Negative Effects Of Micromanagement
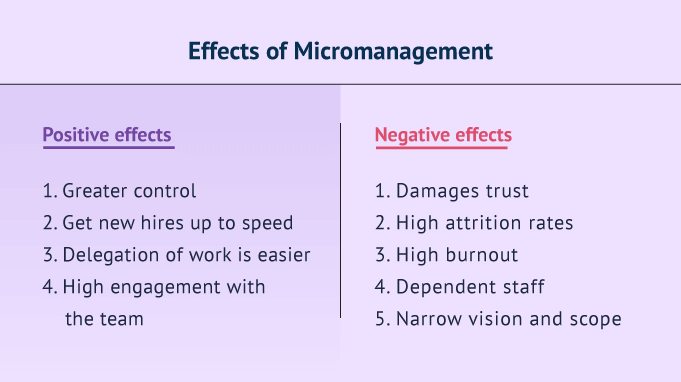
In today's fast-paced work environment, the pressure to deliver results can sometimes lead to management styles that, while seemingly well-intentioned, can have detrimental effects on employees and overall productivity. Micromanagement, characterized by excessive oversight and control, is increasingly being recognized as a significant obstacle to workplace success.
This article examines the negative impacts of micromanagement, drawing on research and expert opinions to illustrate its pervasive effects on employee morale, productivity, and organizational health. Understanding these consequences is crucial for businesses seeking to foster a positive and thriving work environment.
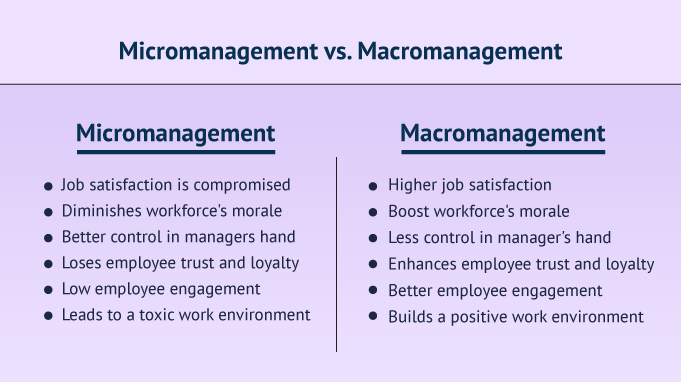
The Stifling Effects on Employee Morale
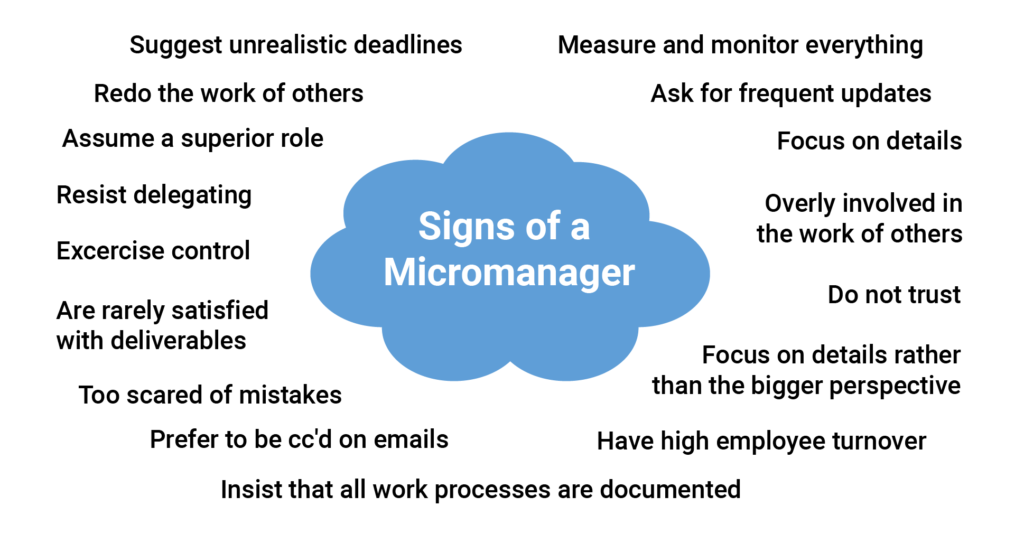
Micromanagement fundamentally undermines employee autonomy and trust. Constant scrutiny and second-guessing can lead to feelings of inadequacy and disempowerment. This erosion of trust often translates into decreased job satisfaction and increased stress levels, according to a 2023 study by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM).
