How To Remember 20 Amino Acids

For biochemistry students, medical professionals, and anyone delving into the intricacies of molecular biology, the 20 common amino acids represent fundamental building blocks. But mastering their names, structures, and properties can feel like an insurmountable challenge, leading to frustration and hindering deeper understanding of biological processes. The sheer volume of information often triggers anxiety, making effective learning strategies crucial for academic success and professional competence.
Memorizing the 20 amino acids is a rite of passage for many science students, essential for understanding protein synthesis, enzyme function, and metabolic pathways. This article provides a comprehensive guide to effective memorization techniques, drawing on mnemonic devices, categorization strategies, and practical application methods. We will explore various approaches, including those favored by experienced biochemists and educators, to help readers conquer this foundational challenge and unlock a deeper appreciation for the chemistry of life.
Understanding the Basics
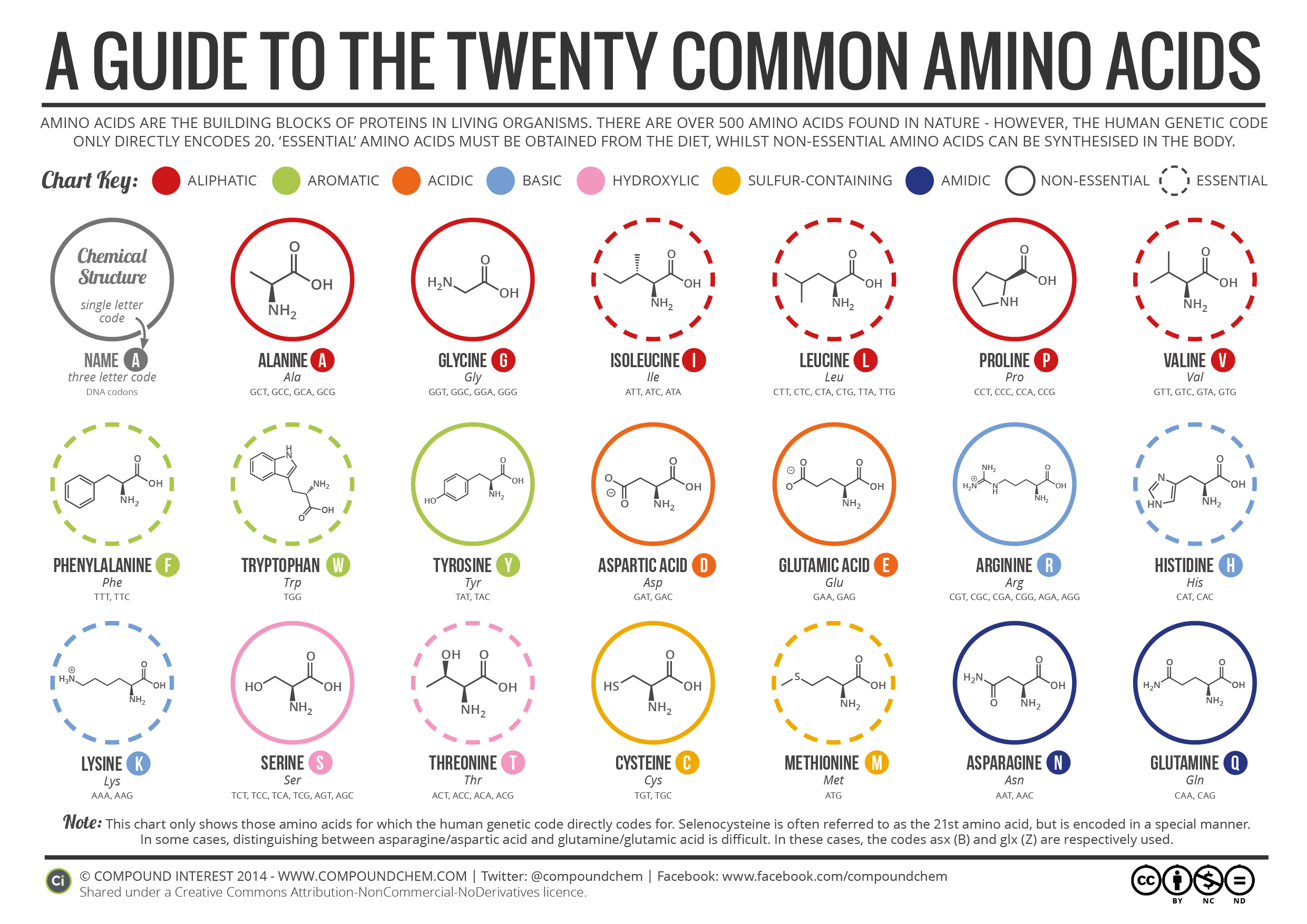
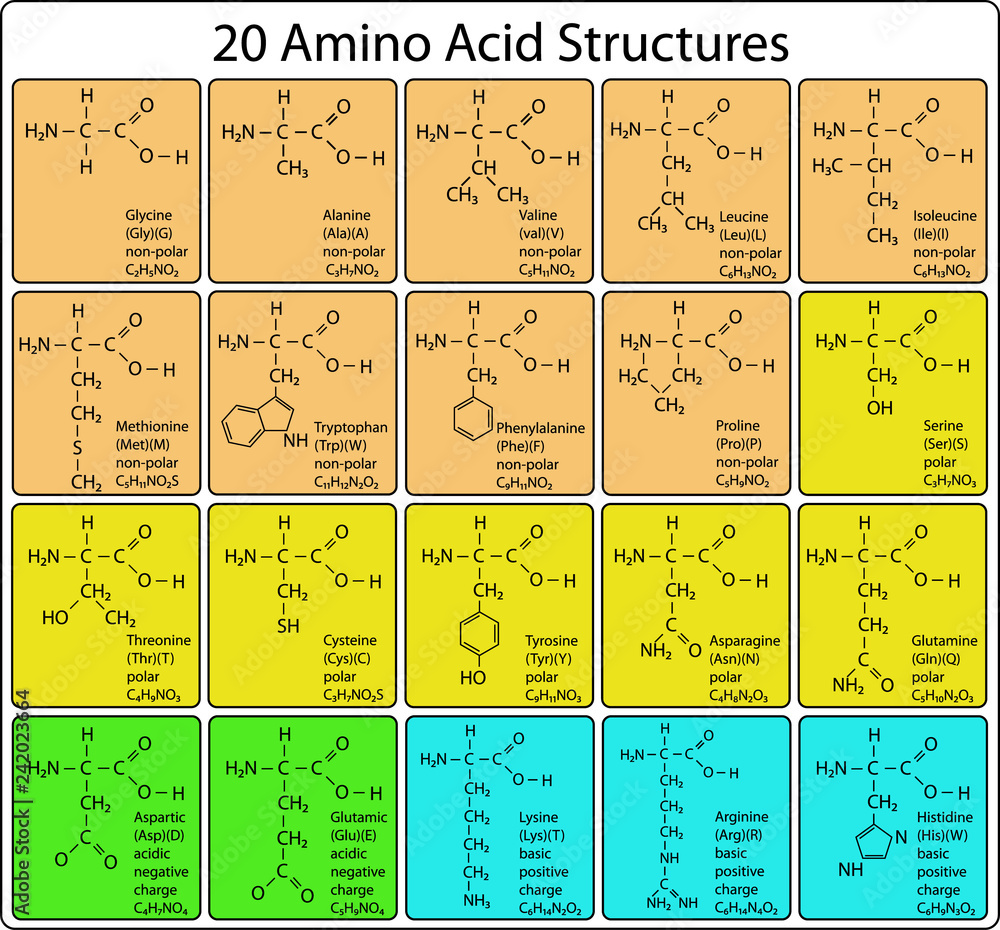
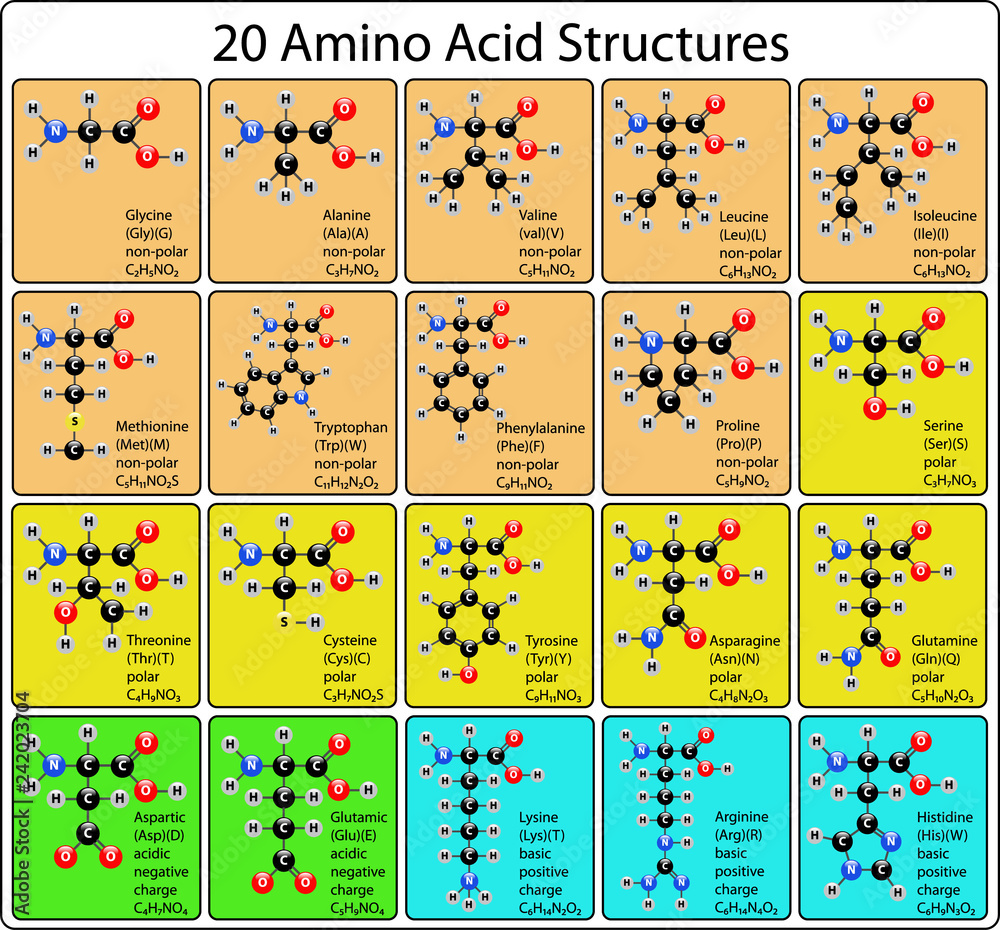
Amino acids share a common structure: a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group (-NH2), a carboxyl group (-COOH), a hydrogen atom, and a distinctive side chain (R-group). It's the R-group that differentiates each amino acid and dictates its unique properties.
These R-groups determine whether an amino acid is hydrophobic (water-repelling), hydrophilic (water-attracting), acidic, or basic. Understanding these broad categories significantly simplifies the memorization process.
Categorization by R-Group Properties
One of the most effective strategies is to group amino acids based on their R-group characteristics. This approach reduces the cognitive load by focusing on shared traits rather than individual details.
