Integrative Physiology Of Exercise Conference 2024
.jpg?sfvrsn=3524deed_0)
Imagine a bustling conference hall, sunlight streaming through large windows illuminating animated discussions. Scientists huddle around posters, sharing data and insights with palpable enthusiasm. Coffee cups litter tables as the air crackles with intellectual energy. This vibrant scene was the heart of the Integrative Physiology of Exercise Conference 2024, a gathering that showcased the cutting edge of exercise science.
The Integrative Physiology of Exercise Conference 2024 served as a crucial platform for researchers to present and discuss the latest findings on how exercise impacts the human body. It highlighted the profound benefits of physical activity, extending beyond simply building muscle or losing weight. The conference focused on exercise's role in disease prevention, cognitive enhancement, and overall well-being.
A Deep Dive into Integrative Physiology
Integrative physiology is a field dedicated to understanding how different systems in the body interact and coordinate to maintain homeostasis. It examines how these interactions are affected by external stimuli such as exercise. This comprehensive approach offers a more holistic understanding of the human body.
Unlike reductionist approaches that focus on isolated components, integrative physiology considers the whole organism. This perspective is essential for appreciating the full impact of exercise on health. By integrating knowledge from various disciplines like molecular biology, biomechanics, and neuroscience, it creates a richer picture.
Historical Context and Evolution
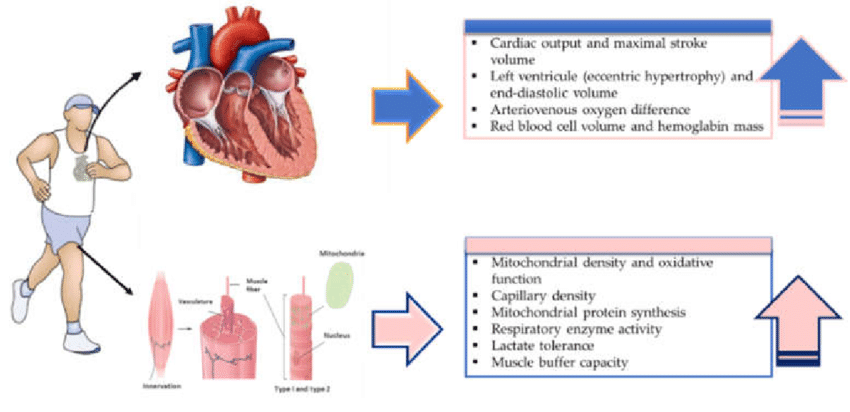
The study of exercise physiology has evolved significantly over the past century. Early research focused primarily on the mechanics of movement and the cardiorespiratory response to physical activity. However, more recently, the focus has shifted to understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms that underlie the benefits of exercise.
Advances in technology, such as sophisticated imaging techniques and omics technologies, have fueled this evolution. These tools have enabled scientists to explore the complex interplay between exercise and various biological processes. This allows for a much more nuanced understanding of exercise's effects.
The conference provided a historical perspective, acknowledging the contributions of pioneering researchers. It also emphasized the importance of building upon this foundation to address current challenges in public health.
Key Themes and Presentations
The conference covered a diverse range of topics, reflecting the breadth of integrative physiology. Several key themes emerged, highlighting the most pressing areas of research in the field. These included the impact of exercise on aging, metabolic disease, and brain health.
Exercise and Aging
One prominent theme was the role of exercise in promoting healthy aging. Research presented at the conference underscored the protective effects of physical activity against age-related decline. Exercise interventions were shown to improve muscle mass, bone density, and cognitive function in older adults.
Specifically, studies highlighted the importance of resistance training for maintaining strength and mobility in later life. Presentations also explored the potential of exercise to mitigate the effects of sarcopenia, the age-related loss of muscle mass.
"Exercise is not just about adding years to your life, but adding life to your years," quoted a speaker from the National Institute on Aging, emphasizing the importance of maintaining physical activity throughout the lifespan.
Exercise and Metabolic Disease
Another major focus was the role of exercise in preventing and managing metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Numerous presentations showcased the beneficial effects of exercise on insulin sensitivity, blood glucose control, and lipid profiles.
Researchers presented evidence that exercise can improve the function of the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels. This improvement reduces the risk of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular complications. Furthermore, studies demonstrated that exercise can help to reduce visceral fat, a key risk factor for metabolic disease.
The conference also addressed the challenges of promoting physical activity in individuals with metabolic diseases. Strategies for overcoming barriers to exercise, such as pain, fatigue, and lack of motivation, were discussed.
Exercise and Brain Health
The impact of exercise on brain health was a rapidly growing area of interest at the conference. Studies presented compelling evidence that physical activity can enhance cognitive function, protect against neurodegenerative diseases, and improve mental well-being.
Researchers discussed the role of exercise in increasing blood flow to the brain and promoting neuroplasticity. Exercise was also shown to stimulate the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that supports the growth and survival of neurons.
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading neuroscientist, presented her findings on the benefits of exercise for preventing Alzheimer's disease. Her work suggests that regular physical activity can reduce the accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain, a hallmark of the disease.
Innovative Research Methodologies
The conference also highlighted innovative research methodologies being used in the field of integrative physiology. These included the use of wearable sensors, big data analytics, and advanced imaging techniques. These tools allow for more precise and comprehensive assessments of the body's response to exercise.
Wearable sensors, such as activity trackers and heart rate monitors, are increasingly being used to collect real-time data on physical activity levels. This data can be used to personalize exercise interventions and track progress over time. Big data analytics are also being applied to identify patterns and trends in large datasets of exercise-related data.
The use of advanced imaging techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), is providing new insights into the effects of exercise on the brain and other organs. These technologies allow researchers to visualize changes in structure and function in response to physical activity.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the significant advances in the field of integrative physiology, several challenges remain. One challenge is translating research findings into practical recommendations for the general public. Another challenge is addressing the disparities in access to physical activity opportunities.
Future research directions include exploring the role of the gut microbiome in mediating the benefits of exercise. The gut microbiome is a complex community of microorganisms that reside in the digestive tract. Emerging evidence suggests that exercise can alter the composition and function of the gut microbiome, which in turn can influence metabolism, immunity, and brain health.
The conference concluded with a call to action for researchers, policymakers, and healthcare professionals to work together to promote physical activity as a cornerstone of health and well-being. Collaboration and interdisciplinary approaches are essential for addressing the complex challenges in this field.
Reflections and Conclusion
The Integrative Physiology of Exercise Conference 2024 was a testament to the growing recognition of the profound impact of physical activity on human health. The presentations and discussions highlighted the importance of exercise for preventing and managing a wide range of diseases, promoting cognitive function, and enhancing overall well-being.
The conference served as a reminder that exercise is not just about physical fitness; it is about optimizing the function of all systems in the body. By integrating knowledge from various disciplines, researchers are gaining a deeper understanding of the complex mechanisms that underlie the benefits of exercise. This knowledge can be used to develop more effective and personalized exercise interventions.
Leaving the conference, attendees felt inspired and empowered to continue pushing the boundaries of exercise science. The collaborative spirit and intellectual curiosity that permeated the event promised continued progress in unlocking the full potential of exercise for human health.