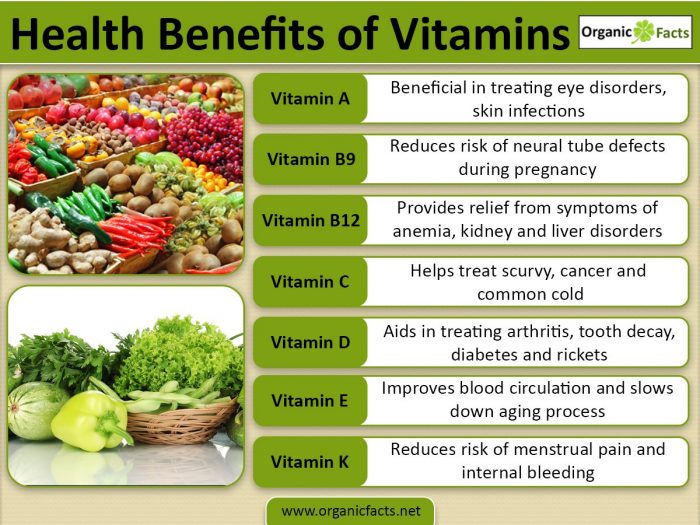
Match The Vitamins With The Health Benefits They Provide.

In an era dominated by health and wellness trends, understanding the crucial role of vitamins and their specific benefits has never been more important. A recent surge in interest regarding the connection between vitamins and their corresponding health impacts has prompted many to seek clarity on this vital topic.
This article aims to provide a clear and concise guide to matching essential vitamins with the health benefits they provide. The information is derived from reputable sources and aims to empower readers to make informed decisions about their nutritional needs.
The Vitamin A to Zinc Overview
Vitamins are organic compounds essential for various bodily functions. They are divided into two main categories: fat-soluble (A, D, E, and K) and water-soluble (B vitamins and C).
Each vitamin plays a unique role, and deficiencies can lead to various health problems. Understanding these roles is vital for maintaining optimal health.
Fat-Soluble Vitamins:
Vitamin A, also known as retinol, is crucial for vision, immune function, and cell growth. It helps maintain healthy skin and mucous membranes, protecting the body from infections. Dietary sources include liver, dairy products, and orange and yellow vegetables like carrots and sweet potatoes.
Vitamin D, often called the "sunshine vitamin," is essential for calcium absorption and bone health. It also supports immune function and may play a role in preventing chronic diseases. Supplementation is often recommended, especially for individuals with limited sun exposure.
Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. It also supports immune function and blood vessel health. Sources include vegetable oils, nuts, and seeds.
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting and bone health. It helps the body produce proteins that are necessary for these processes. Green leafy vegetables like spinach and kale are excellent sources.
Water-Soluble Vitamins:
The B vitamins are a group of eight essential nutrients that play crucial roles in energy metabolism, nerve function, and cell growth. These include thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5), pyridoxine (B6), biotin (B7), folate (B9), and cobalamin (B12).
Each B vitamin has specific functions. For instance, Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation, while folate is vital for cell growth and development, especially during pregnancy.
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a powerful antioxidant that supports immune function, collagen production, and iron absorption. It is found in citrus fruits, berries, and vegetables like broccoli and peppers.
The Significance of Minerals
While not vitamins, minerals are equally crucial for health. Calcium, for example, is not a vitamin, but a vital mineral needed for bone health, muscle function, and nerve transmission.
Iron is essential for carrying oxygen in the blood, and Zinc plays a role in immune function and wound healing. A balanced intake of minerals is essential for overall well-being.
Addressing Deficiencies
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies can lead to various health problems. Vitamin D deficiency, for example, is common and can lead to bone weakness and increased risk of infections.
Iron deficiency can cause anemia, leading to fatigue and weakness. Identifying and addressing deficiencies through diet or supplementation is crucial for maintaining optimal health.
How to Ensure Adequate Intake
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is the best way to ensure adequate vitamin and mineral intake. However, some individuals may benefit from supplementation.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended to determine individual needs and appropriate dosages. Self-treating with high doses of vitamins can be harmful.
The Future of Vitamin Research
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the roles of vitamins and minerals in health and disease prevention. Studies are exploring the potential of vitamins in preventing chronic diseases like heart disease, cancer, and Alzheimer's disease.
Future research may lead to more personalized recommendations for vitamin intake based on individual genetics and lifestyle factors. Stay informed about the latest findings from reputable sources to make evidence-based decisions about your health.
Conclusion
Matching vitamins with their health benefits is essential for making informed decisions about nutrition and well-being. By understanding the roles of different vitamins and minerals, individuals can take proactive steps to optimize their health.
Remember to prioritize a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplementation regimen. Maintaining optimal vitamin and mineral levels is a crucial aspect of a healthy lifestyle.













![Match The Vitamins With The Health Benefits They Provide. [FREE] Match the vitamins with the health benefits - brainly.com](https://media.brainly.com/image/rs:fill/w:750/q:75/plain/https://us-static.z-dn.net/files/d9f/2e595375ca74cf56eac30ff259e18b14.png)



