Natural Gas Composition In Malaysia

Imagine the gentle sway of palm trees against a vibrant sunset in Malaysia, the air thick with humidity and the promise of a bustling evening. Beneath the surface, unseen but vital, flows a resource powering homes, industries, and the nation's economic engine: natural gas. But what exactly makes up this crucial fuel that fuels Malaysia's progress?
Understanding the composition of natural gas in Malaysia is paramount for optimizing energy production, ensuring efficient utilization, and mitigating environmental impact. This article delves into the specific components that make up Malaysia's natural gas reserves, exploring its origin, significance, and the implications for the nation's energy future.
A Deep Dive into Malaysia's Natural Gas Composition
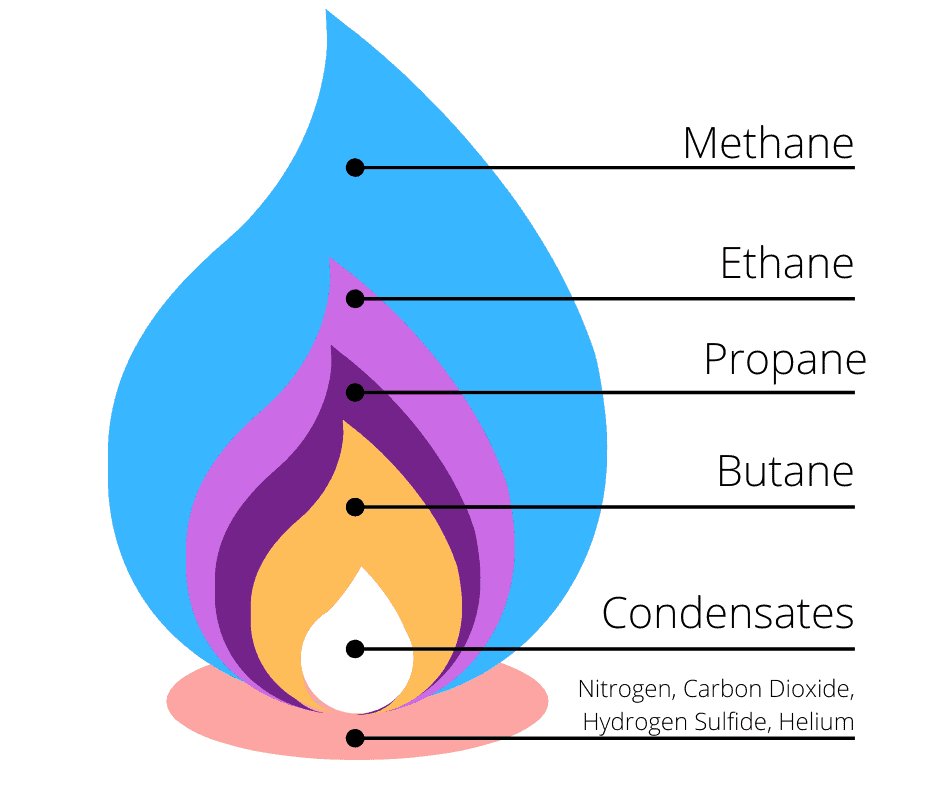
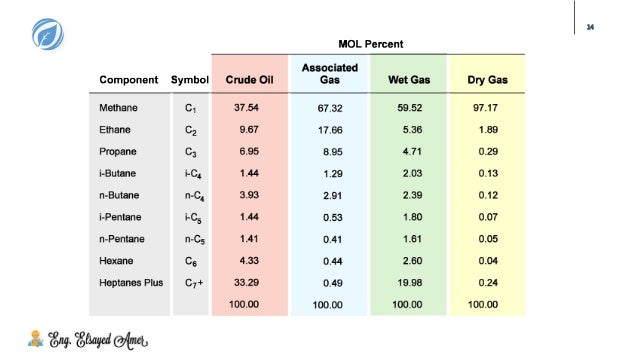
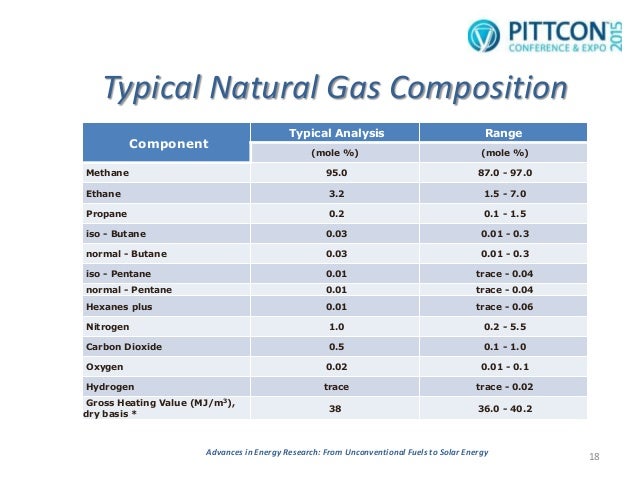
Natural gas, as extracted from the earth, isn't a single, pure substance. Instead, it's a complex mixture of various hydrocarbon gases, with methane (CH4) typically being the dominant component. Other constituents often include ethane, propane, butane, and smaller amounts of heavier hydrocarbons. These components contribute differently to the gas's energy content and properties.
In Malaysia, the composition of natural gas can vary depending on the specific field from which it is extracted. Generally, Malaysian natural gas is considered to be of good quality, with a high methane content, typically ranging from 85% to 95%. This high methane concentration contributes to its high calorific value, making it an efficient energy source.
However, it's crucial to note that natural gas also contains non-hydrocarbon components, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen (N2), hydrogen sulfide (H2S), and water vapor. These impurities can pose operational challenges and environmental concerns, requiring processing and treatment before the gas can be used.
The Significance of Gas Composition
The precise composition of natural gas directly impacts its suitability for various applications. For instance, gas with a high CO2 content requires extensive processing to meet pipeline specifications and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Similarly, the presence of H2S, a toxic and corrosive gas, necessitates specialized removal processes to protect pipelines and equipment, as well as to prevent environmental pollution and health hazards. According to a PETRONAS report, careful monitoring and appropriate treatment technologies are essential.
Moreover, the concentrations of heavier hydrocarbons like ethane, propane, and butane are important determinants of the gas's value. These components can be extracted and processed into valuable petrochemical feedstocks, adding to the economic value of the resource.
The Journey from Reservoir to Consumer
The process of extracting, processing, and delivering natural gas in Malaysia is a complex and sophisticated undertaking. After extraction from onshore and offshore fields, the raw gas undergoes processing at facilities designed to remove impurities and separate the various hydrocarbon components.
These processing plants are critical for ensuring that the natural gas meets the stringent quality standards required for pipeline transportation and end-use applications. These standards are often regulated by the Malaysian Gas Association (MGA) and other relevant authorities.
The treated gas is then transported through an extensive network of pipelines to power plants, industrial facilities, and residential areas across the country. This infrastructure plays a vital role in ensuring a reliable and secure supply of energy to meet Malaysia's growing demands.
Environmental Considerations and Future Trends
While natural gas is considered a cleaner-burning fossil fuel compared to coal and oil, it's not without its environmental challenges. Methane, the primary component of natural gas, is a potent greenhouse gas, and even small leaks during production and transportation can have a significant impact on climate change.
Therefore, there is a growing emphasis on reducing methane emissions through improved leak detection and repair technologies, as well as the development of more efficient gas-powered technologies. Malaysia is committed to reducing its carbon footprint and exploring alternative energy sources.
Looking ahead, Malaysia is also exploring the potential of biogas and other renewable sources to supplement its natural gas supply and further decarbonize its energy sector. This forward-thinking approach is essential for ensuring a sustainable and secure energy future for the nation.
Understanding the composition of Malaysia's natural gas, its processing, and its environmental impact paints a comprehensive picture of this vital resource. It highlights the ongoing efforts to optimize its utilization, mitigate its environmental footprint, and pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable energy future for Malaysia. The careful stewardship of this resource is vital for the nation’s continued progress and prosperity.

