Of The Following Nutrients Which Contains Nitrogen
The air we breathe, the food we consume, and the very fabric of life are inextricably linked to a single, crucial element: nitrogen. Its presence, or absence, can dictate the health of ecosystems, the productivity of agriculture, and even the stability of our climate.
But where exactly does this vital element reside within the nutrients we ingest? Understanding the answer to this question is paramount for anyone seeking to optimize their diet, comprehend the fundamentals of plant nutrition, or grapple with the complexities of global food security.
This article delves into the realm of essential nutrients to pinpoint which among them harbors the power of nitrogen, exploring its critical role in building blocks of life.
The Core Question: Identifying Nitrogen-Containing Nutrients
The key nitrogen-containing nutrients are amino acids, the building blocks of proteins, and nucleic acids, which include DNA and RNA.
While other nutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and vitamins are crucial for health, they generally do not contain nitrogen as part of their chemical structure.
Therefore, when asked which of the nutrients contains nitrogen, the answer invariably points to proteins and nucleic acids, highlighting their unique and indispensable role in living organisms.
Amino Acids and Proteins: The Nitrogen Backbone
Proteins are complex molecules essential for virtually all biological processes. They function as enzymes, hormones, structural components, and antibodies.
These complex molecules are built from smaller units called amino acids, each containing an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) attached to a central carbon atom.
The presence of the amino group (-NH2) is what defines an amino acid and what introduces nitrogen into the structure of the protein.
Nucleic Acids: The Blueprint of Life
Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA contains the instructions for building and operating an organism, while RNA helps carry out these instructions.
These complex molecules are composed of nucleotides, each containing a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine or uracil), a sugar molecule (deoxyribose or ribose), and a phosphate group.
The nitrogenous bases are what give nucleic acids their nitrogen content. These bases are ring-shaped structures composed of carbon and nitrogen atoms.
Why Nitrogen Matters: Biological Significance
Nitrogen is not merely a component of proteins and nucleic acids; it plays a crucial role in their functions.
For example, the nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA are essential for coding genetic information, and the amino groups in amino acids are involved in forming peptide bonds that link these building blocks together to form proteins.
Furthermore, nitrogen is a key component of many other biologically important molecules, including chlorophyll (essential for photosynthesis) and certain vitamins and hormones.
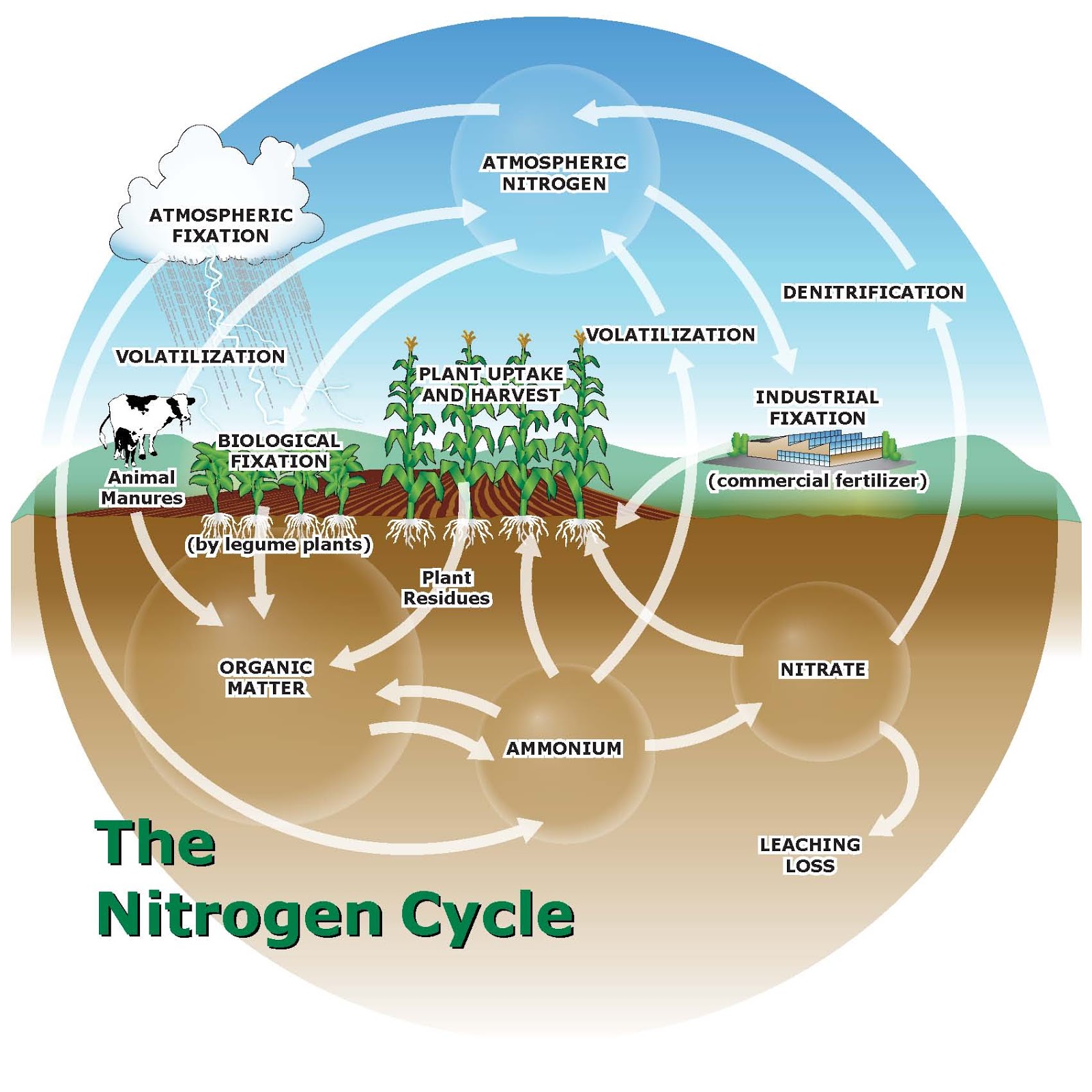
Nitrogen in Agriculture: A Crucial Nutrient for Plant Growth
Beyond its role in animal and human nutrition, nitrogen is a critical nutrient for plant growth. Plants require nitrogen to synthesize proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll.