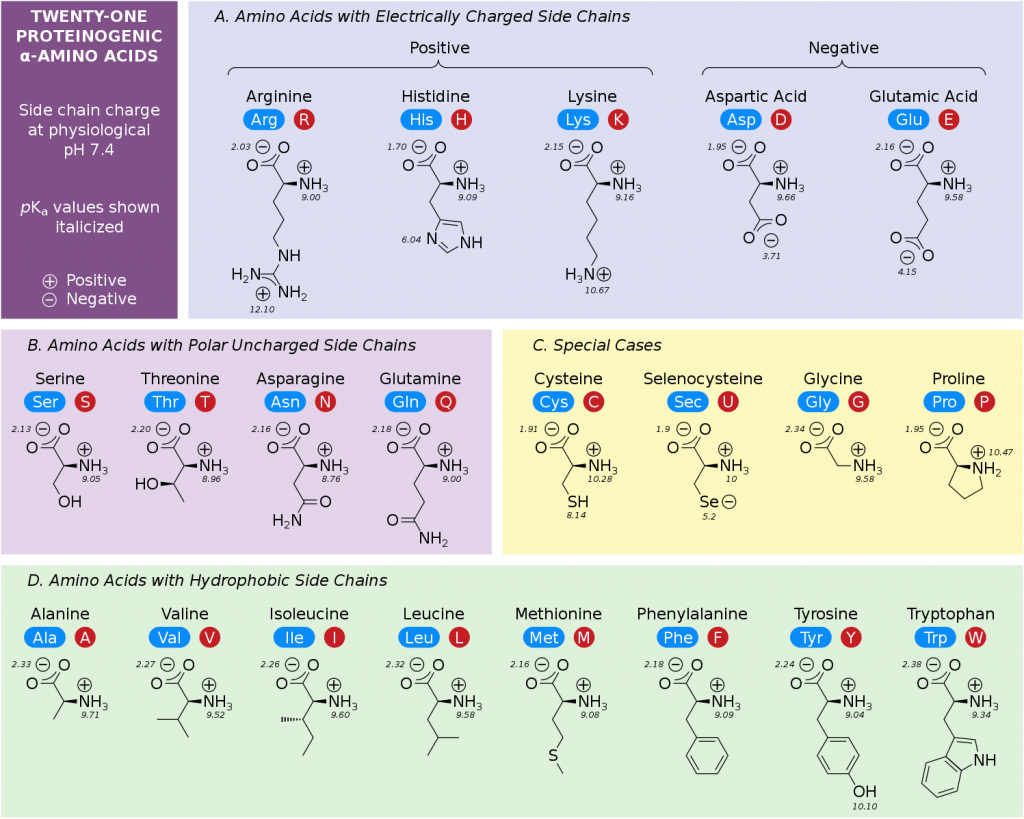
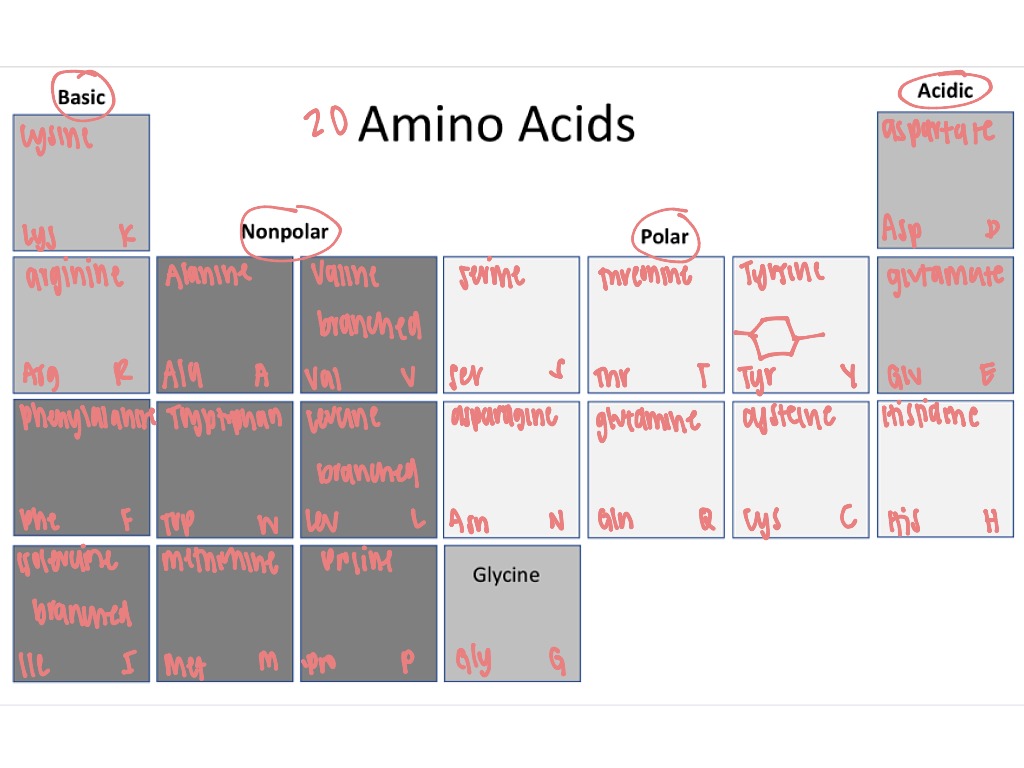
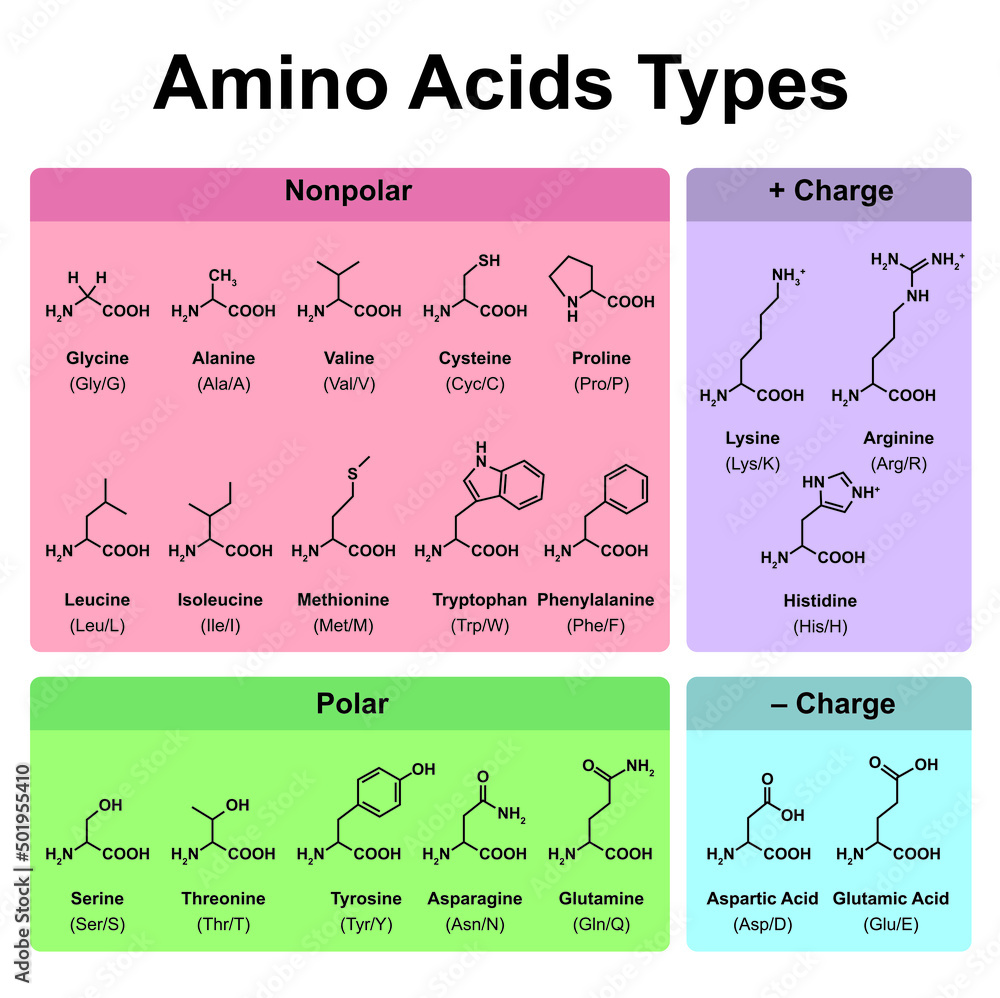
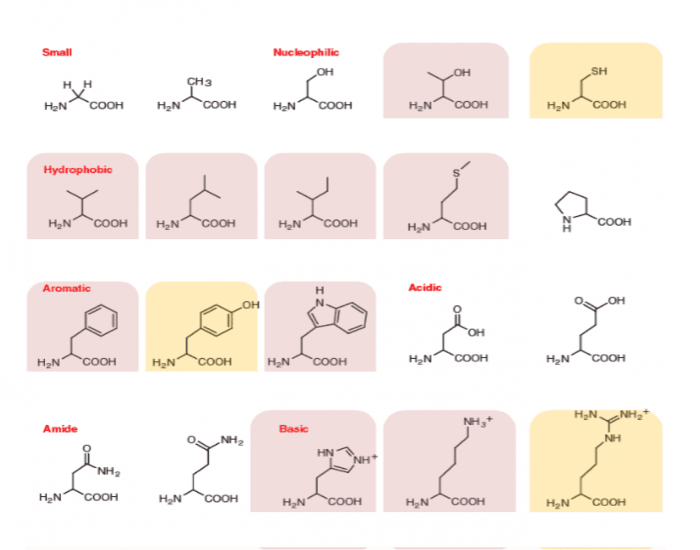
Consider the following categories: Nonpolar, Aliphatic R-Groups (Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, Proline), Aromatic R-Groups (Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, Tryptophan), Polar, Uncharged R-Groups (Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine), Positively Charged (Basic) R-Groups (Lysine, Arginine, Histidine), and Negatively Charged (Acidic) R-Groups (Aspartate, Glutamate).
