Is 21 A Prime Number Or Composite
The digital world recently experienced a peculiar, yet telling, moment of collective introspection. A deceptively simple question gripped social media platforms and online forums: Is 21 a prime number? The seemingly straightforward query sparked a surprisingly widespread debate, highlighting a potential gap in basic mathematical understanding amongst the general population.
At the heart of this digital discourse lies the distinction between prime and composite numbers. This fundamental mathematical concept is crucial for understanding various algorithms, cryptographic systems, and even seemingly mundane tasks like data organization. This article delves into the specifics of why 21 is classified as a composite number, exploring the implications of this common misconception and what it reveals about mathematical literacy.
Prime vs. Composite: A Mathematical Divide
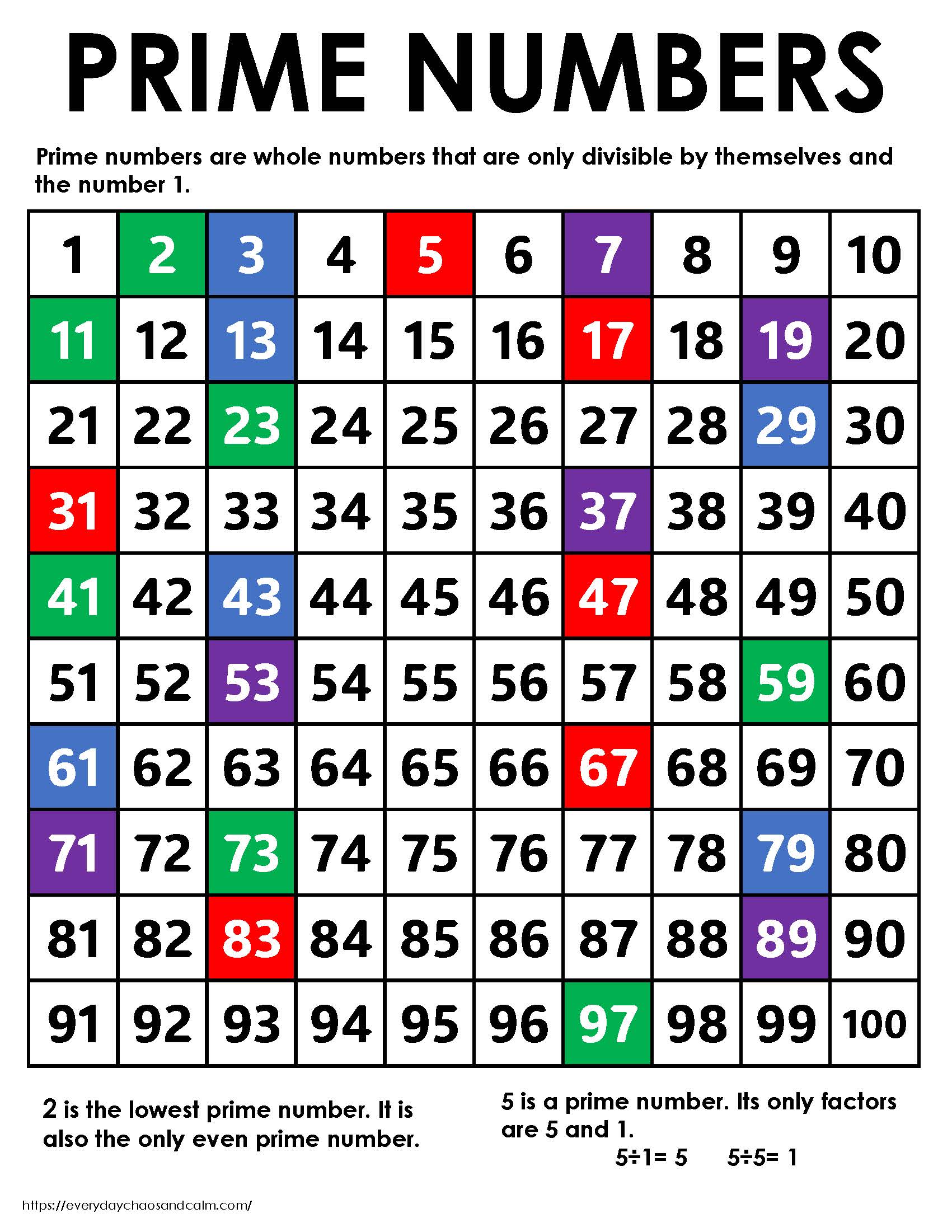
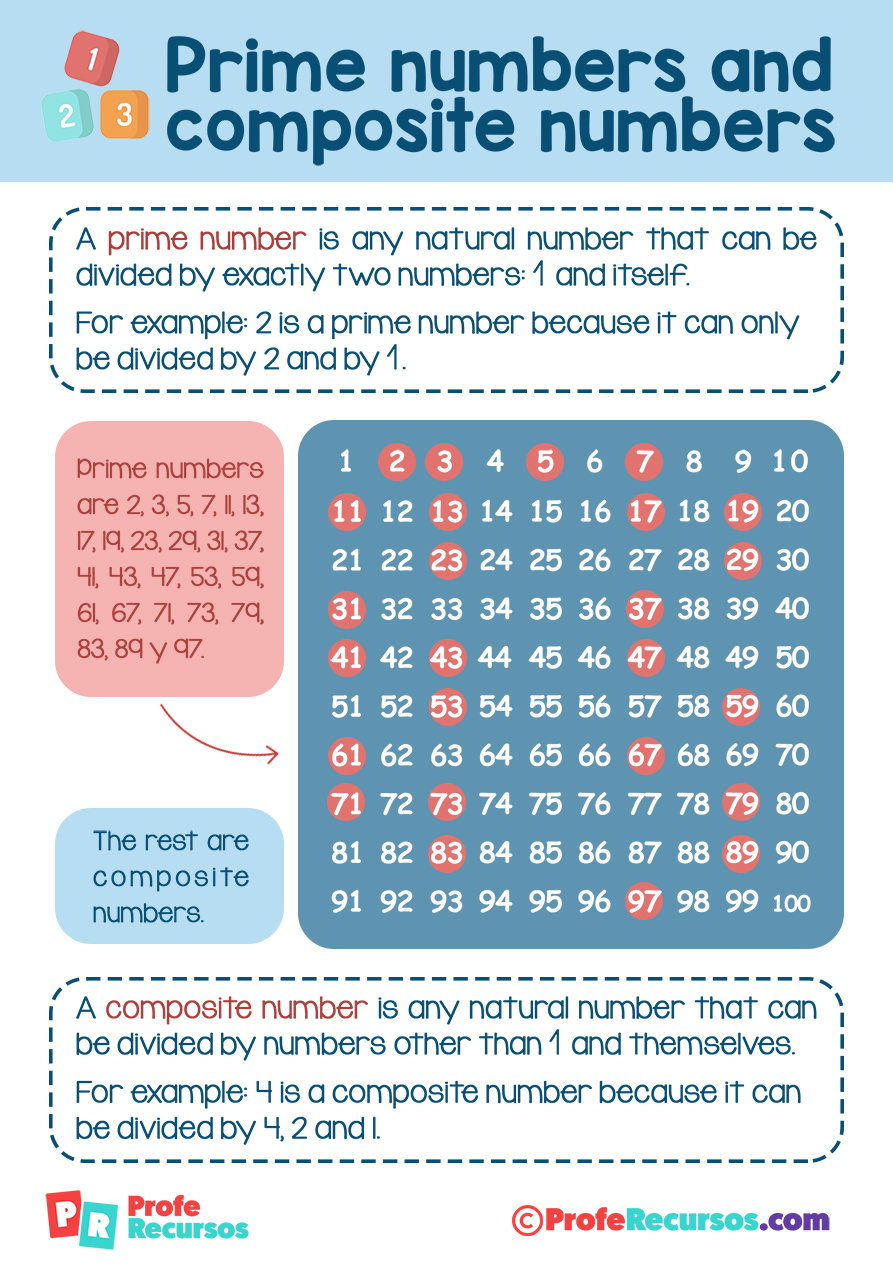
