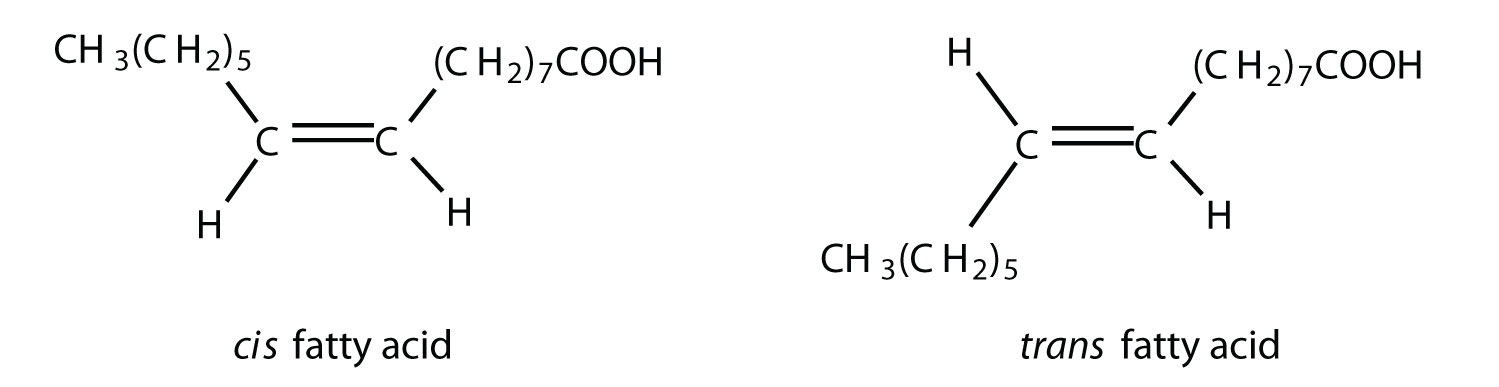What Is The General Formula For Fatty Acids
Breaking: Scientists have confirmed the definitive general formula for fatty acids, a crucial component of biological life. Understanding this formula is paramount for advancements in medicine, nutrition, and industrial chemistry.
This announcement provides researchers worldwide with a solid foundation for