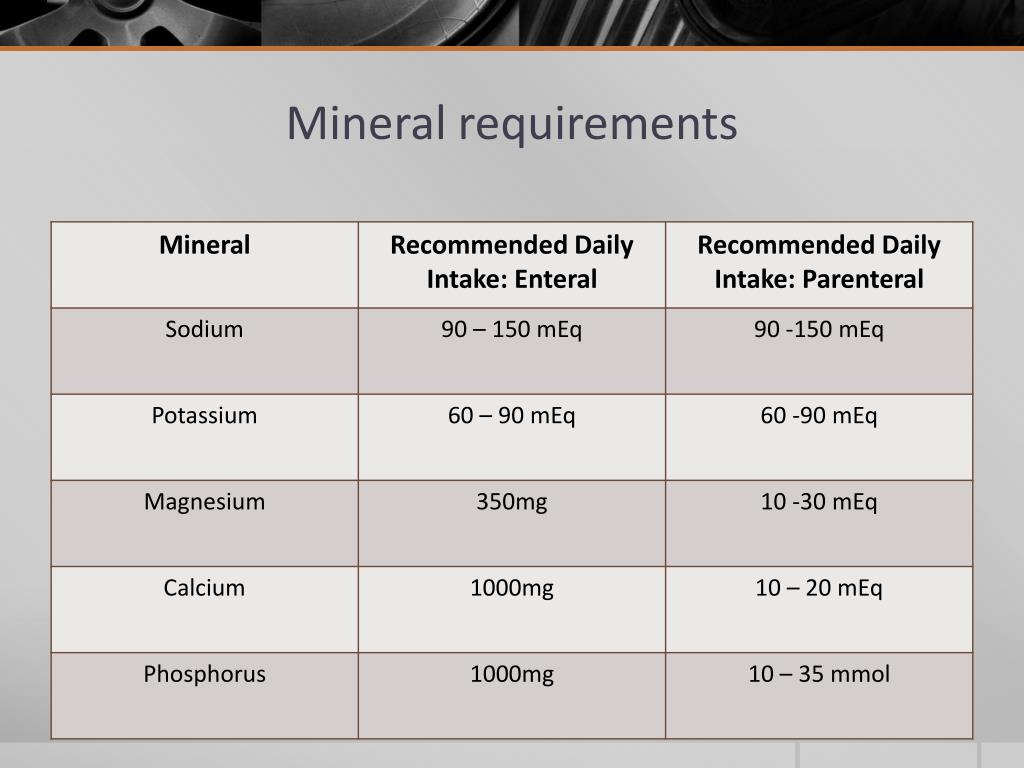
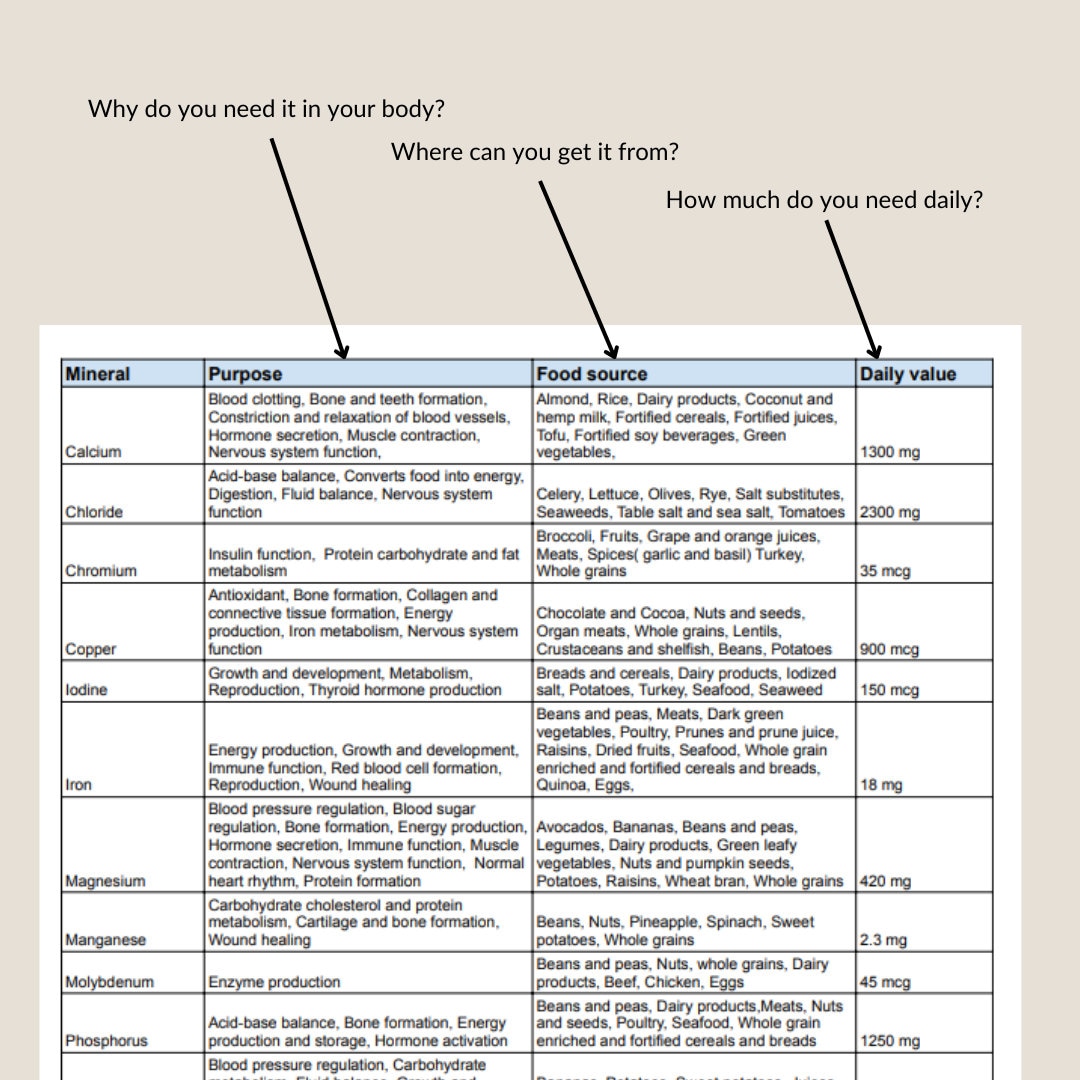
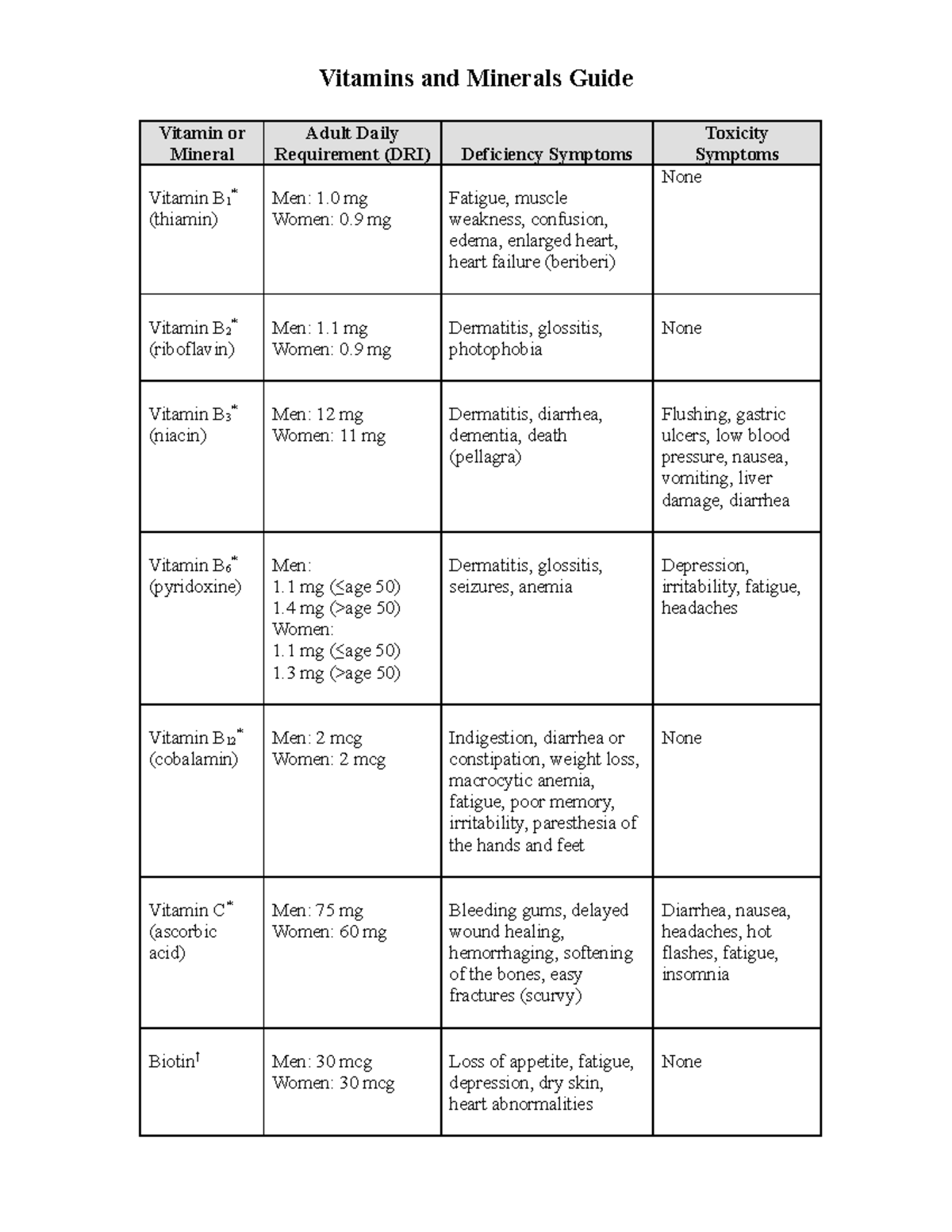
In General Daily Mineral Requirements Are Correlated With What

For decades, nutritionists and health professionals have relied on Recommended Daily Allowances (RDAs) and other dietary reference intakes to guide individuals on their mineral needs. But what exactly are these recommendations based on, and are they universally applicable? Emerging research and established scientific principles point to a complex interplay of factors influencing these requirements, going far beyond simple age or gender categories.