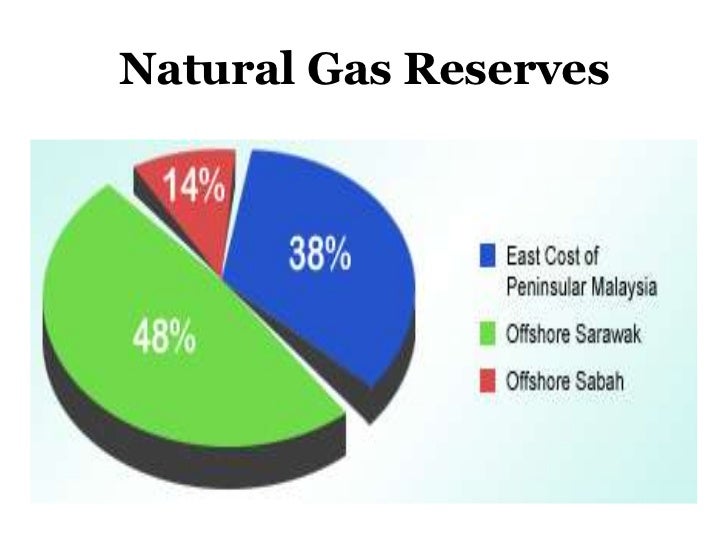





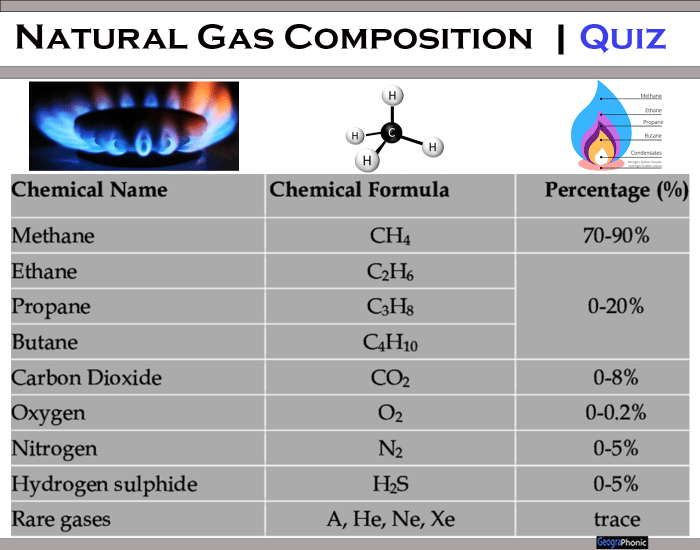





![Natural Gas Composition In Malaysia Composition of natural gas obtained from [7], which may vary depending](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363926619/figure/fig2/AS:11431281087056554@1664454412123/Composition-of-natural-gas-obtained-from-7-which-may-vary-depending-on-the-extraction.png)

