Law And Order Cost Of Capital
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/COST-OF-CAPITAL-FINAL-HR-f3d41d21c66a494ea77eec360a6a3857.jpg)
A recent surge in discussions surrounding the "law and order" approach to governance has sparked a parallel debate: its economic implications, specifically the cost of capital. While proponents argue that stringent law enforcement fosters stability and attracts investment, critics contend that excessive reliance on punitive measures can stifle economic growth and disproportionately burden certain communities.
The intersection of law enforcement strategies and economic prosperity is complex. Examining the cost of capital within the context of "law and order" requires a nuanced understanding of its impact on investment, innovation, and overall economic well-being.
What is the Cost of Capital?
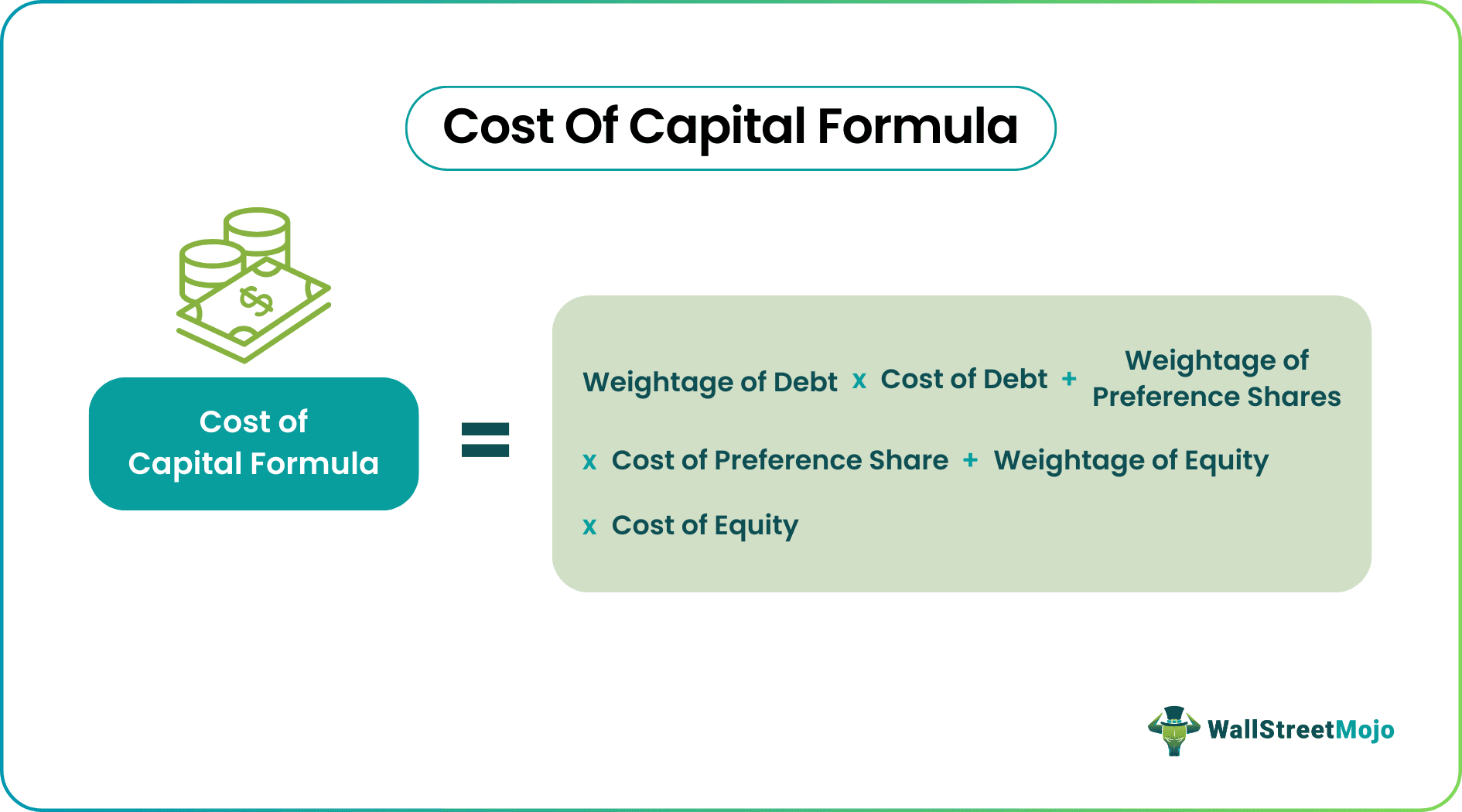
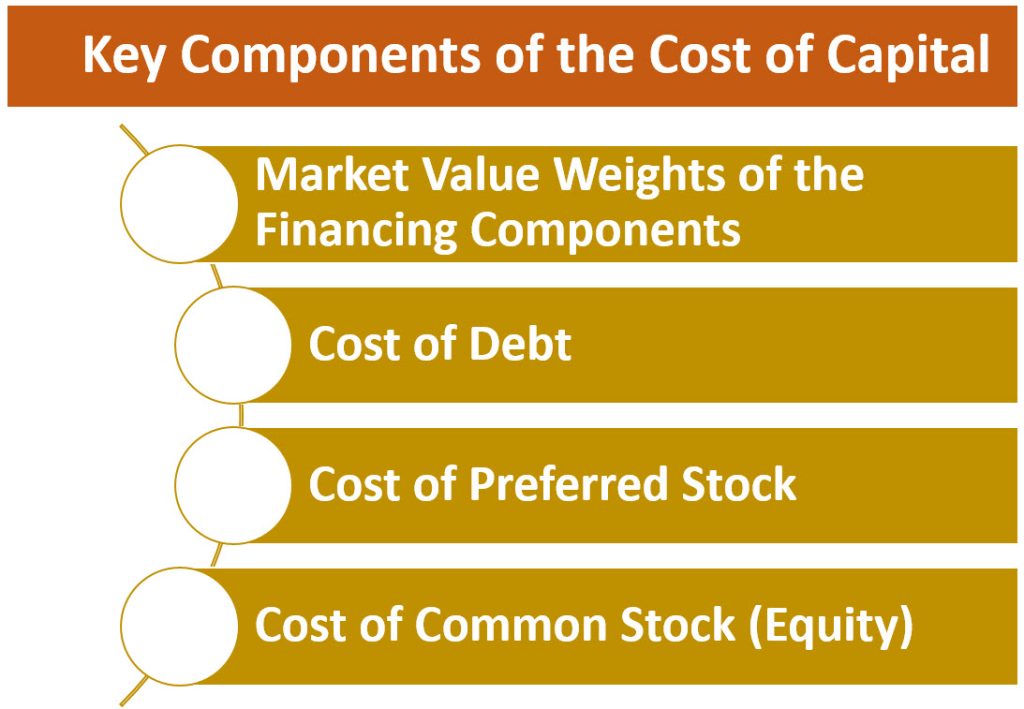
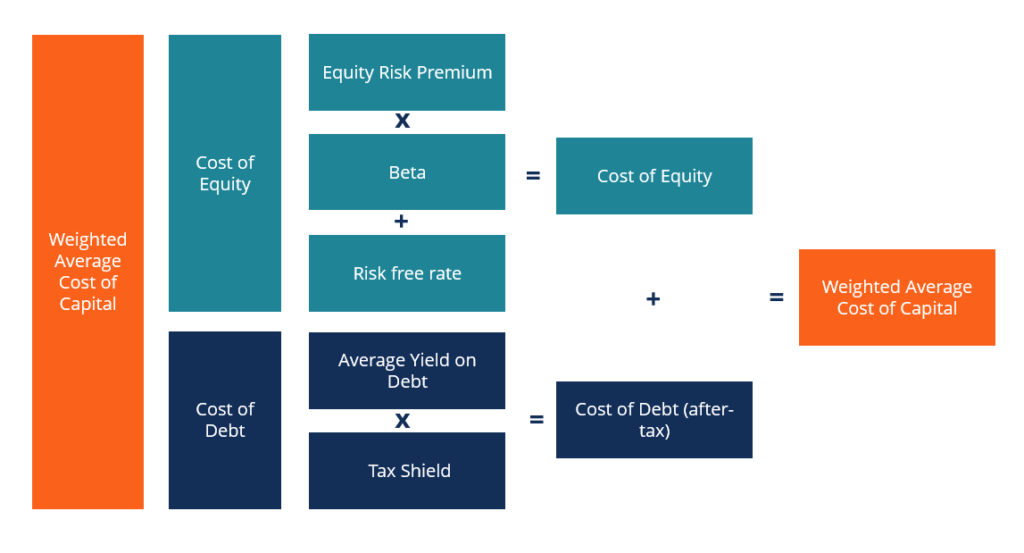
The cost of capital represents the rate of return a company or investor requires from an investment to compensate for its risk. It encompasses the cost of equity, debt, and other financing sources.
