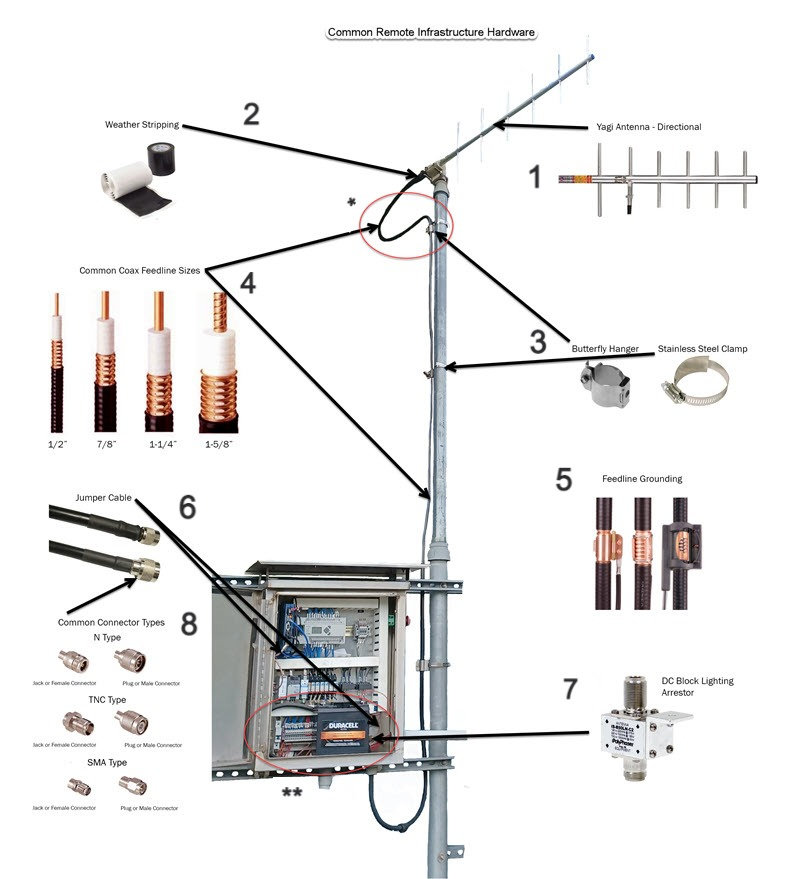
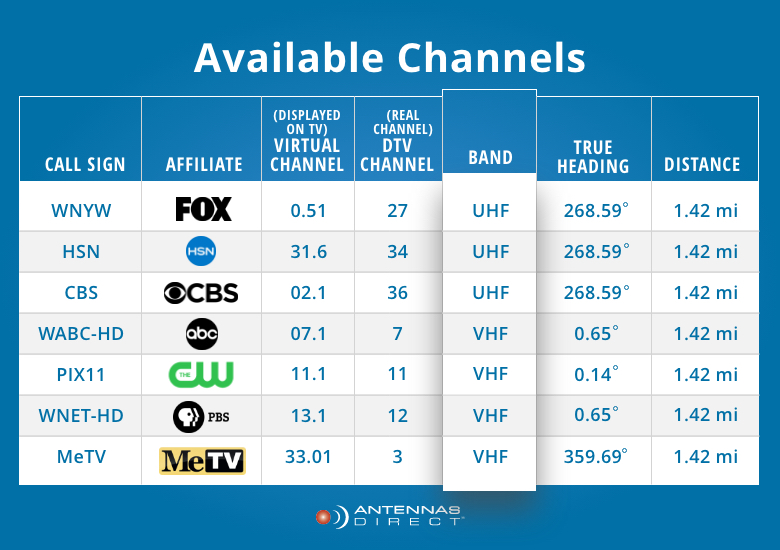
How To Watch Rf Channels On Tv
Imagine a cozy evening, the scent of freshly brewed coffee filling the air, and the warm glow of the television screen illuminating the room. The news anchor is reporting the local headlines, the details of the sports scores are displayed, and the weather forecast predicting a sunny weekend. But have you ever stopped to think about the invisible pathways that bring those images and sounds into your home, specifically through the often-overlooked world of Radio Frequency (RF) channels?
This article serves as a guide for understanding and accessing RF channels on your television. We'll navigate the basics of what they are, how they function, and the steps you can take to tune into them, offering a blend of technical insight and practical advice.