predicting and manipulating the behavior of these essential molecules. The formula clarifies the structure and properties of fatty acids, influencing everything from drug development to food production.
The Core Formula: Unveiled
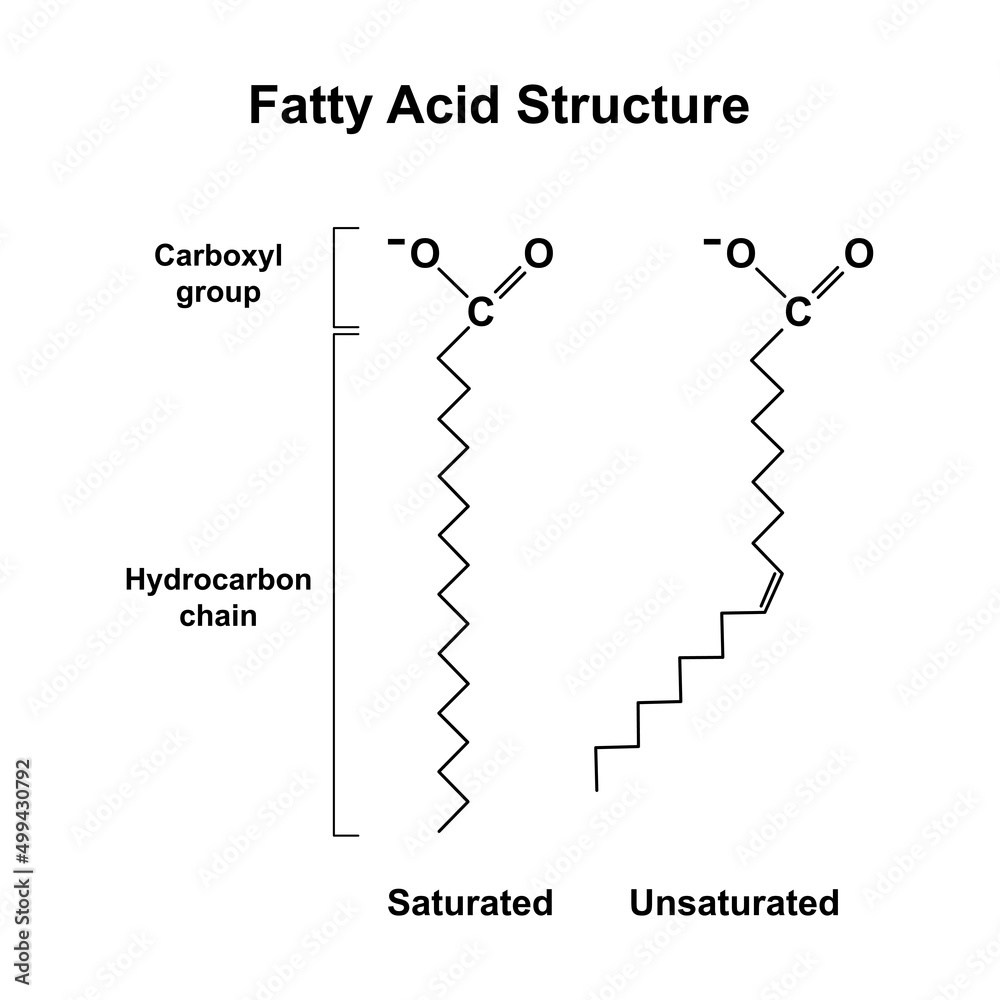
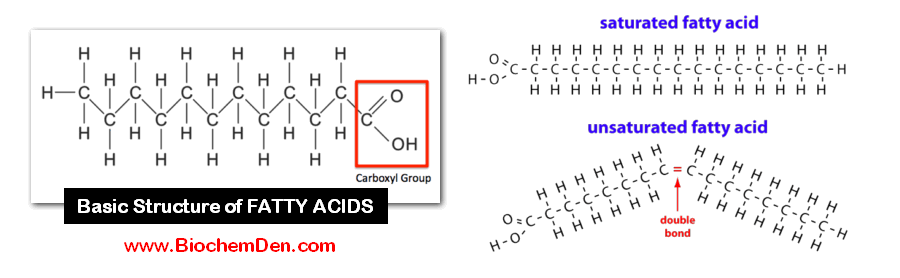
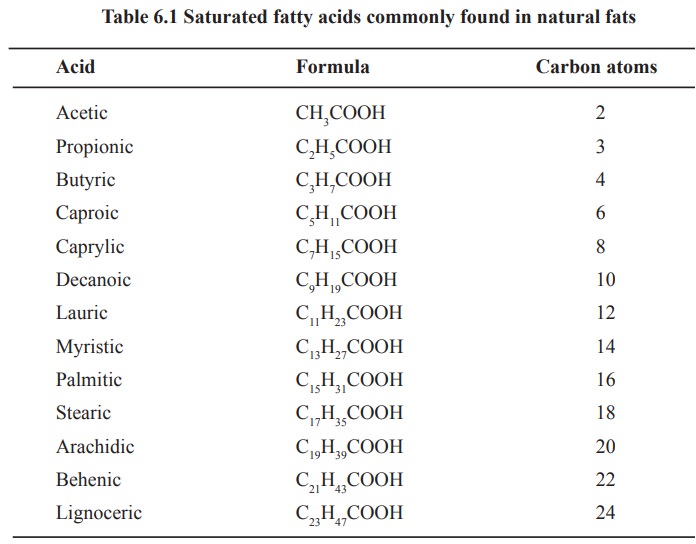
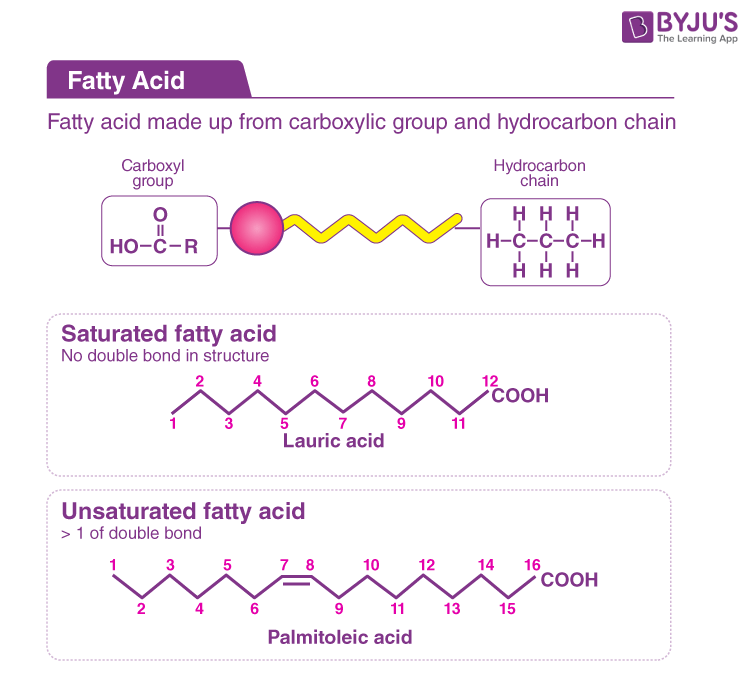
