Label The Structures Associated With A Hair Follicle
Understanding the intricate architecture of a hair follicle is crucial for advancements in dermatology, cosmetic science, and regenerative medicine.
This article delves into the key structures associated with a hair follicle, providing a comprehensive overview based on established scientific literature and anatomical studies.
The Hair Follicle: An Overview
A hair follicle is a complex skin appendage responsible for hair growth. It’s not just a simple pore but a dynamic mini-organ composed of various interacting components.
These components work in harmony to regulate hair production, pigmentation, and shedding.
Key Structures and Their Functions
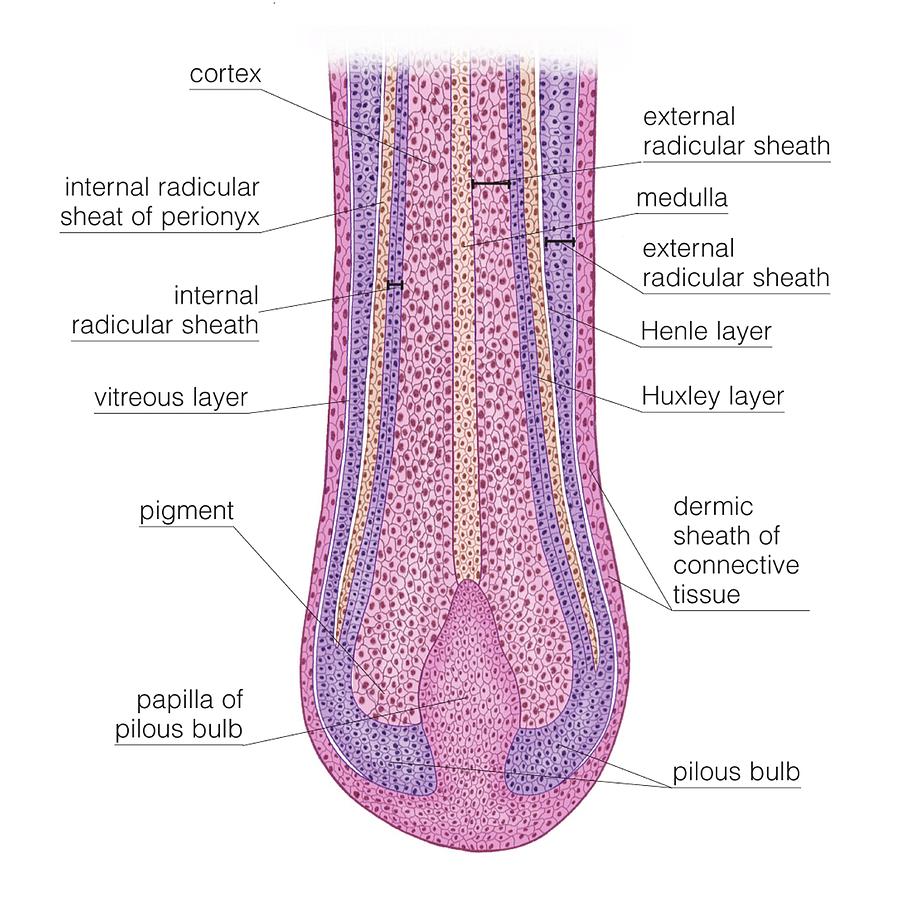
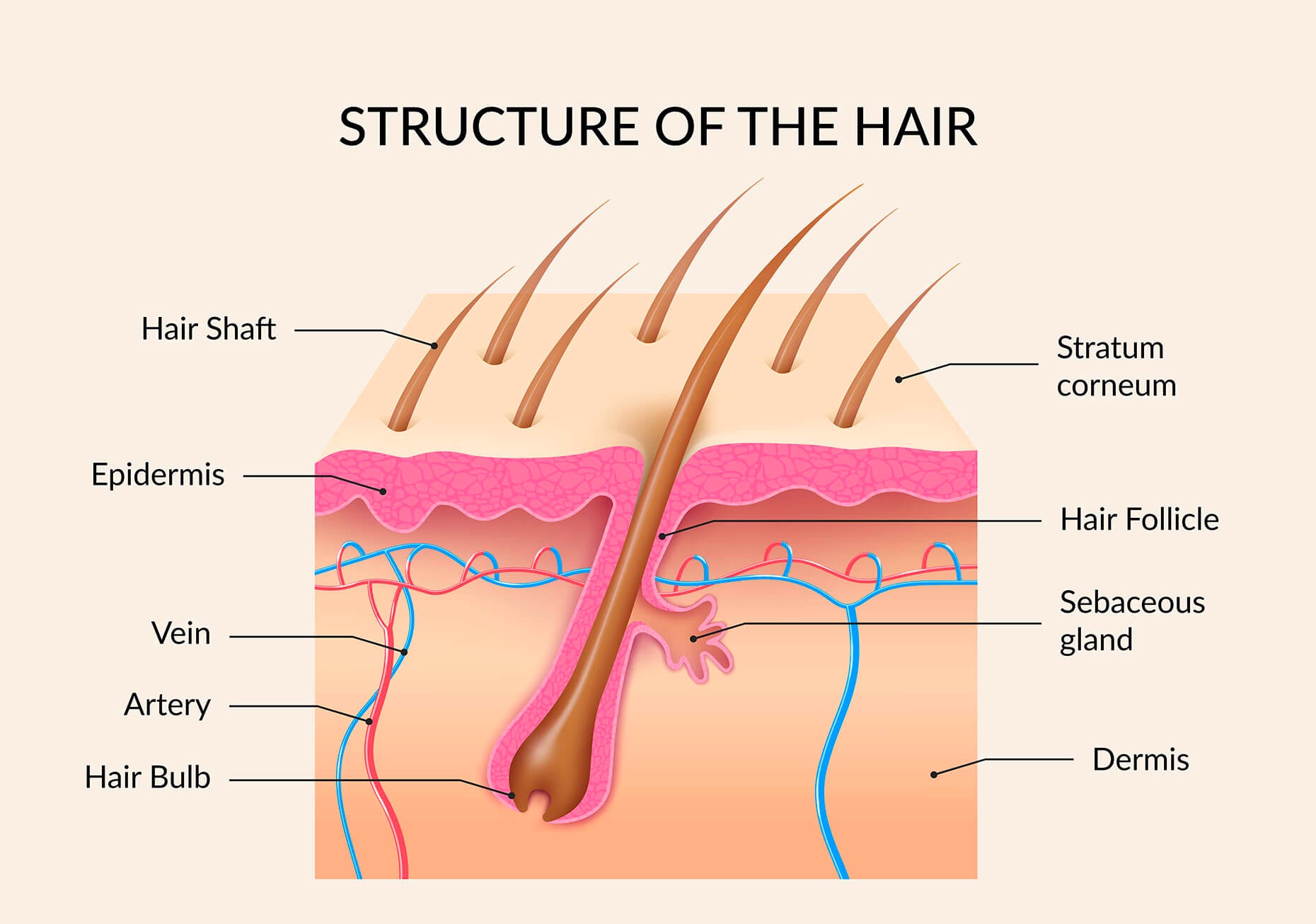
The hair bulb, located at the base of the follicle, is the expanded, bulb-shaped structure where hair growth originates.