Understanding RF Channels
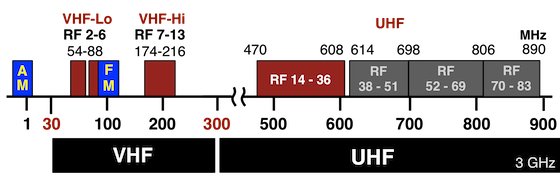
RF channels are the specific frequencies used to transmit television signals. These signals, carrying both audio and video data, travel through the air or cable infrastructure to reach your TV.
Think of them like radio stations, but instead of just sound, they also carry pictures. Older analog TVs relied almost exclusively on RF signals, while modern digital TVs also use them for over-the-air broadcasts.
The History of RF and Television
The story of RF channels and television is a fascinating journey that began in the early 20th century. Pioneers like Philo Farnsworth and Vladimir Zworykin experimented with transmitting images using radio waves, laying the groundwork for the technology we use today.
As television technology advanced, standardized RF channels were established to ensure compatibility between broadcasting stations and receiving sets. These channels, initially analog, were assigned specific frequencies to avoid interference and ensure a clear picture.
The transition from analog to digital television (DTV) marked a significant shift in the way RF channels were used. Digital signals allowed for more efficient use of the spectrum, enabling broadcasters to transmit multiple channels (subchannels) on a single RF channel.
How to Access RF Channels on Your TV
Accessing RF channels on your TV is typically a straightforward process, but it can vary slightly depending on your TV model and whether you're using an antenna or cable connection.
Using an Antenna
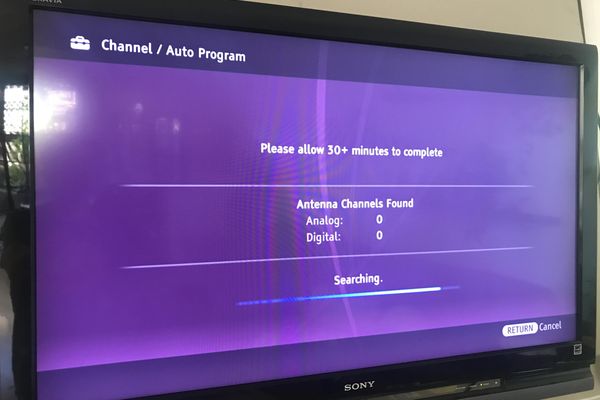
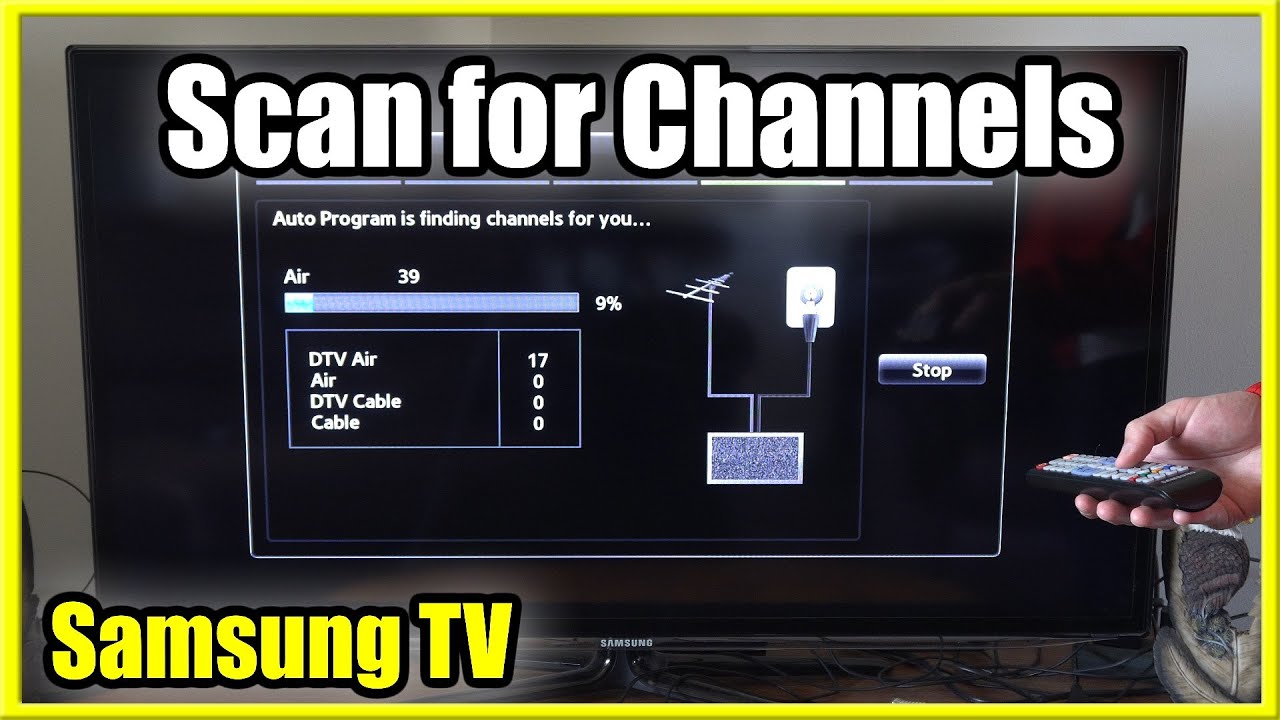
If you're using an antenna to receive over-the-air broadcasts, you'll need to perform a channel scan on your TV. This process allows the TV to search for available RF channels and store them in its memory.
