Keytruda For Stage 4 Stomach Cancer
In a significant development for patients battling advanced stomach cancer, the immunotherapy drug Keytruda (pembrolizumab) has demonstrated promising results in extending survival when combined with chemotherapy. Recent clinical trial data suggest a potential new standard of care for those diagnosed with previously untreated, advanced-stage stomach cancer.
This advancement offers hope to individuals facing a disease with historically limited treatment options and poor prognosis. The data, presented at a major oncology conference, showcases the potential of immunotherapy to significantly impact patient outcomes in a challenging cancer type.
Key Trial Results and Methodology
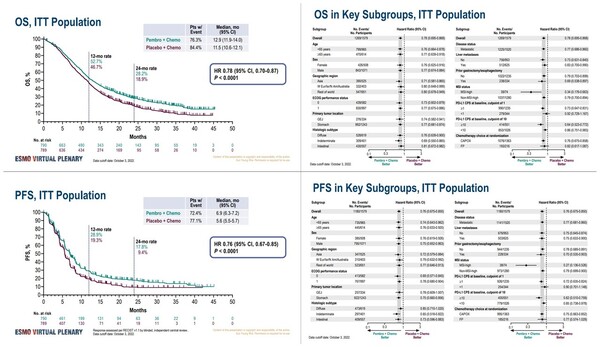
The pivotal clinical trial, known as KEYNOTE-859, involved a large cohort of patients with previously untreated, advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. The study compared the outcomes of patients receiving Keytruda in combination with chemotherapy to those receiving chemotherapy alone.
The primary endpoint of the trial was overall survival (OS), a crucial measure of treatment effectiveness. Secondary endpoints included progression-free survival (PFS) and objective response rate (ORR).
Results indicated a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in overall survival for the Keytruda combination group. Patients receiving Keytruda plus chemotherapy lived significantly longer than those receiving chemotherapy alone, representing a substantial advancement in treatment.
Who is Affected and Why This Matters
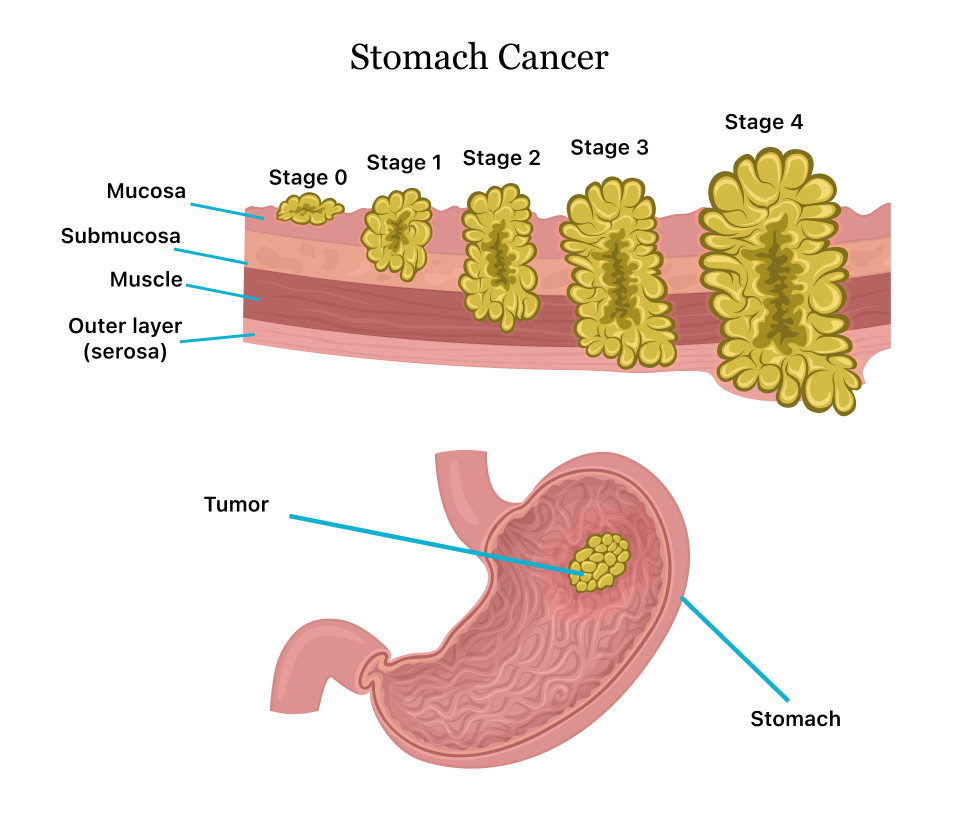
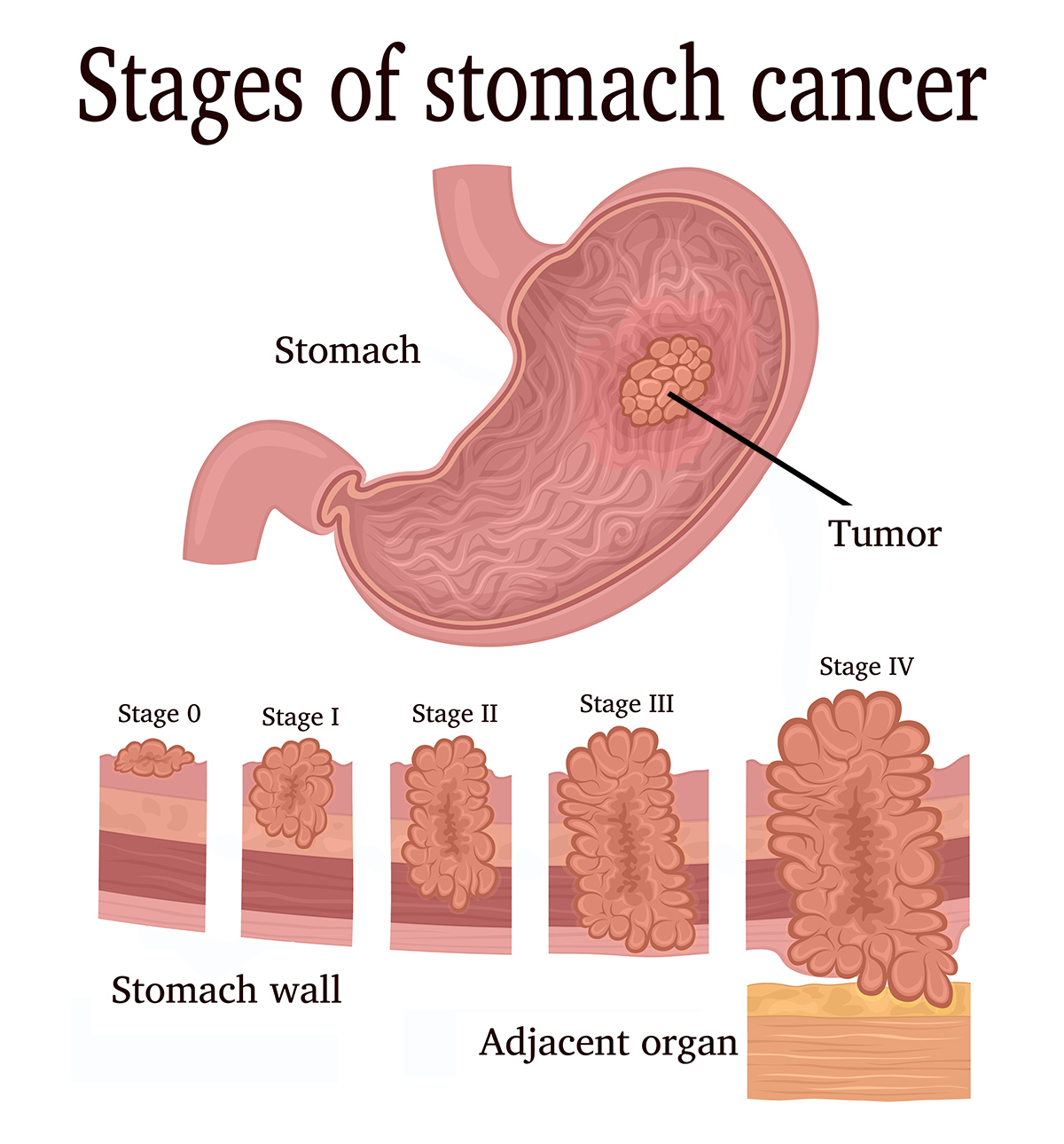
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a disease in which malignant cells form in the lining of the stomach. Advanced-stage stomach cancer, particularly stage 4, indicates that the cancer has spread to distant parts of the body, making it significantly more difficult to treat.
For these patients, treatment options have traditionally been limited to chemotherapy and, in some cases, targeted therapies. The addition of Keytruda offers a new approach by harnessing the power of the immune system to fight the cancer.