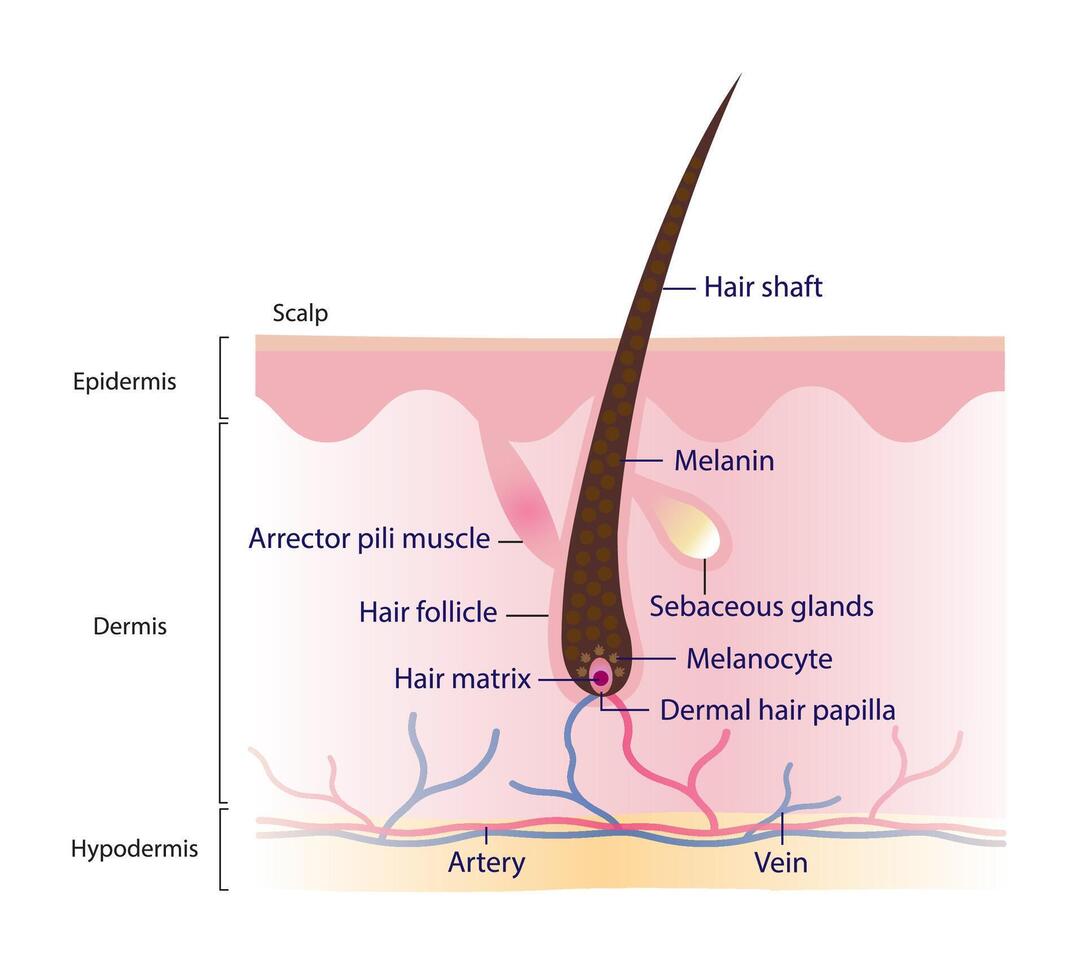
Within the bulb resides the dermal papilla, a specialized mesenchymal cell cluster providing signals that control hair follicle development and cycling. The dermal papilla supplies nutrients to the growing hair.
The hair matrix surrounds the dermal papilla and contains rapidly dividing keratinocytes that differentiate into the hair shaft. Melanocytes within the matrix contribute to hair color by producing melanin.
The hair shaft is the visible portion of the hair, composed primarily of keratin. It emerges from the skin surface.
