Is Co An Element Or Compound

Confusion swirls in academic circles and online forums alike: Is Co, the chemical symbol prominently displayed on the periodic table, an element or a compound? This seemingly simple question sparks intense debate, highlighting the fundamental principles of chemistry and the very definition of matter.
This article cuts through the ambiguity, providing a definitive answer based on established scientific principles and validated data from reputable scientific organizations. It will explore the atomic structure of Co, its placement within the periodic table, and how its properties definitively classify it as an element, not a compound.
The Elemental Nature of Cobalt (Co)
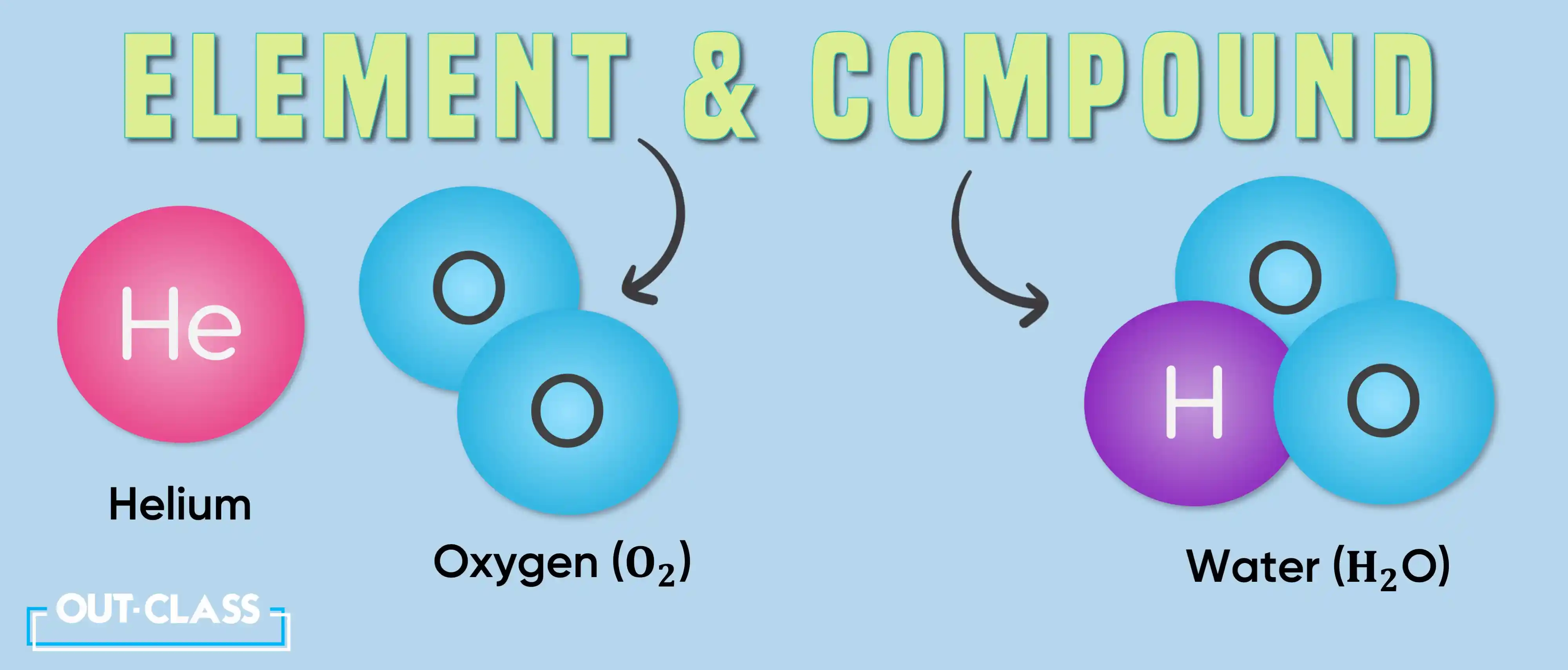
Cobalt (Co), identified by atomic number 27, is unequivocally an element. This classification stems directly from its atomic structure and its representation on the periodic table, the definitive chart of all known elements.