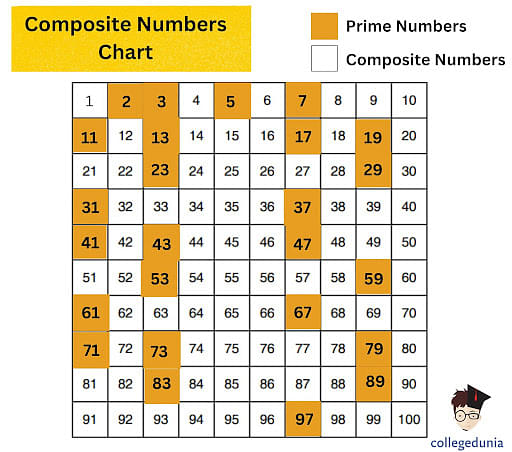
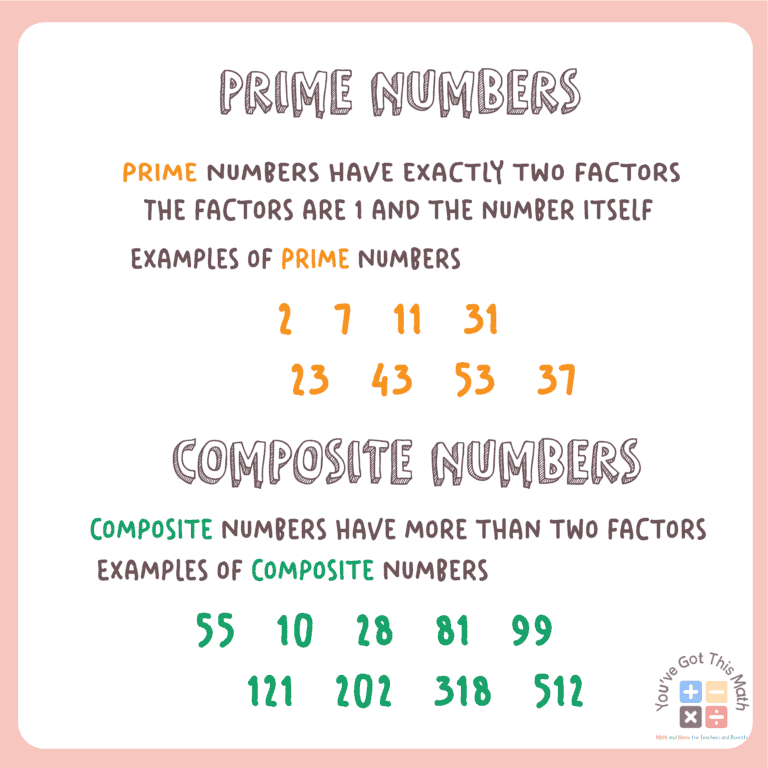
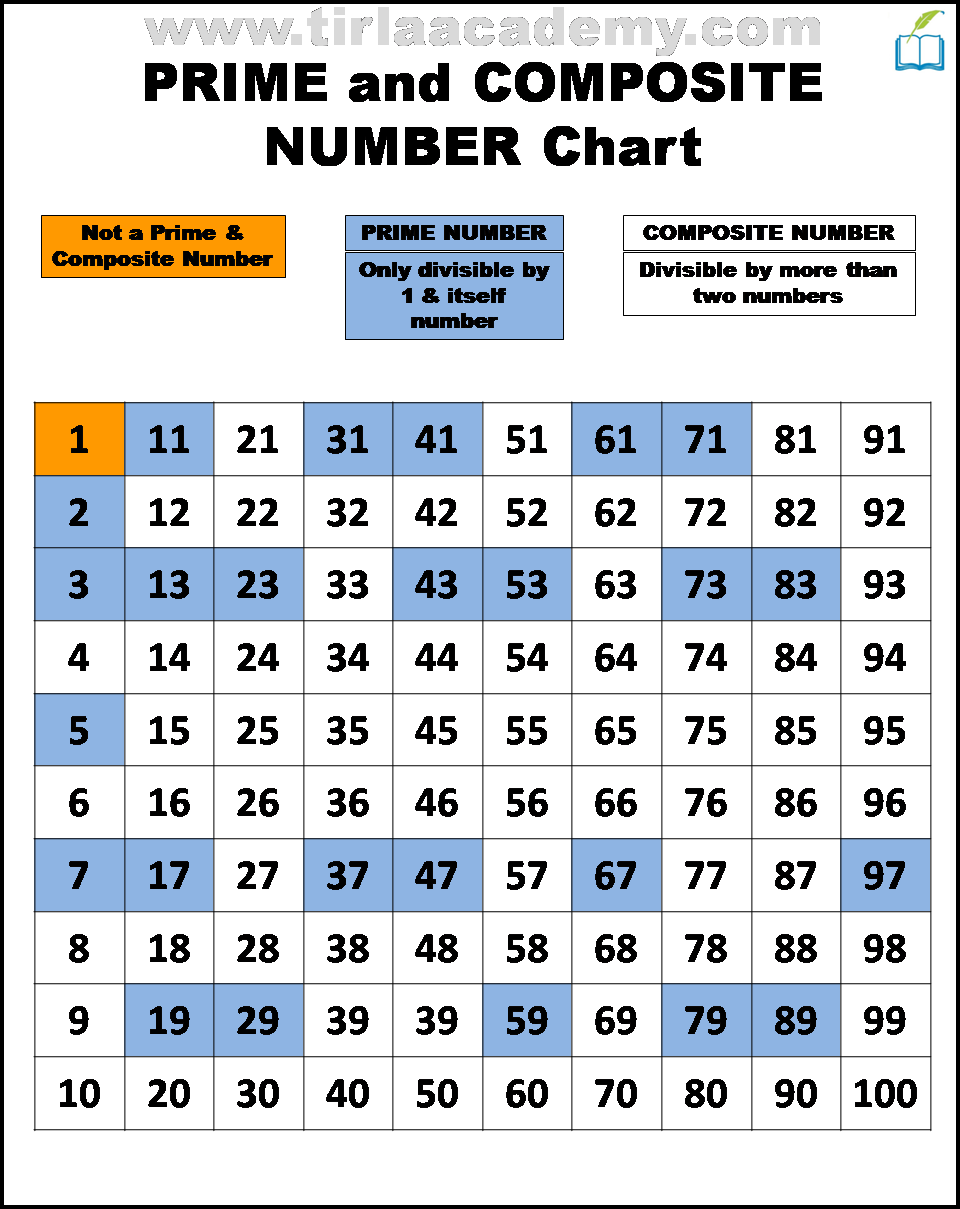
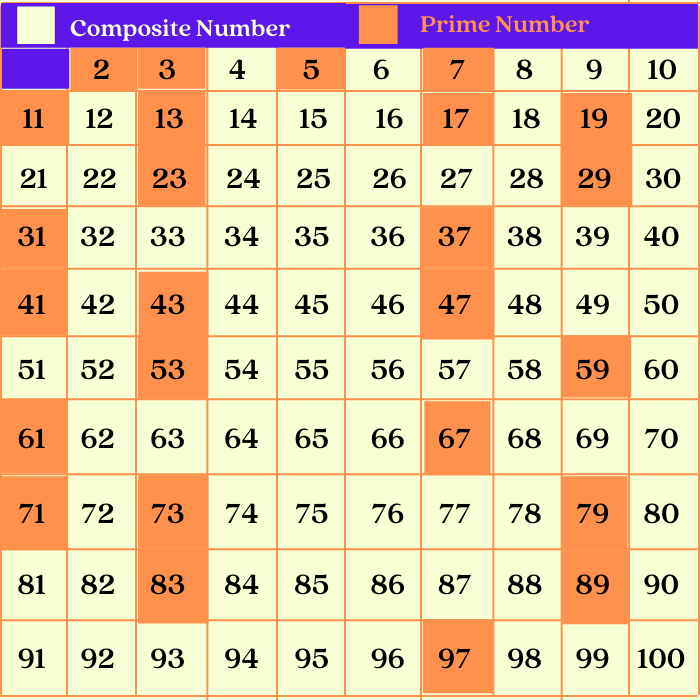
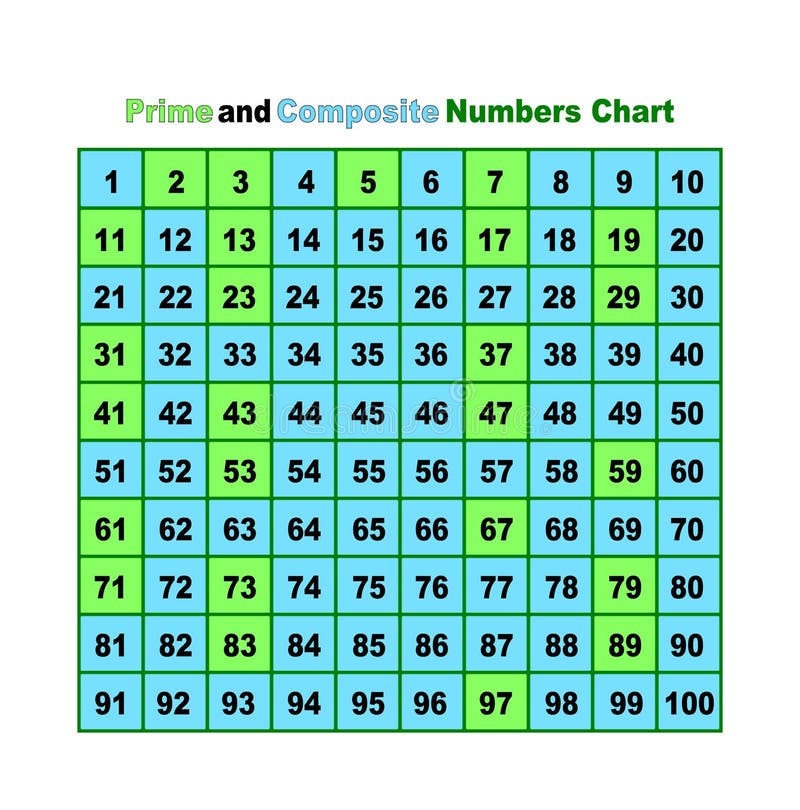
A prime number, by definition, is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. Numbers like 2, 3, 5, 7, and 11 fit this definition perfectly.