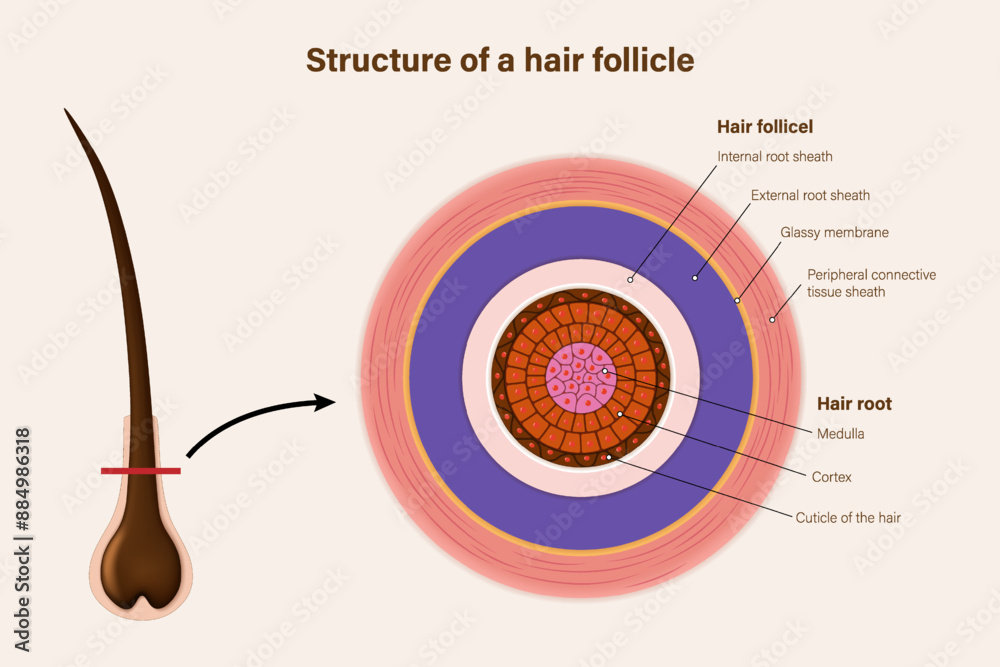
The inner root sheath (IRS) is a multi-layered cellular structure surrounding the hair shaft within the follicle. It helps shape the hair shaft and protect it during its upward journey.
The IRS disintegrates before the hair reaches the skin surface.
The outer root sheath (ORS) is a continuous extension of the epidermis that envelops the IRS and plays a role in follicle anchoring and stem cell reservoir. It extends from the bulb to the sebaceous gland.
The sebaceous gland is a small, sac-like gland associated with the hair follicle that produces sebum, an oily substance that lubricates and protects the hair and skin. These glands are usually connected to the upper part of the hair follicle.
The arrector pili muscle is a small smooth muscle attached to the hair follicle and the epidermis. Contraction of this muscle causes the hair to stand on end, resulting in "goosebumps."
The connective tissue sheath surrounds the hair follicle, providing structural support and anchoring it to the surrounding dermis. It’s composed of collagen fibers and other extracellular matrix components.
"Understanding the precise function of each follicular component is vital for developing targeted therapies for hair loss and other hair-related disorders," states Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading dermatologist at the National Institute of Dermatology.
Significance and Potential Impact
A detailed understanding of hair follicle anatomy has significant implications for treating conditions like alopecia (hair loss). Research focused on stimulating the dermal papilla or promoting hair matrix cell proliferation holds promise for hair regrowth.
Cosmetic procedures, such as hair transplantation, rely heavily on knowledge of follicular structure and function. Minimizing damage to the follicle during transplantation is critical for successful engraftment.
Furthermore, studying hair follicles can provide insights into skin biology and regenerative processes. Hair follicles possess stem cells that can potentially be used for tissue repair and regeneration in other parts of the body.
Ongoing Research and Future Directions
Researchers are actively exploring the molecular mechanisms regulating hair follicle cycling and development. Gene expression studies and advanced imaging techniques are shedding light on the complex interactions within the follicle.
Scientists are also investigating the role of various growth factors and signaling pathways in hair growth. This knowledge could lead to the development of more effective and targeted therapies for hair disorders.
Personalized medicine approaches, tailored to individual genetic profiles, may offer the potential for customized hair loss treatments in the future.
In conclusion, the hair follicle is a fascinating and complex structure with significant implications for human health and well-being. Ongoing research continues to unravel its mysteries, paving the way for innovative solutions to hair-related problems and potential applications in regenerative medicine.