To initiate a channel scan, navigate to the settings menu on your TV, usually found under "Channel," "Tuning," or "Setup." Select the "Auto Program," "Auto Tune," or "Channel Scan" option. The TV will then automatically search for available RF channels and add them to your channel list.
During the scanning process, it's essential to ensure your antenna is properly positioned and connected to the TV. Experimenting with different antenna locations and orientations can improve signal strength and the number of channels you receive.
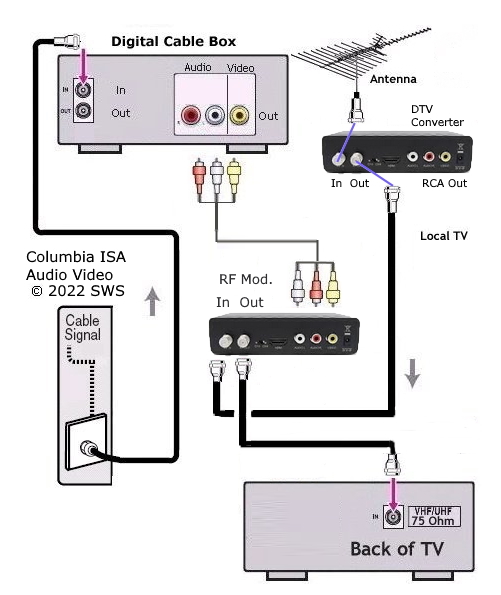
Using Cable
If you have cable service, your TV will typically receive channels through a cable box. In this case, you don't need to perform a channel scan on the TV itself, as the cable box handles the channel tuning. Connect your cable box to the television.
However, if you have basic cable without a box, you may be able to access some local channels directly through your TV's tuner. In this scenario, you'll need to perform a channel scan as described above for antenna users.
Consult your cable provider for specific instructions on how to access channels and program your cable box if necessary. This will give you a better idea of how to access and arrange the channels on your television.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Sometimes, you might encounter problems accessing RF channels on your TV. These issues can range from weak signals to interference to incorrect settings.
If you're experiencing a weak signal, try repositioning your antenna or using an amplified antenna to boost the signal strength. Check that all cable connections are secure.
Interference can also disrupt RF signals. Common sources of interference include other electronic devices, such as microwave ovens and cordless phones. Try moving these devices away from your TV and antenna.
Double-check your TV's settings to ensure that the correct input source is selected and that the channel scan was completed successfully. A factory reset can sometimes resolve persistent issues, but remember that you will lose all personalized settings.
The Future of RF Channels
The future of RF channels is closely intertwined with the evolution of broadcasting technology. As technology advances, the role of RF and the channels it uses evolves.
NextGen TV, also known as ATSC 3.0, represents the next generation of over-the-air broadcasting. It offers improved picture and sound quality, as well as interactive features and targeted advertising.
ATSC 3.0 utilizes advanced modulation techniques to transmit more data over the same RF channel bandwidth. It requires new TV tuners to decode the signals, but it promises a significantly enhanced viewing experience.
The Enduring Value of RF
Despite the rise of streaming services and on-demand content, RF channels continue to hold value for many viewers. They provide access to local news, weather, and sports programming without requiring a subscription.
RF channels also serve as a vital source of information during emergencies. Over-the-air broadcasts can remain accessible even when internet and cable services are disrupted.
Understanding how to access and troubleshoot RF channels can empower you to get the most out of your television, ensuring that you can stay informed and entertained even in the face of technological changes.
As the world of television continues to evolve, with streaming services battling for dominance and new technologies constantly emerging, the humble RF channel remains a testament to the ingenuity of early broadcast pioneers. It also represents a resilient and reliable pathway to the information and entertainment that connects us all.






![How To Watch Rf Channels On Tv [HOW] to select best transmit channels for Access Points in the network](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/TKlYPJ29jUY/maxresdefault.jpg)