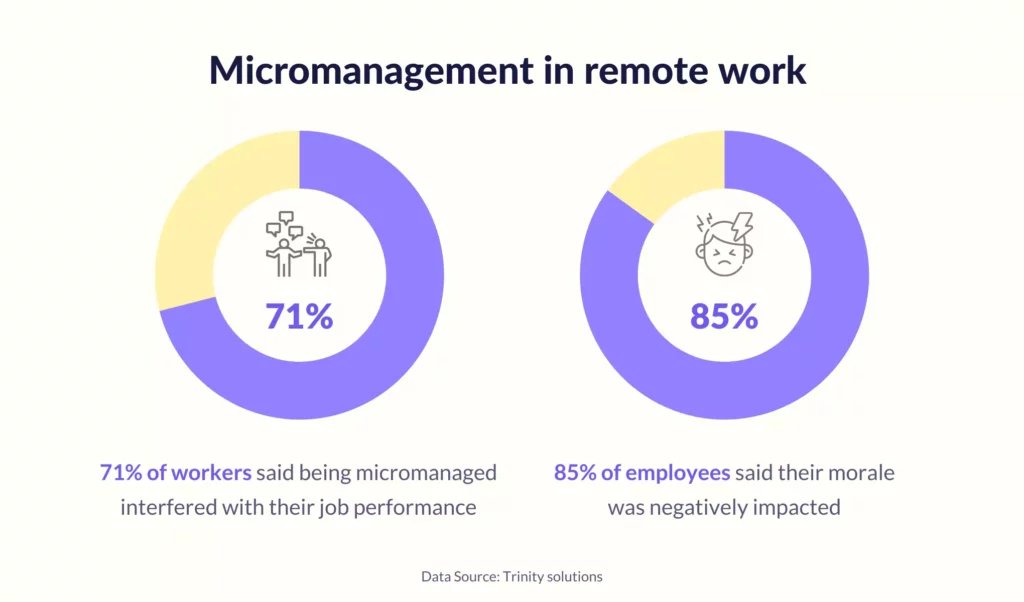
Employees subjected to micromanagement often feel undervalued and unappreciated. The perception that their skills and judgment are not respected can lead to resentment and a decline in their commitment to the organization. A sense of being constantly watched can stifle creativity and innovation, hindering employees from taking initiative and exploring new ideas.
Diminished Productivity and Efficiency
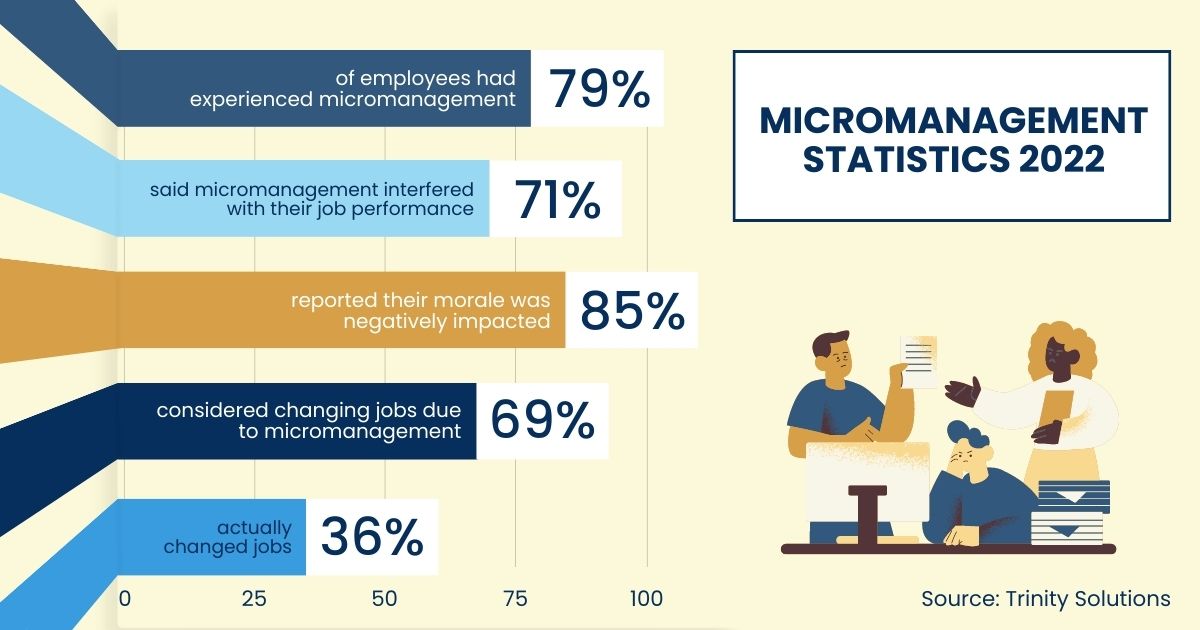
Contrary to its intended purpose, micromanagement frequently leads to decreased productivity. Employees spend more time worrying about adhering to minute details dictated by their managers than focusing on the overall goals of their tasks. According to a Gallup poll, employees who feel micromanaged are less likely to be engaged and productive.