Nitrogen deficiency can lead to stunted growth, yellowing of leaves, and reduced crop yields. Consequently, nitrogen fertilizers are widely used in agriculture to enhance plant growth and productivity.
However, the overuse of nitrogen fertilizers can have negative environmental consequences, such as water pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
"Sustainable nitrogen management is crucial for balancing the need for food production with the protection of the environment," - Dr. Emily Carter, Environmental Scientist at Stanford University.
Beyond Basic Nutrition: Advanced Perspectives
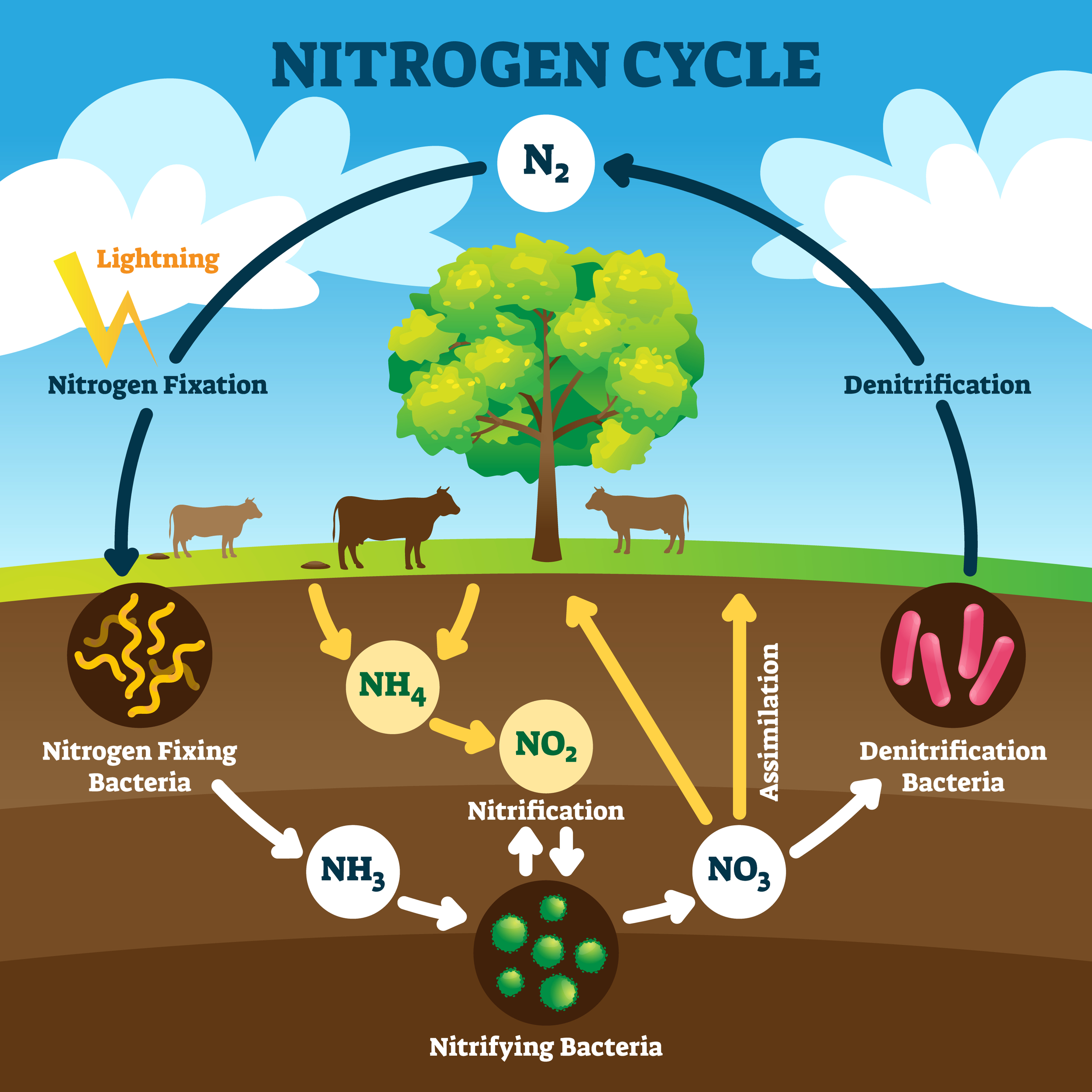
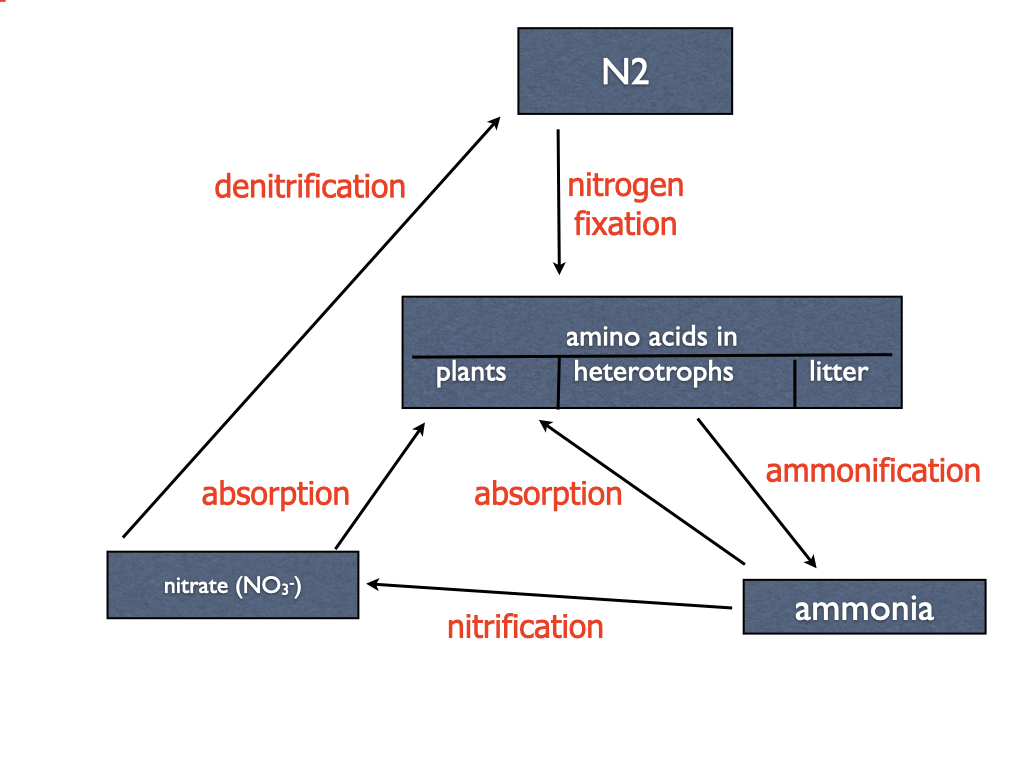
The discussion surrounding nitrogen-containing nutrients extends into more complex areas of study, like metabolic pathways and the nitrogen cycle.
Understanding how the body processes nitrogen from proteins and nucleic acids is crucial for managing conditions like kidney disease, where nitrogen waste products can accumulate in the blood.
Furthermore, comprehending the nitrogen cycle, which involves the conversion of nitrogen between different forms in the environment, is critical for addressing environmental challenges like nitrogen pollution and climate change.
Different dietary patterns can also impact nitrogen balance within the body. For example, high-protein diets can increase nitrogen excretion, while low-protein diets may lead to nitrogen deficiency.
Vegans and vegetarians need to ensure they consume a balanced diet with sufficient plant-based proteins to meet their nitrogen requirements.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Nitrogen Research
Research into nitrogen-containing nutrients is ongoing, with a focus on developing more efficient and sustainable ways to manage nitrogen in agriculture and human health.
Scientists are exploring new types of nitrogen fertilizers that release nitrogen more slowly, reducing the risk of water pollution. They are also investigating ways to improve nitrogen use efficiency in crops, minimizing the need for fertilizer application.
In human health, researchers are studying the role of nitrogen-containing compounds in various diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.
By further understanding the intricate relationship between nitrogen and life, we can develop innovative solutions for enhancing food security, protecting the environment, and improving human health.
Ultimately, recognizing that proteins and nucleic acids are the key nitrogen-containing nutrients serves as a foundational step towards a deeper understanding of biology, agriculture, and environmental science.