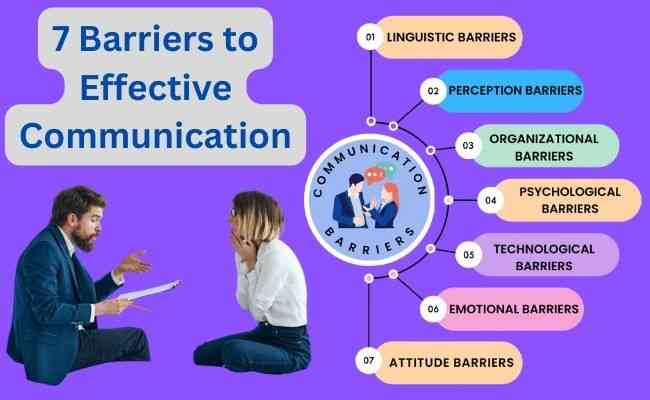
List 6 Barriers To Effective Communication
Effective communication is the cornerstone of successful relationships, thriving workplaces, and a well-functioning society. However, the path to clear and meaningful exchanges is often riddled with obstacles. These barriers can impede understanding, create misunderstandings, and ultimately hinder progress.
Understanding these barriers is crucial for individuals and organizations alike. By recognizing and addressing these challenges, we can foster stronger connections and improve overall communication effectiveness. This article delves into six common barriers to effective communication, providing insights into their nature and potential impact.
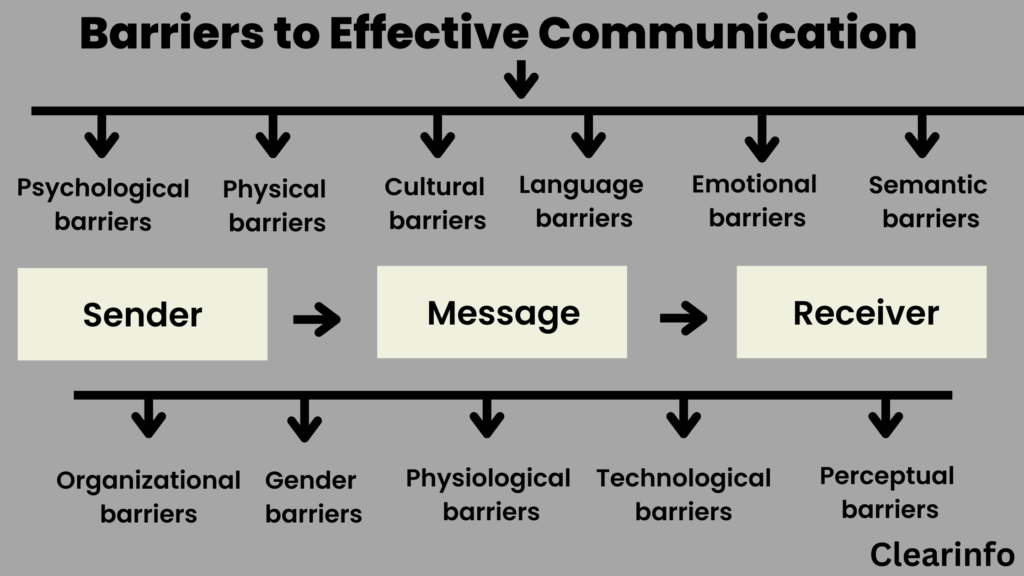
Barriers to Effective Communication
Numerous factors can disrupt the communication process. From subtle nuances in language to deeply ingrained cultural differences, these barriers can significantly affect the clarity and accuracy of messages.
1. Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are perhaps the most obvious impediments to communication. Noise, distance, and technological malfunctions all fall under this category. A noisy construction site, for instance, can make verbal communication nearly impossible, forcing reliance on visual cues or alternative methods.
Similarly, geographical distance can hinder communication, especially in the absence of reliable technology. A faulty internet connection during a video conference can disrupt the flow of information and lead to frustration.