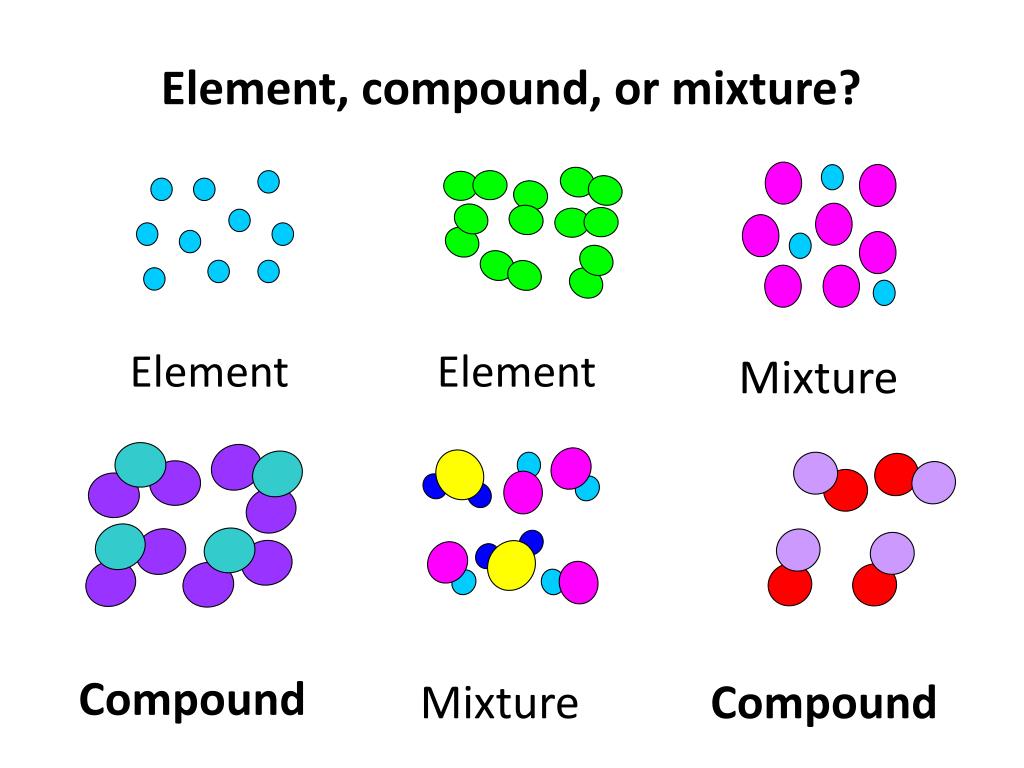
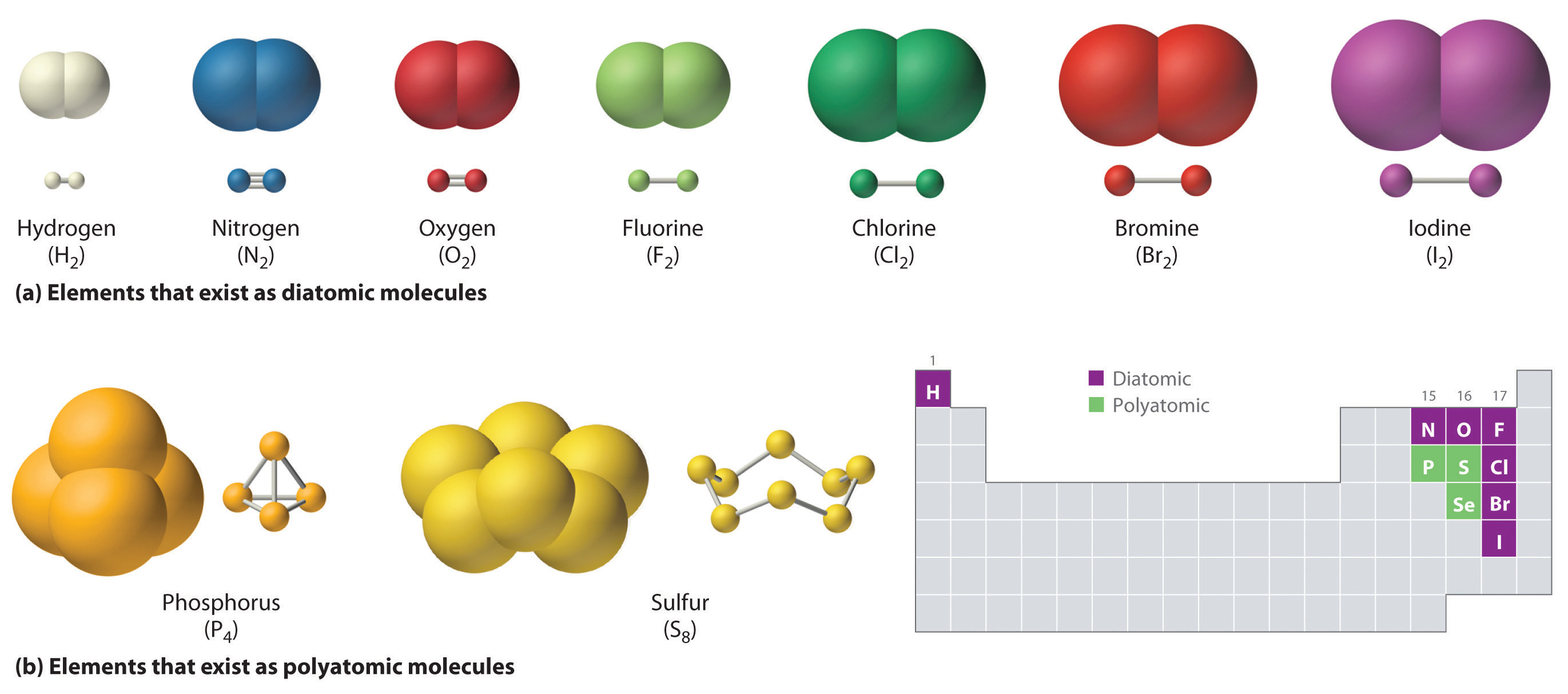
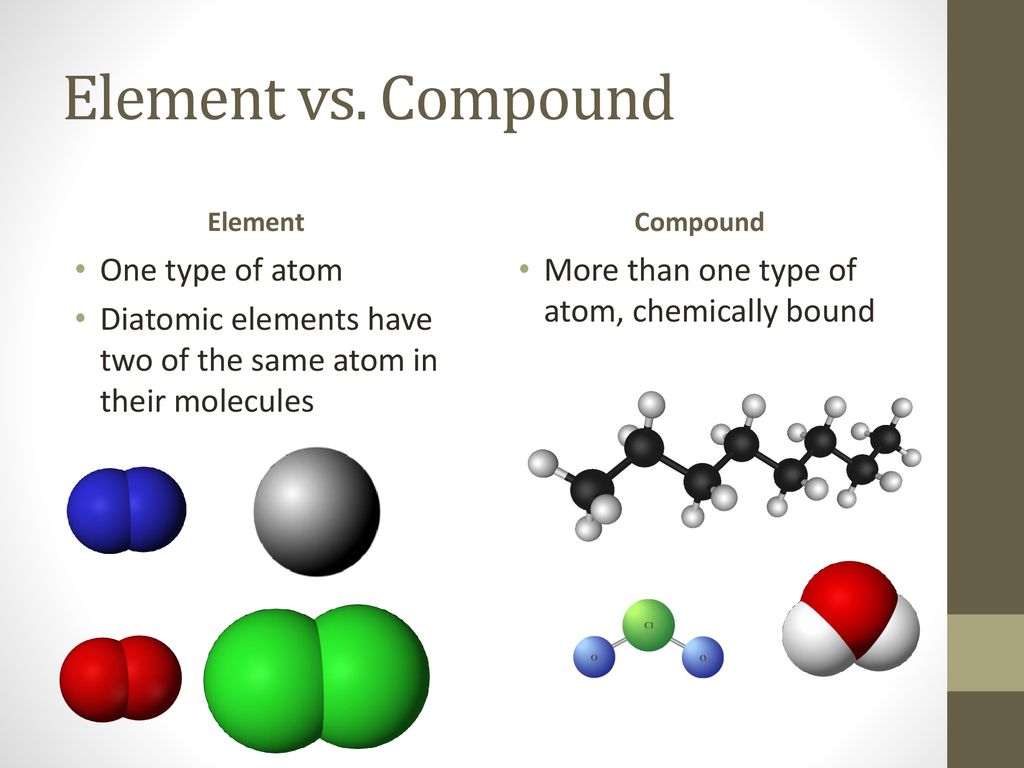
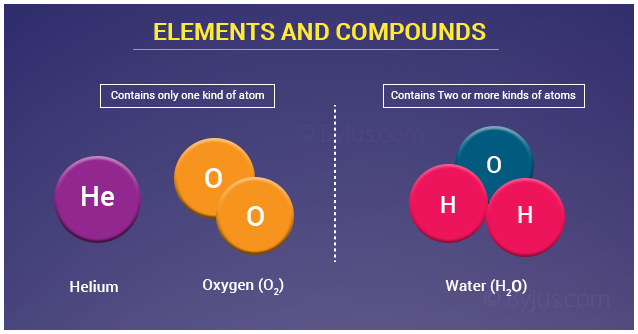
Elements are defined as substances composed of only one type of atom. A single cobalt atom contains 27 protons in its nucleus, along with varying numbers of neutrons, defining its isotopes, and 27 electrons orbiting the nucleus.
