Identify And Discuss The Needs Of A Society

In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, shifting demographics, and escalating global challenges, understanding the fundamental needs of society is more crucial than ever. From the provision of basic necessities to the pursuit of higher ideals like justice and equality, a society's ability to meet these needs dictates its overall health, stability, and progress.
This article delves into the core needs of a thriving society, examining them through a multi-faceted lens. We will explore both the tangible and intangible requirements, drawing on data and expert insights to provide a comprehensive overview. Further, we will also investigate how these needs are evolving in the 21st century and what strategies are most effective in addressing them.
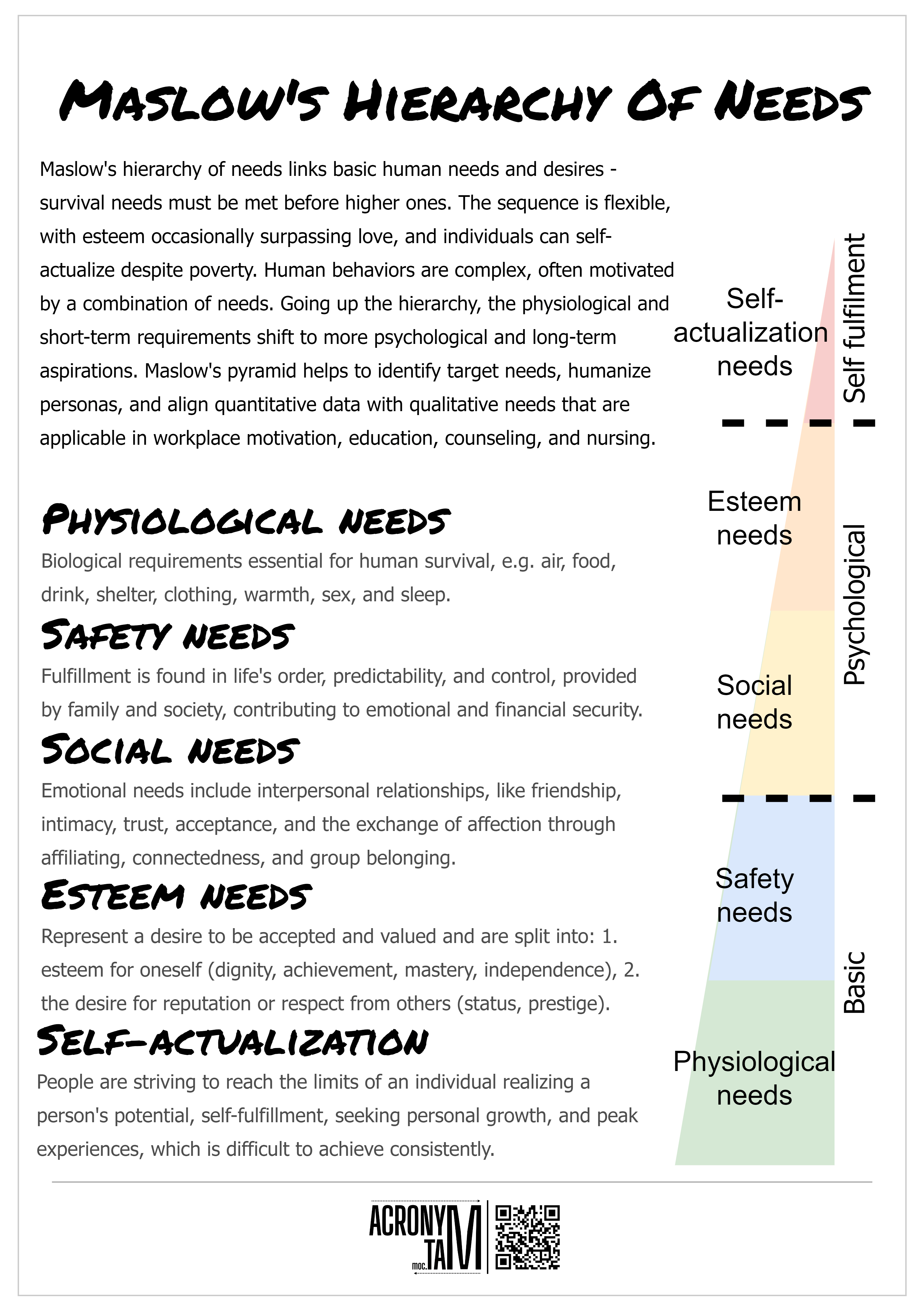
Basic Physiological and Safety Needs
At the foundation of any society lies the imperative to fulfill the basic physiological needs of its members. These encompass access to adequate food, clean water, shelter, and healthcare.