Conversely, a composite number is a whole number that can be formed by multiplying two smaller positive integers. Composite numbers have more than two factors.
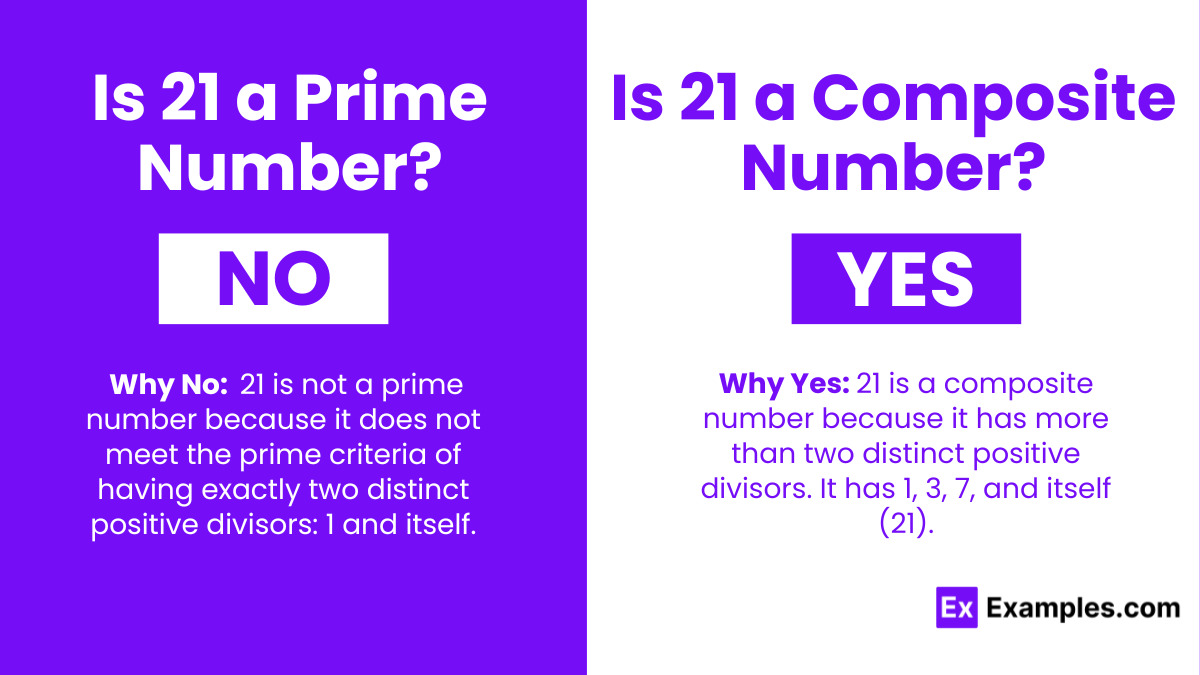
Why 21 is Composite
The number 21 is easily divisible by 1, 3, 7, and 21. This readily demonstrates that it has more than two factors.