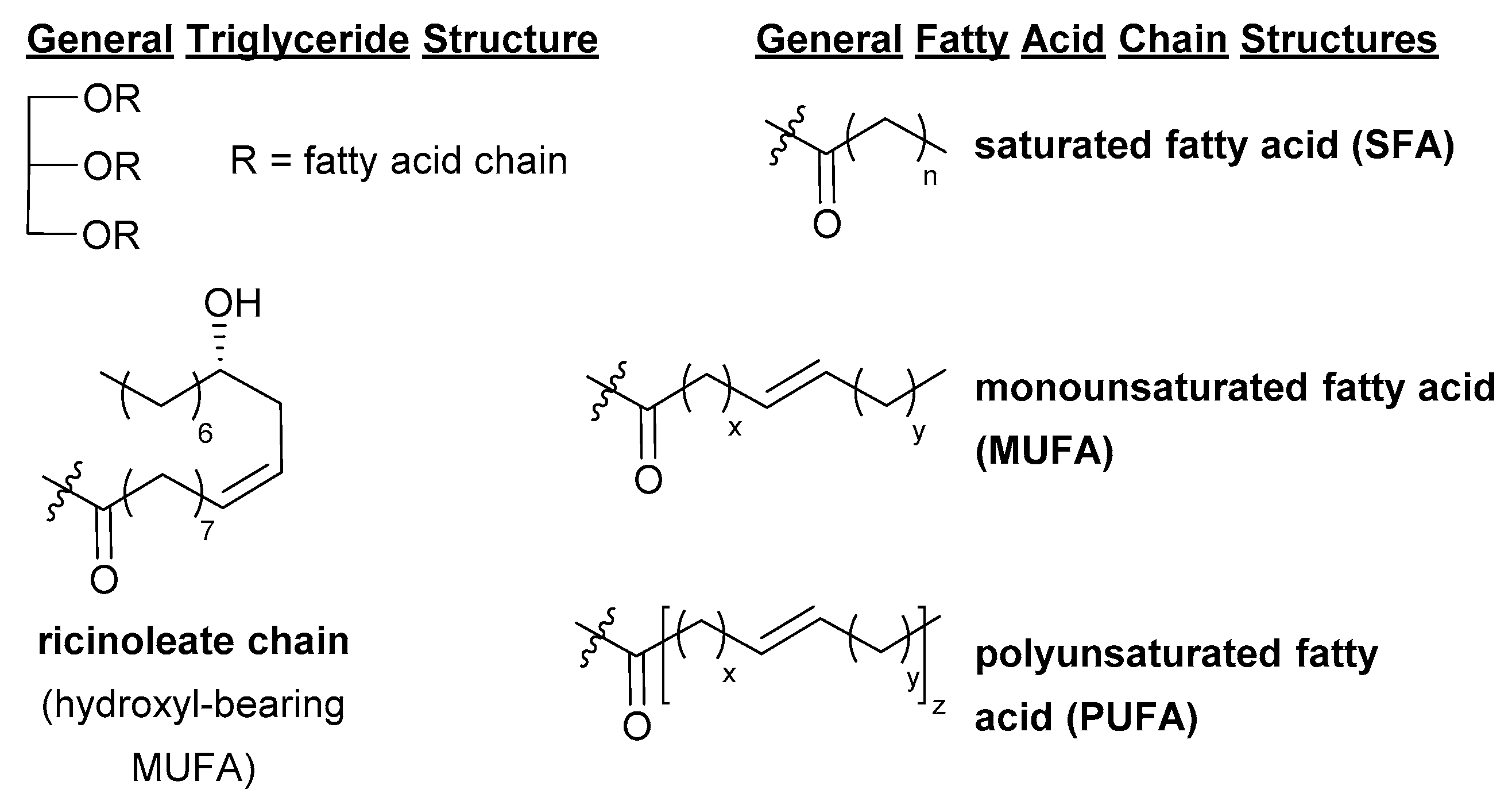
The general formula for a fatty acid is CH3(CH2)nCOOH. This structure represents a hydrocarbon chain (CH3(CH2)n) with a carboxyl group (COOH) at one end.
Here's a breakdown:
- CH3: Represents the methyl group at one end of the chain.
- (CH2)n: Denotes a repeating methylene unit, where 'n' indicates the number of these units. This determines the chain length.