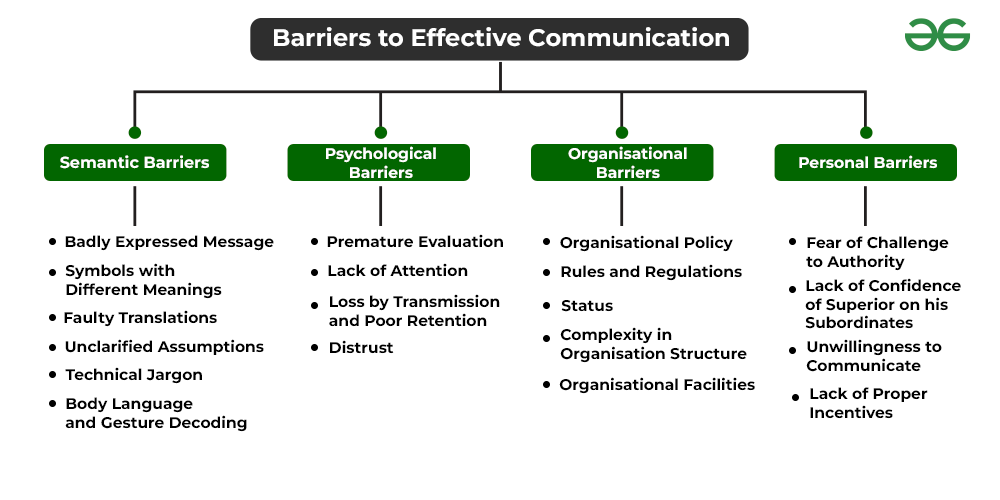
2. Psychological Barriers
Psychological barriers stem from the mental and emotional state of the communicator or receiver. These barriers can include biases, prejudices, and preconceived notions. Someone with a strong negative bias towards a particular group may misinterpret or disregard messages from members of that group.
Stress, anxiety, and emotional distress can also cloud judgment and impair communication. A person experiencing high levels of stress may have difficulty concentrating and processing information effectively.
3. Semantic Barriers
Semantic barriers arise from problems with the meaning of words or symbols. Jargon, technical terms, and ambiguous language can all contribute to miscommunication. Imagine a doctor using highly specialized medical terminology when speaking to a patient; the patient may struggle to understand the diagnosis and treatment plan.
Differences in language and dialect also fall under semantic barriers. Even within the same language, regional variations in vocabulary and pronunciation can lead to confusion.
4. Cultural Barriers
Culture plays a significant role in shaping communication styles and norms. Cultural differences in nonverbal communication, such as eye contact and personal space, can lead to misunderstandings. For example, direct eye contact is considered a sign of respect in some cultures, while it is seen as confrontational in others.
Cultural differences in communication styles, such as directness versus indirectness, can also create barriers. In some cultures, people prefer to communicate directly and explicitly, while in others, indirect communication and subtle cues are preferred.
5. Physiological Barriers
Physiological barriers relate to physical limitations or conditions that affect communication. Hearing impairments, speech impediments, and vision problems can all hinder the communication process. Someone with a hearing impairment may miss crucial information during a conversation, leading to misunderstandings.
Similarly, a speech impediment can make it difficult for someone to express themselves clearly and effectively. These barriers often require assistive technologies or alternative communication methods to overcome.
6. Organizational Barriers
Organizational barriers arise from the structure and culture of an organization. Poor communication channels, lack of transparency, and hierarchical structures can all impede effective communication. A company with a rigid top-down communication style may stifle feedback from employees and hinder innovation.
Furthermore, a lack of clear communication policies and procedures can create confusion and uncertainty. Employees may be unsure of who to contact for information or how to report problems.
The Impact of Communication Barriers
The consequences of ineffective communication can be far-reaching. Misunderstandings can lead to conflict, errors, and inefficiencies in the workplace. In personal relationships, poor communication can erode trust and create distance.
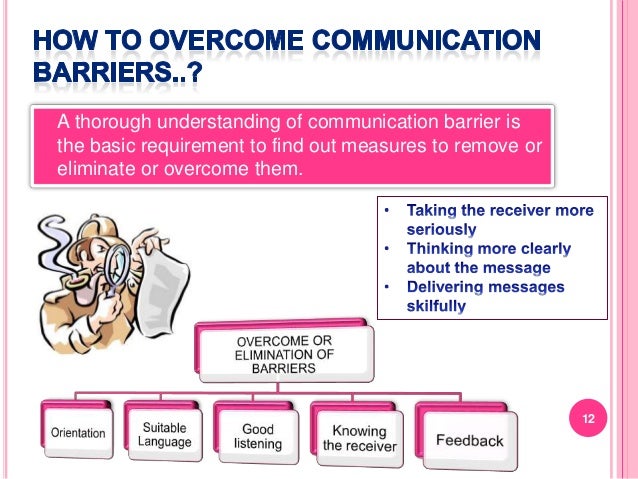
Addressing these barriers requires a proactive approach. Individuals and organizations must be mindful of the potential obstacles to communication and take steps to mitigate their impact.
By fostering a culture of open and honest communication, promoting active listening, and embracing diversity, we can create environments where everyone feels heard and understood. Overcoming these barriers is not simply about improving communication; it's about building stronger relationships, fostering collaboration, and creating a more inclusive and equitable society.









.webp)