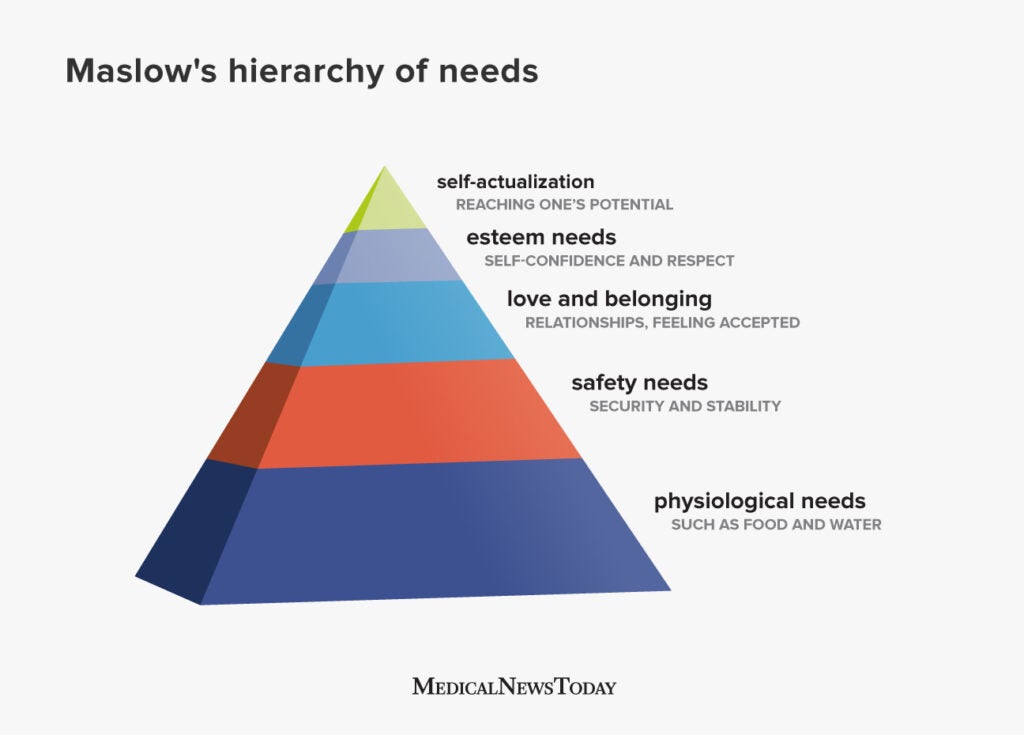
Failure to meet these fundamental requirements leads to widespread suffering, instability, and ultimately, societal collapse, according to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. The World Health Organization (WHO) consistently emphasizes the link between access to clean water and sanitation and overall public health.
Beyond survival, safety and security are paramount. This includes protection from violence, crime, and environmental hazards.
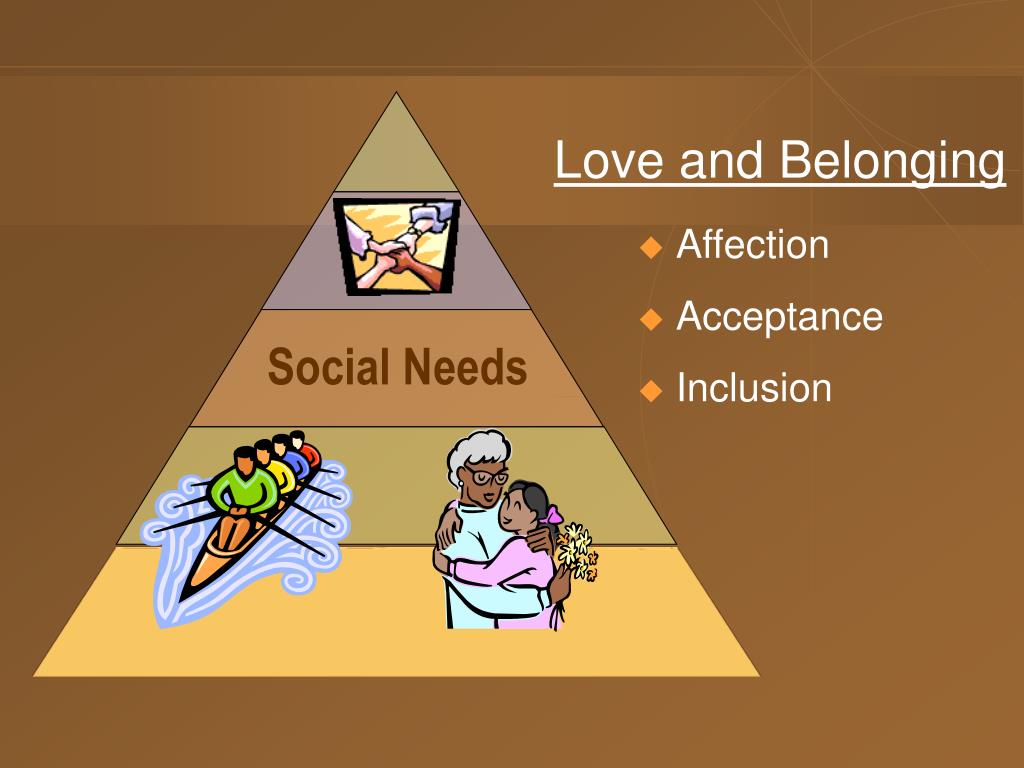
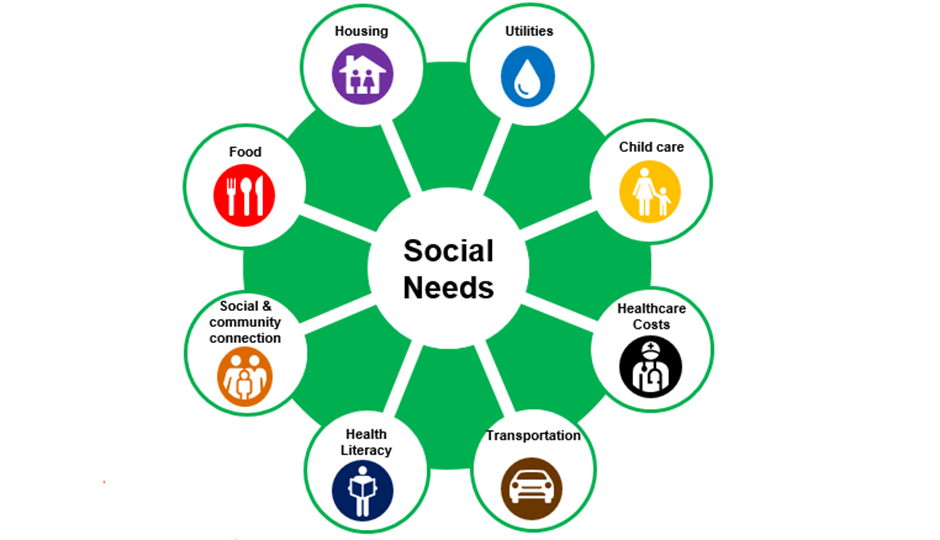
Social Needs: Belonging and Connection
Humans are inherently social beings, and the need for belonging and connection is deeply ingrained in our psychology. This manifests as the desire for meaningful relationships, community involvement, and a sense of belonging.
Strong social connections are essential for mental well-being and can act as a buffer against stress and adversity. Social isolation and loneliness, on the other hand, have been linked to a range of negative health outcomes, highlighting the importance of fostering strong social networks.
Societies that prioritize social cohesion tend to be more resilient and better equipped to navigate challenges. A study from Harvard University, revealed that close relationships are more important than money or fame for happiness.
Esteem Needs: Recognition and Respect
Once basic physiological, safety, and social needs are met, individuals seek esteem and recognition from themselves and others. This includes the need for self-respect, confidence, achievement, and recognition from peers.
A society that values hard work, meritocracy, and individual contributions fosters a sense of accomplishment and purpose among its members. Opportunities for personal and professional growth are crucial for fulfilling esteem needs.
Furthermore, a culture of respect and tolerance is essential for ensuring that all individuals feel valued and appreciated regardless of their background or circumstances.
Cognitive and Aesthetic Needs: Learning and Beauty
The pursuit of knowledge and beauty are integral to human flourishing. Cognitive needs encompass the desire to learn, explore, and understand the world around us.