Specifically, 21 can be expressed as the product of 3 and 7 (3 x 7 = 21). Therefore, according to the fundamental definition, 21 is undoubtedly a composite number.
The Social Media Frenzy
The online debate surrounding 21's classification revealed a significant number of individuals who incorrectly believed it to be prime. This misconception stemmed from a variety of sources, including rushed calculations, forgotten definitions, or simply a lack of exposure to basic number theory.
Posts questioning the nature of 21 quickly went viral, prompting responses from mathematicians, educators, and even casual observers. Some expressed amusement, while others voiced concern about the apparent lack of fundamental mathematical knowledge.
"It's alarming to see so many people unsure about such a basic concept," commented Dr. Emily Carter, a mathematics professor at the University of California, Berkeley, in a widely shared tweet. "It underscores the need for more effective math education at all levels."
Implications and Concerns
While the "21 debate" might seem like a trivial online moment, it highlights a potentially broader issue: the state of mathematical literacy. A weak grasp of basic mathematical principles can have significant consequences in a world increasingly driven by data and technology.
From understanding financial concepts to interpreting scientific data, mathematical skills are essential for informed decision-making. The misconception surrounding prime and composite numbers could indicate a deeper problem in how math is taught and perceived.
Concerns arise that the digital age, with its reliance on calculators and readily available answers, may be inadvertently hindering the development of fundamental mathematical reasoning skills. The ease of outsourcing calculations may be leading to a decline in mental math proficiency and a decreased understanding of underlying mathematical principles.
Addressing the Gap in Mathematical Literacy
Several initiatives are underway to improve mathematical literacy and foster a greater appreciation for the subject. These include innovative teaching methods that emphasize conceptual understanding over rote memorization.
Interactive online resources and educational games are also being developed to make learning math more engaging and accessible. Moreover, encouraging a positive attitude towards mathematics is crucial.
Many people develop math anxiety early in life, which can impede their ability to learn and apply mathematical concepts effectively. Overcoming this anxiety requires a supportive and encouraging learning environment that emphasizes effort and understanding rather than innate ability.
Looking Ahead
The "21 debate" serves as a valuable reminder of the importance of fundamental mathematical knowledge in an increasingly complex world. It highlights the need for continuous efforts to improve mathematical literacy and address common misconceptions.
While the digital world can sometimes amplify misinformation, it also provides powerful tools for education and knowledge dissemination. By leveraging these tools effectively, we can foster a greater appreciation for mathematics and empower individuals to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century with confidence.
Ultimately, ensuring a strong foundation in mathematical principles is not just about answering trivial questions online. It’s about equipping individuals with the critical thinking skills they need to succeed in a rapidly evolving world. The question of whether 21 is prime or composite may be simple, but the implications of that question are profound.


![Is 21 A Prime Number Or Composite Is 21 a Prime Number or Composite Number [Why & Why not Detailed Guide]](https://images.examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Is-21-a-Prime-Number.png)







![Is 21 A Prime Number Or Composite Is 21 a Prime Number or Composite Number [Why & Why not Detailed Guide]](https://images.examples.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Is-21-a-Composite-Number-1.png)