting effective goals. Each goal needs to be explicitly defined and achievable.
For example, instead of setting a vague goal like "improve communication skills," a SMART goal would be "conduct three presentations to different teams by the end of Q3, incorporating feedback from each session to improve clarity and engagement scores by 10%."
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Metrics
Once goals are defined, identifying relevant KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) is crucial. KPIs provide quantifiable measures of progress towards those goals.
The specific KPIs will vary depending on your role and industry. For example, a sales representative might track sales revenue and conversion rates, while a software developer may focus on code quality and project completion timelines.
Metrics help track and measure the performance in real time. Make sure that your KPIs and metrics are up to date, and review it regularly.
Methods for Measuring Performance
Self-Assessment: A Critical First Step
Before seeking external feedback, a self-assessment is vital. This involves reflecting on your performance against your goals and KPIs. Be honest about your achievements and shortcomings.
Consider using a self-assessment template that outlines your key responsibilities, achievements, challenges, and areas for development. Tools like StrengthsFinder can also aid in recognizing areas for performance improvement.
Seeking Feedback from Others
Gathering feedback from colleagues, supervisors, and even clients provides a more comprehensive perspective on your performance. Constructive feedback can highlight blind spots and offer valuable insights.
Regular performance reviews are a formal opportunity to receive feedback from your manager. However, don't wait for these formal reviews. Proactively seek informal feedback on a regular basis.
Consider using a 360-degree feedback process, which involves collecting feedback from multiple sources. This can provide a well-rounded view of your strengths and areas for improvement.
Data-Driven Analysis
In many roles, data provides objective measures of performance. Analyzing metrics and data trends can reveal patterns and insights that might not be apparent through self-assessment or feedback alone.
Utilize tools like Google Analytics, Excel, or specialized software to track and analyze your performance data. Look for trends and patterns that indicate areas for improvement or areas where you excel.
Tools and Resources
Numerous tools and resources can assist in measuring performance. Project management software like Asana and Trello can help track progress on projects and tasks.
Performance management software like BambooHR offers comprehensive tools for goal setting, performance tracking, and feedback management. There are also open-source options available.
Moreover, taking advantage of online courses, workshops, and certifications relevant to your field can improve your skills and, consequently, your performance.
Turning Measurement into Improvement
The ultimate goal of measuring performance is to drive improvement. Don't view the measurement process as an end in itself.
Develop an action plan based on your self-assessment, feedback, and data analysis. Focus on addressing areas for improvement and leveraging your strengths. Act on the action plan that you developed.
Regularly monitor your progress and adjust your approach as needed. Continuous improvement is a key ingredient for long-term success.
By embracing a proactive approach to measuring performance, employees can gain a clearer understanding of their contributions, identify areas for growth, and ultimately achieve greater success in their careers. Remember that consistent self-reflection and open communication are key to effectively managing and improving your performance at work.









.png)