This article explores the primary correlations influencing general daily mineral requirements, examining the scientific basis behind these recommendations and their potential implications for public health. Understanding these connections is crucial for tailoring dietary advice and addressing potential nutrient deficiencies or excesses in diverse populations.
Key Factors Influencing Mineral Needs
Several factors significantly impact an individual's daily mineral requirements. These include body size and composition, physiological state, activity level, and existing health conditions. Understanding these correlations is fundamental to personalizing nutritional recommendations.
Body Size and Composition
Larger individuals, logically, generally require larger quantities of minerals than smaller individuals. This is due to the greater overall mass of tissue requiring mineral support. Bone mineral density is also a key consideration, with individuals with higher bone density often requiring more calcium and phosphorus.
Body composition, specifically the ratio of lean muscle mass to fat mass, also plays a role. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active than fat tissue, leading to increased mineral needs for individuals with higher muscle mass.
Physiological State
Certain physiological states dramatically alter mineral requirements. Pregnancy, for example, significantly increases the need for iron, folate, and calcium to support fetal development. Lactation also elevates calcium demands to ensure adequate levels in breast milk.
Infants and children have uniquely high mineral needs relative to their size due to rapid growth and development. Conversely, older adults may have altered mineral absorption and utilization, requiring adjustments to their intake despite potentially lower overall energy needs.
Activity Level
Physical activity increases mineral requirements due to losses through sweat and increased metabolic demands. Athletes, in particular, need higher intakes of electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium to maintain fluid balance and support muscle function.
Endurance athletes may also have higher iron needs to compensate for iron losses through sweat and gastrointestinal bleeding. The intensity and duration of activity significantly influence the extent of these increased requirements.
Health Conditions and Medications
Certain health conditions can significantly impact mineral absorption, utilization, and excretion. Individuals with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), for example, may have impaired absorption of various minerals, including iron, zinc, and calcium.
Kidney disease can also disrupt mineral balance, leading to deficiencies or excesses of minerals like potassium, phosphorus, and calcium. Some medications can interfere with mineral absorption or increase their excretion, necessitating adjustments to dietary intake.
The Significance of Individualized Recommendations
The correlation between these factors and mineral requirements underscores the importance of individualized dietary recommendations. Blanket recommendations, while useful as general guidelines, may not adequately address the specific needs of all individuals.
Registered dietitians and other qualified healthcare professionals can assess individual needs and provide personalized recommendations based on a comprehensive evaluation of factors like body composition, activity level, medical history, and medication use. This approach optimizes mineral intake to support overall health and well-being.
Furthermore, understanding these correlations empowers individuals to make more informed dietary choices. By recognizing the factors that influence their own mineral needs, people can proactively adjust their diets to address potential deficiencies or excesses.
Potential Impact on Public Health
A greater awareness of the factors influencing mineral requirements can have a significant impact on public health. By identifying populations at risk of mineral deficiencies or excesses, targeted interventions can be developed to address these issues.
For example, pregnant women can be encouraged to take iron and folate supplements to prevent neural tube defects and anemia. Older adults can be educated on the importance of calcium and vitamin D for bone health. Public health campaigns can also promote healthy eating habits that support adequate mineral intake across all age groups.
The ongoing research into the complex interactions between minerals and other nutrients is continuously refining our understanding of optimal mineral intake. Staying informed about these advancements and seeking personalized dietary advice is essential for maintaining optimal health throughout life. This information is for educational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or supplement regimen.