Higher perceived risks often lead to a higher cost of capital, discouraging investment and hindering economic expansion. How do "law and order" policies influence this perception of risk?
The Argument for "Law and Order" and Lower Capital Costs
Advocates of stricter law enforcement argue that it creates a more predictable and secure environment for businesses. Reduced crime rates, they say, translate to lower insurance costs, less property damage, and increased consumer confidence.
This enhanced stability, in turn, attracts both domestic and foreign investment, driving down the cost of capital and fostering economic growth. Some studies suggest a correlation between lower crime rates and increased foreign direct investment.
According to a statement from the Department of Justice, "A commitment to enforcing the law and maintaining order is essential for creating an environment where businesses can thrive and create jobs."
The Counterargument: "Law and Order" and Increased Capital Costs
Critics contend that a "law and order" approach, particularly when implemented through aggressive policing and mass incarceration, can have detrimental economic consequences. They argue that excessive policing can disproportionately target minority communities, leading to social unrest and economic instability.
Furthermore, the high costs associated with maintaining a large prison population divert resources from education, infrastructure, and other essential public services. This resource allocation can negatively impact long-term economic prospects.
Data from the Prison Policy Initiative reveals that the United States spends tens of billions of dollars annually on incarceration. This spending is often concentrated in specific regions, impacting local economies.
The Impact on Specific Industries
The "law and order" approach can have varying effects on different sectors of the economy. For example, the private prison industry benefits directly from increased incarceration rates, while other industries, such as tourism and hospitality, may suffer from a perceived increase in crime.
Real estate values in areas with high crime rates may also decline, impacting property taxes and local government revenue. This can create a cycle of disinvestment and economic decline.
"The economic impact of mass incarceration extends far beyond the prison walls," explains Dr. Emily Carter, an economist at the University of California, Berkeley. "It affects families, communities, and the overall economy."
The Role of Public Perception and Risk Assessment
Ultimately, the impact of "law and order" on the cost of capital depends on how it is perceived by investors and businesses. If stricter law enforcement is seen as a legitimate and effective way to reduce crime and maintain order, it may lead to lower capital costs.
However, if it is perceived as heavy-handed, discriminatory, or ineffective, it could increase perceived risk and drive up the cost of capital. This highlights the importance of transparency, accountability, and community engagement in law enforcement.
Transparency in policing and justice systems is key. Investor confidence hinges on whether law enforcement actions are predictable and based on the rule of law.
Case Studies and Examples
Examining specific cities or regions that have implemented "law and order" policies can provide valuable insights into their economic consequences. For example, comparing cities with different policing strategies and incarceration rates can reveal the impact on economic growth, job creation, and investment.
Analyzing the impact of specific law enforcement initiatives on local businesses and communities can also offer a more nuanced understanding of the trade-offs involved. These case studies may highlight the difference between perceived security and actual economic outcomes.
One example could be comparing economic data from cities with "broken windows" policing strategies versus those with community-oriented policing approaches.
Conclusion: A Balancing Act
The relationship between "law and order" and the cost of capital is complex and multifaceted. While maintaining order and reducing crime are essential for economic prosperity, excessive reliance on punitive measures can have unintended consequences.
A balanced approach that prioritizes both public safety and economic opportunity is crucial. This includes investing in education, job training, and community development programs, as well as promoting fair and equitable law enforcement practices.
Ultimately, creating a thriving economy requires a holistic approach that addresses the root causes of crime and promotes opportunity for all. The focus should be on *long-term strategies* that lead to sustainable economic growth alongside *reduced recidivism*.