Atomic Structure as Proof
The number of protons in the nucleus, known as the atomic number, is the unique identifier for each element. If a substance contains only atoms with 27 protons, then that substance is, by definition, cobalt.
This crucial point underscores why Co cannot be a compound. Compounds are substances formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together in fixed proportions.
The Periodic Table's Verdict
The periodic table is organized based on increasing atomic number. Cobalt occupies a specific square, clearly indicating its elemental status. No compound can occupy a single square on the periodic table.
The placement of Co among elements like iron (Fe) and nickel (Ni) further solidifies its elemental categorization. These neighboring elements, also characterized by unique atomic numbers and properties, are distinct entities, just like cobalt.
Differentiating Elements from Compounds
Understanding the distinction between elements and compounds is crucial to resolving any confusion. Elements, like cobalt, cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Compounds, on the other hand, can be decomposed into their constituent elements through chemical reactions. Water (H2O), for example, can be broken down into hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) through electrolysis.
Chemical Bonding and Compound Formation
Compounds are formed through chemical bonds, which are attractions between atoms. These bonds result from the sharing or transfer of electrons between different atoms.
In the case of cobalt oxide (CoO), cobalt atoms are chemically bonded to oxygen atoms, forming a compound with properties different from those of either cobalt or oxygen alone. This contrasts starkly with pure cobalt metal, where only cobalt atoms exist.
Physical Properties as Indicators
Elements and compounds often exhibit distinct physical properties. Cobalt, in its elemental form, is a hard, silvery-blue metal.
Cobalt compounds, such as cobalt chloride (CoCl2), can appear as colored crystals, significantly differing from the metallic luster of elemental cobalt. These variations in appearance are a direct consequence of the chemical bonding between cobalt and other elements.
Addressing Misconceptions and Confusion
The occasional confusion surrounding cobalt's classification likely stems from the common presence of cobalt in various compounds and alloys. Cobalt is rarely found in its pure elemental form in nature.
It readily combines with other elements, forming a wide range of compounds used in various industrial applications, including batteries, magnets, and pigments. However, the existence of these compounds does not negate the fundamental fact that Co itself is an element.
The Role of Alloys and Mixtures
Alloys, such as steel containing cobalt, are mixtures of metals. While cobalt contributes its properties to the alloy, it remains present as elemental cobalt within the mixture, not chemically bonded to the other metals.
This contrasts with compounds, where the constituent elements are chemically bound and have altered properties compared to their elemental forms. Alloys and mixtures can be physically separated, unlike the elements in a compound that can only be separated through chemical reactions.
Conclusion: Cobalt's Undeniable Elemental Status
Based on established scientific principles, atomic structure analysis, and its position within the periodic table, cobalt (Co) is definitively an element. Any perceived ambiguity arises from the existence of cobalt-containing compounds and alloys, not from any inherent uncertainty about cobalt's elemental nature.
Moving forward, it is vital to reinforce the understanding of fundamental chemical concepts, distinguishing between elements, compounds, and mixtures. This clarity ensures accuracy in scientific discourse and promotes a more profound comprehension of the world around us.
Continued scientific research and educational outreach remain crucial to solidify these core principles and dispel any lingering misconceptions concerning the fundamental building blocks of matter.
+is+a+compound.+It+is+made+up+of+two+or+more+elements+CHEMICALLY+combined..jpg)





.jpg)
+is+CO+..jpg)