Mnemonic Devices and Memory Aids
Mnemonic devices are powerful tools for associating information with memorable phrases or images. They transform abstract concepts into relatable and easily recalled narratives.
For example, "GAVLIMP are aliphatic," can help remember Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Methionine, and Proline. Another common mnemonic is "FAT W," representing Phenylalanine, Tyrosine, and Tryptophan as the aromatic amino acids. The key is to create mnemonics that resonate personally, enhancing recall.
Creating Your Own Mnemonics
The most effective mnemonics are often those you create yourself. Consider associating each amino acid with a vivid image or a short, funny sentence that incorporates its name or abbreviation.
For instance, visualize Lysine as "Lies seen," imagining someone caught in a lie. Arginine could be "Argh, you need to grow!" associating it with growth and development, a key function of proteins often involving arginine. Don't be afraid to be creative and even absurd – the more memorable, the better.
Visual Learning and Flashcards
Visual aids are invaluable for memorizing the chemical structures of amino acids. Draw each amino acid repeatedly, focusing on the key differences in their R-groups.
Use color-coding to highlight specific functional groups or structural features. Flashcards with the amino acid name on one side and its structure on the other are also highly effective for spaced repetition.
Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition involves reviewing information at increasing intervals. This technique leverages the forgetting curve, reinforcing memory and improving long-term retention.
Software like Anki can automate spaced repetition, scheduling flashcard reviews based on your recall performance. Consistent, spaced practice is far more effective than cramming.
Practical Application and Contextual Learning
Memorization becomes easier when you understand the context in which amino acids function. Learn about their roles in protein folding, enzyme catalysis, and signaling pathways.
Explore how specific amino acid mutations can lead to diseases. This contextual understanding transforms rote memorization into meaningful knowledge.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Studying case studies involving protein misfolding diseases like Alzheimer's or cystic fibrosis can provide a tangible connection to the importance of amino acids. Analyzing how a single amino acid substitution can disrupt protein function highlights the significance of mastering this foundational knowledge.
For example, understanding the role of Phenylalanine in the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase and its implications in phenylketonuria (PKU) makes the memorization more relevant.
The Role of Practice and Patience
Mastering the 20 amino acids requires consistent effort and a patient approach. Don't get discouraged by initial difficulties.
Break down the learning process into manageable chunks and celebrate small victories. Regular review and application of the knowledge are crucial for long-term retention.
Building a Strong Foundation
View memorizing the amino acids not as a burdensome task, but as a crucial step towards a deeper understanding of biochemistry and molecular biology. This foundational knowledge will serve you well throughout your academic and professional journey. Seek out opportunities to apply your knowledge, such as discussing protein structures or enzyme mechanisms with peers.
The journey to mastering these building blocks of life might seem daunting initially, but with strategic approaches, personalized mnemonics, and consistent practice, it becomes an achievable and rewarding endeavor. By focusing on understanding the underlying principles and applying the knowledge in context, you can unlock a deeper appreciation for the elegance and complexity of the molecular world. Remember to utilize the techniques best suited for your learning style.