- COOH: Represents the carboxyl group, which imparts acidic properties.
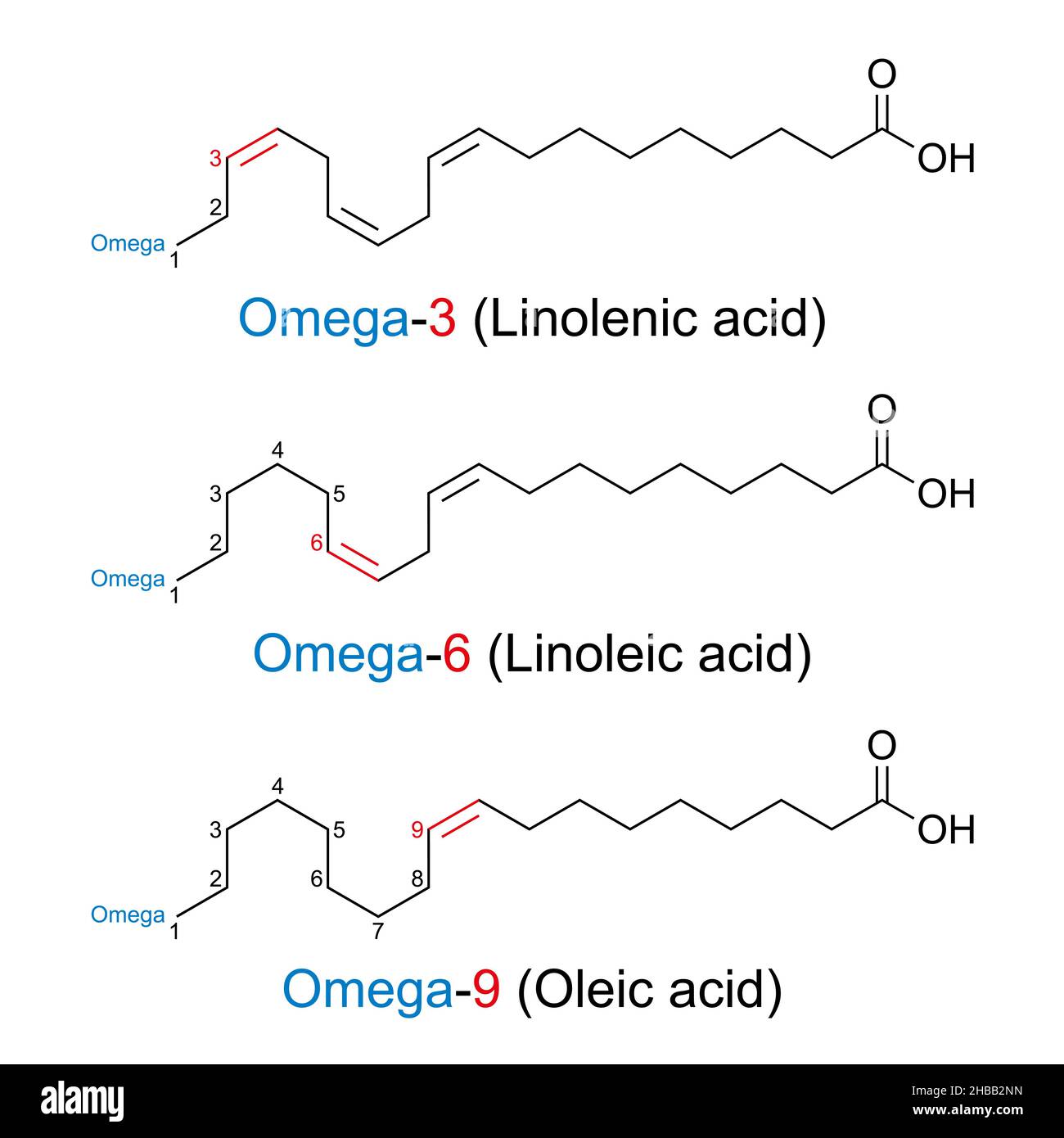
Variations exist in the chain length ('n' value) and the presence of double bonds within the