The constant need for approval and the lack of autonomy can slow down decision-making processes. Simple tasks become bottlenecks as employees wait for their managers to sign off on every step. This inefficiency can significantly impact project timelines and overall organizational performance.
Furthermore, micromanagement can foster a culture of dependency, where employees become hesitant to make independent decisions. This lack of self-reliance not only hinders productivity but also limits the growth and development of employees' skills.
Increased Employee Turnover and Absenteeism
The negative impacts of micromanagement extend beyond individual performance, contributing to higher rates of employee turnover. Employees who feel suffocated and undervalued are more likely to seek employment opportunities elsewhere. The cost of replacing and retraining employees can be substantial, placing a significant financial burden on organizations.
Moreover, the stress and anxiety associated with micromanagement can lead to increased absenteeism. Employees experiencing burnout and dissatisfaction may take more sick days, impacting team dynamics and overall productivity. This cycle of stress, absenteeism, and turnover can create a toxic work environment that is difficult to reverse.
"Micromanagement is a symptom of a deeper problem – a lack of trust and delegation skills," says Dr. Anya Sharma, a leading organizational psychologist.
Cultivating a Culture of Trust and Empowerment
To mitigate the negative effects of micromanagement, organizations must prioritize building a culture of trust and empowerment. Managers should focus on setting clear goals and expectations while allowing employees the autonomy to determine how best to achieve them. Regular feedback and open communication are essential for fostering a supportive and collaborative work environment.
Investing in leadership training can equip managers with the skills necessary to delegate effectively and provide constructive feedback. By empowering employees and trusting their abilities, organizations can unlock their full potential and create a more engaged and productive workforce. This shift requires a conscious effort to move away from control and towards support, recognizing that a thriving work environment is built on trust, respect, and open communication.
In conclusion, micromanagement is a counterproductive practice that can have far-reaching negative consequences for employees and organizations alike. By fostering a culture of trust and empowerment, businesses can create a more positive and productive work environment, ultimately leading to greater success and sustainability.

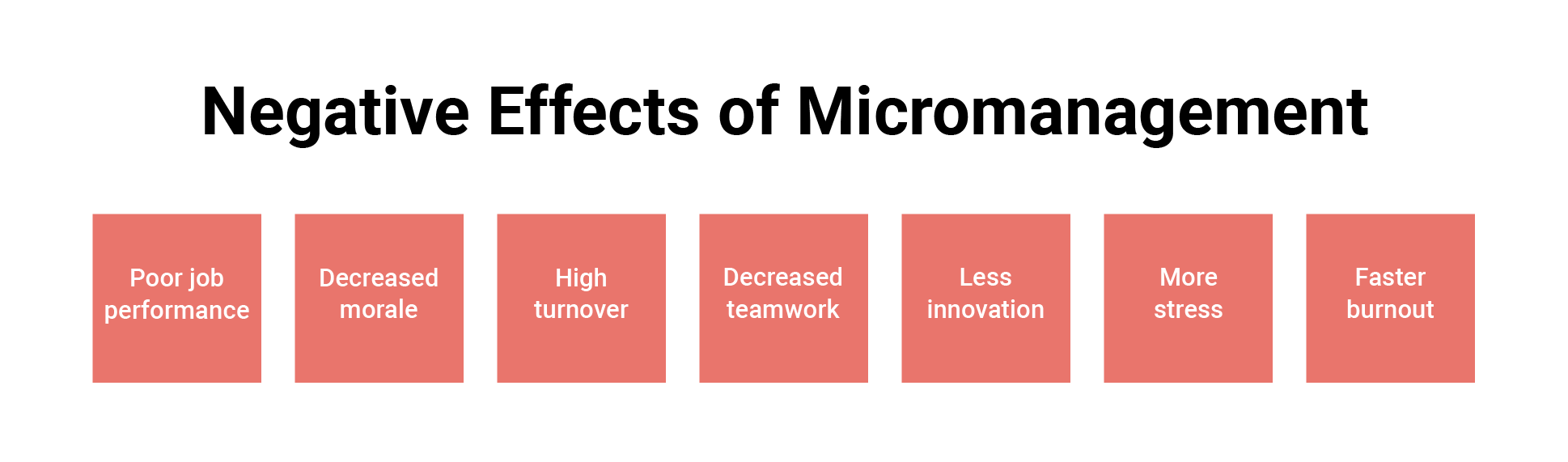
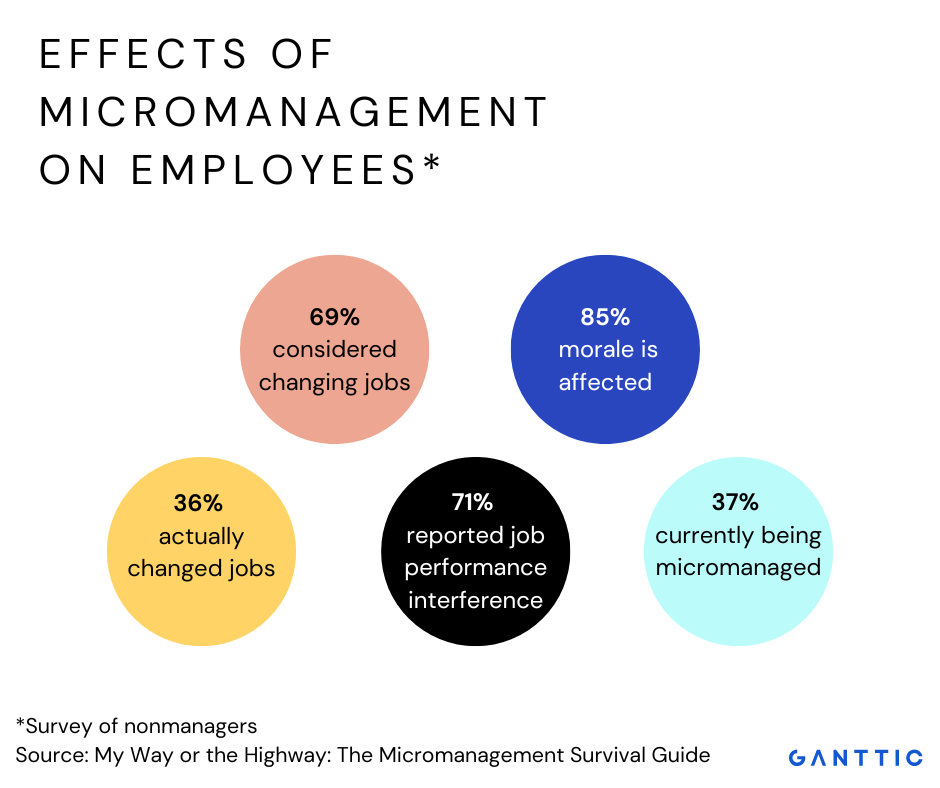




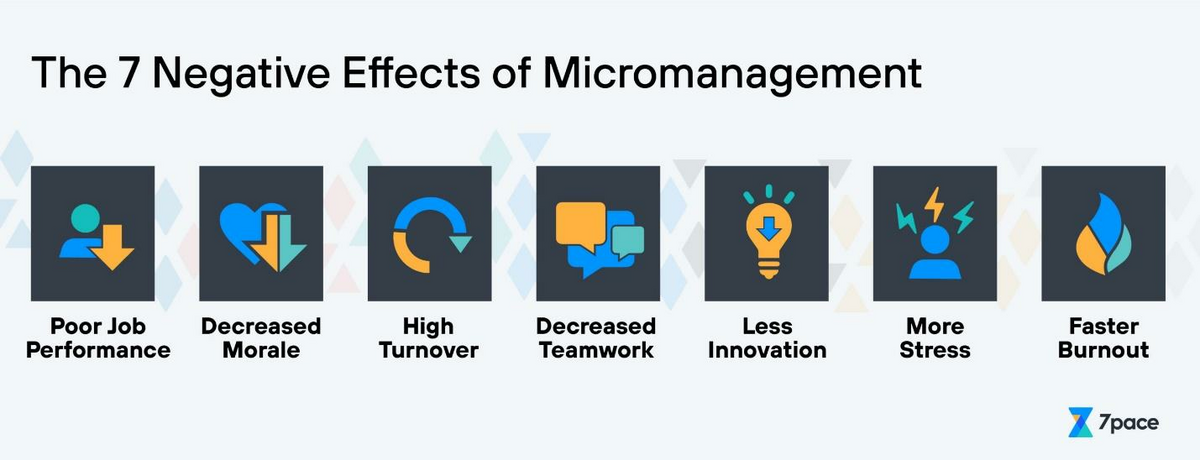





![Negative Effects Of Micromanagement The Negative Effects of Micromanagement [How Micromanaging Hurts]](https://www.teamly.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Negative-effects-of-micromanagement.png)