Access to education and opportunities for intellectual stimulation are crucial for fostering innovation and critical thinking. Aesthetic needs, on the other hand, involve the appreciation of beauty, order, and harmony.
A society that invests in the arts, culture, and natural environment enriches the lives of its citizens and promotes a sense of well-being.
Self-Actualization Needs: Reaching Full Potential
At the pinnacle of human needs lies self-actualization – the desire to reach one's full potential and to live a life of purpose and meaning. This involves pursuing one's passions, contributing to society, and living in accordance with one's values.
Societies that provide opportunities for self-expression, creativity, and personal growth empower individuals to achieve self-actualization. Furthermore, a culture of innovation and experimentation can foster a sense of possibility and inspire individuals to push the boundaries of human potential. UN's Sustainable Development Goals aimed at fostering innovation and creativity worldwide.
A society that supports this is a society that thrives.
Challenges and Future Directions
In the 21st century, societies face a complex array of challenges in meeting the needs of their populations. Climate change, economic inequality, and political polarization are just a few of the issues that threaten social cohesion and well-being.
Addressing these challenges requires innovative solutions, collaborative partnerships, and a commitment to social justice. Investing in education, healthcare, and infrastructure is essential for building a more equitable and sustainable future.
Moreover, fostering a culture of empathy, compassion, and civic engagement is crucial for strengthening social bonds and promoting collective action. The World Bank acknowledges these issues and suggests that international cooperation is fundamental.
Ultimately, the ability of a society to meet the needs of its members is a reflection of its values, priorities, and collective will. By prioritizing human well-being, promoting social justice, and investing in a sustainable future, societies can create a world where everyone has the opportunity to thrive. Continuously reassessing and adapting to the changing needs of society is imperative for long-term prosperity and resilience.