Is Keto The Same As Gluten Free

The world of dietary restrictions can feel like a tangled web of acronyms and buzzwords. Two terms frequently encountered, and often conflated, are keto and gluten-free. But despite some surface-level similarities, these are fundamentally different approaches to eating, each addressing distinct health concerns.
This article delves into the core differences between the ketogenic diet and a gluten-free diet, exploring their distinct purposes, allowable foods, and potential health implications. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals making informed choices about their dietary needs and overall well-being.
Keto vs. Gluten-Free: Unpacking the Definitions
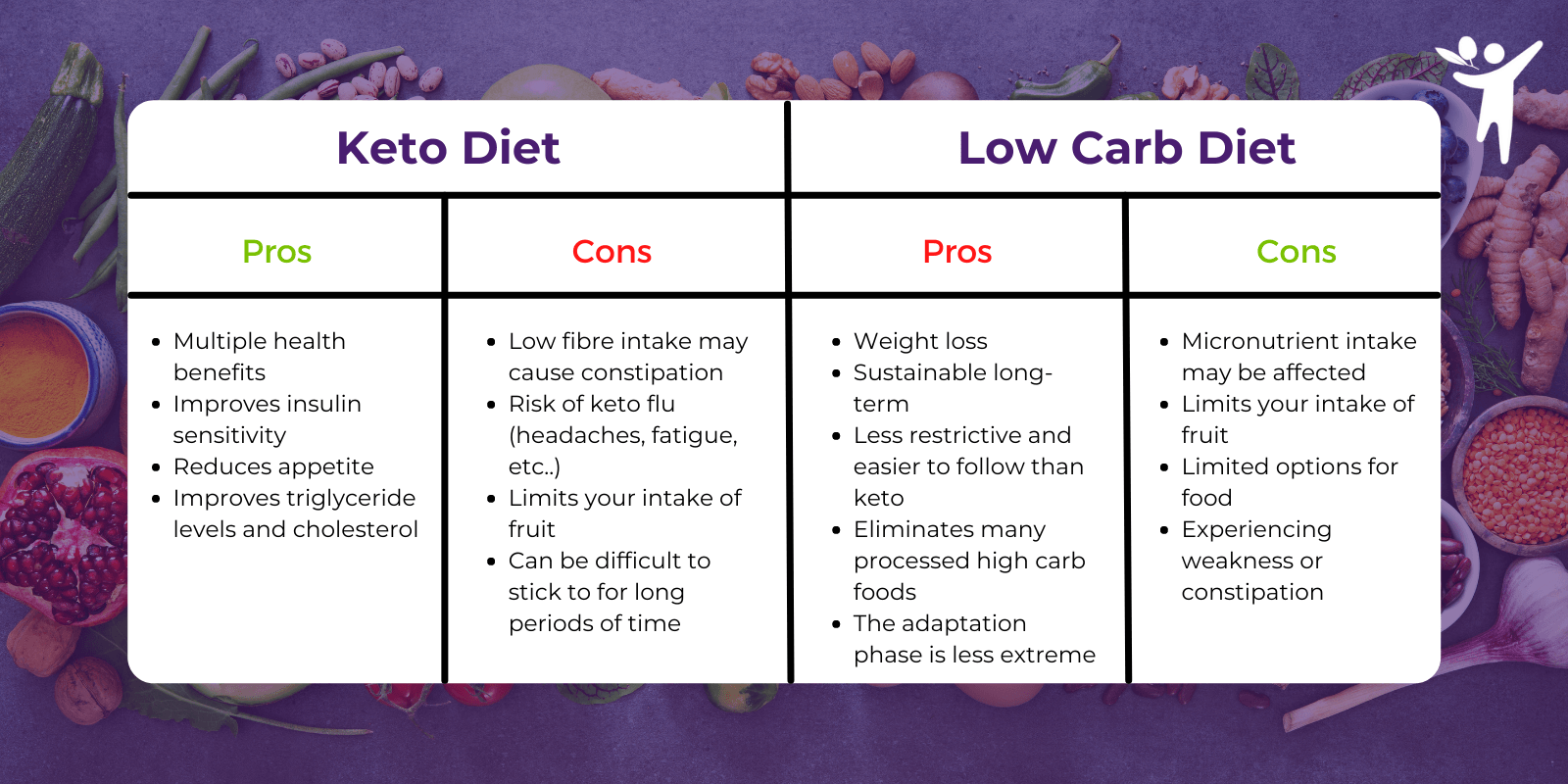
The ketogenic diet, often shortened to keto, is a high-fat, very-low-carbohydrate diet designed to shift the body's primary fuel source from glucose (derived from carbohydrates) to ketones (derived from fat). This metabolic state, called ketosis, is achieved by drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, typically to less than 50 grams per day.