The KEYNOTE-859 trial included patients regardless of their PD-L1 status, making the findings relevant to a broad range of individuals with advanced gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma. PD-L1 is a protein that can help cancer cells evade the immune system.
How Keytruda Works and Potential Side Effects
Keytruda is a type of immunotherapy known as a checkpoint inhibitor. It works by blocking the PD-1 protein on immune cells, preventing cancer cells from suppressing the immune system's ability to attack them.
By releasing the brakes on the immune system, Keytruda allows immune cells to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively. This mechanism of action differs significantly from traditional chemotherapy, which directly targets rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells.
While Keytruda can be highly effective, it is also associated with potential side effects. Common side effects include fatigue, rash, diarrhea, and nausea. In rare cases, more serious immune-related adverse events can occur, requiring careful monitoring and management by healthcare professionals.
Impact on Standard of Care and Future Directions
The positive results from the KEYNOTE-859 trial are likely to lead to changes in the standard of care for patients with previously untreated, advanced gastric or GEJ adenocarcinoma. Oncologists may increasingly incorporate Keytruda into their treatment regimens for these patients.
The long-term impact of Keytruda on overall survival and quality of life is still being investigated. Further research is ongoing to identify biomarkers that can help predict which patients are most likely to benefit from Keytruda therapy.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of combining Keytruda with other therapies, such as targeted agents and radiation, to further improve outcomes for patients with stomach cancer. The landscape of stomach cancer treatment is evolving, and the integration of immunotherapy represents a significant step forward.