A keto diet prioritizes foods like meats, poultry, fish, eggs, cheese, avocados, nuts, and oils. It restricts or eliminates grains, starchy vegetables, fruits high in sugar, legumes, and most processed foods.
A gluten-free diet, on the other hand, focuses on the elimination of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. This dietary approach is essential for individuals with celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten ingestion, and those with non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
A gluten-free diet emphasizes naturally gluten-free foods such as fruits, vegetables, meats, poultry, fish, beans, legumes, and many grains like rice, corn, and quinoa. It requires careful avoidance of foods containing wheat, barley, and rye, as well as products that may be cross-contaminated with gluten during processing.
Distinct Purposes: Managing Different Health Conditions
The keto diet is primarily used for weight loss, blood sugar control in individuals with type 2 diabetes, and, in some cases, managing neurological conditions like epilepsy. The shift to ketosis forces the body to burn fat for fuel, potentially leading to weight reduction and improved metabolic markers.
Conversely, a gluten-free diet is a medical necessity for individuals with celiac disease, preventing the autoimmune reaction that damages the small intestine. It also provides relief from symptoms like bloating, abdominal pain, and fatigue for individuals with non-celiac gluten sensitivity.
"Adhering to a strict gluten-free diet is the cornerstone of treatment for celiac disease," states the Celiac Disease Foundation.
While some individuals may experience weight loss on a gluten-free diet, this is often due to the elimination of processed foods and refined carbohydrates that commonly contain gluten, rather than a direct effect of removing gluten itself.
Overlapping Foods and Potential Confusion
Some foods are naturally both keto-friendly and gluten-free, such as meats, poultry, fish, and non-starchy vegetables. This overlap can lead to confusion about the core purpose of each diet.
However, the dietary approaches diverge significantly when considering grains and processed foods. For example, gluten-free bread and pasta substitutes made from rice flour or cornstarch are permitted on a gluten-free diet but are generally too high in carbohydrates for a keto diet.
Similarly, many keto-friendly processed foods, such as those made with almond flour or artificial sweeteners, may or may not be gluten-free, depending on the specific ingredients and manufacturing processes.
Navigating Dietary Choices: Considerations and Caveats
Before adopting either a keto or gluten-free diet, consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional is crucial. These experts can provide personalized guidance based on individual health needs, medical history, and lifestyle.
A keto diet can be restrictive and may not be suitable for everyone, particularly individuals with certain medical conditions like kidney disease or pancreatic disorders. It can also lead to nutrient deficiencies if not carefully planned.
Similarly, adopting a gluten-free diet without a confirmed diagnosis of celiac disease or gluten sensitivity may mask underlying medical conditions or lead to unnecessary dietary restrictions. The Gluten Intolerance Group emphasizes the importance of proper testing before eliminating gluten.
The Future of Dietary Approaches
The understanding of both keto and gluten-free diets is constantly evolving, with ongoing research exploring their potential benefits and risks. Personalized nutrition, tailored to individual genetic makeup and metabolic needs, is likely to play an increasingly important role in dietary recommendations.
As awareness of food sensitivities and metabolic health grows, individuals will need clear and accurate information to navigate the complex landscape of dietary choices. Distinguishing between keto and gluten-free diets is a crucial step toward making informed decisions about one's health and well-being.
Ultimately, the best dietary approach is one that is sustainable, enjoyable, and tailored to individual needs, under the guidance of qualified healthcare professionals.