hydrocarbon chain, leading to saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Saturated vs. Unsaturated: Key Differences
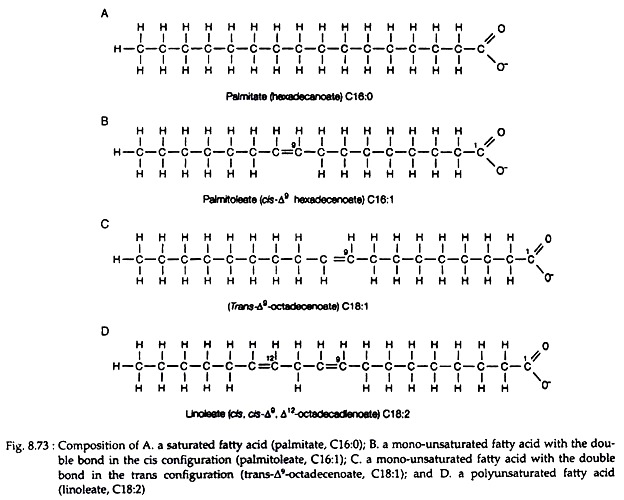
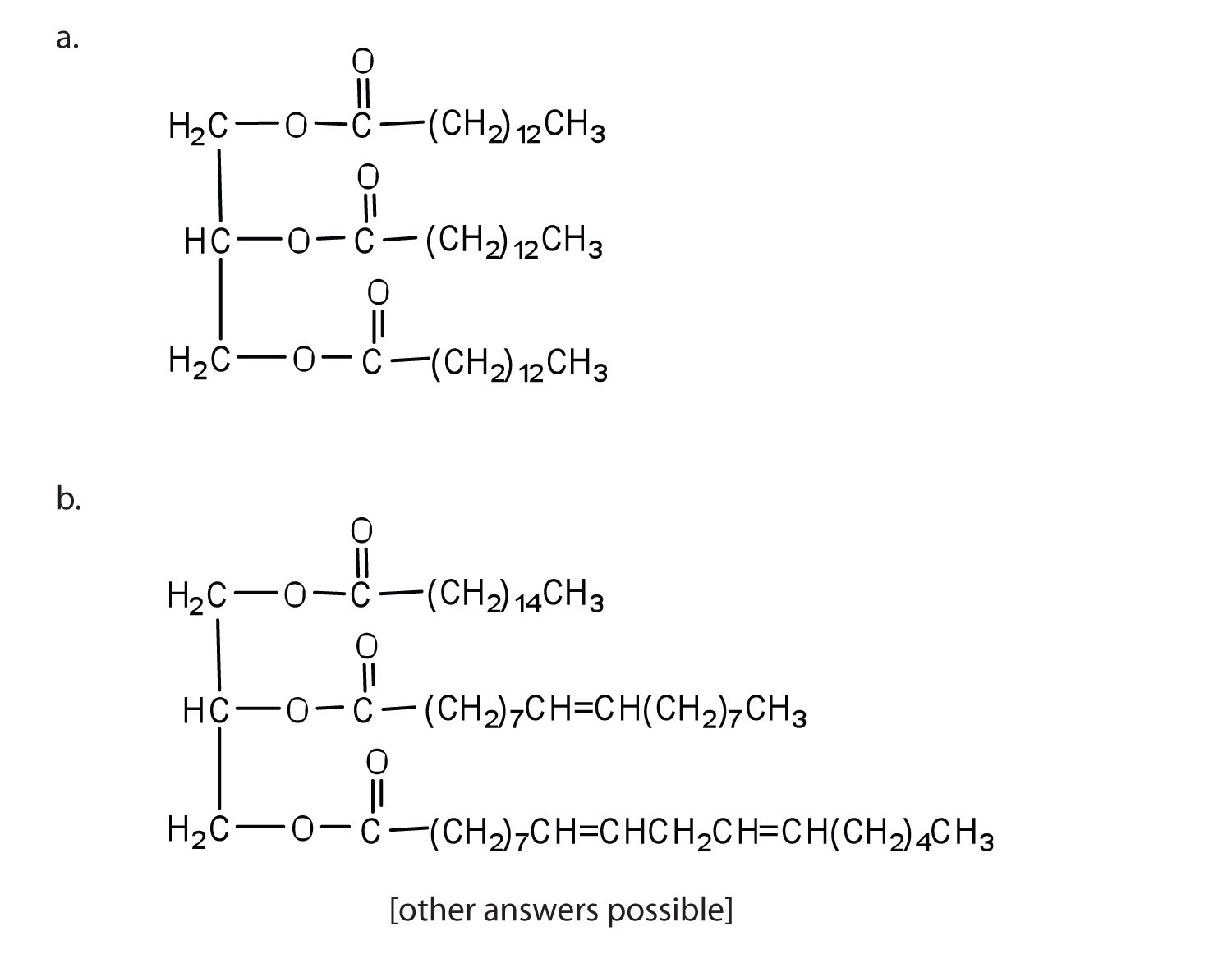
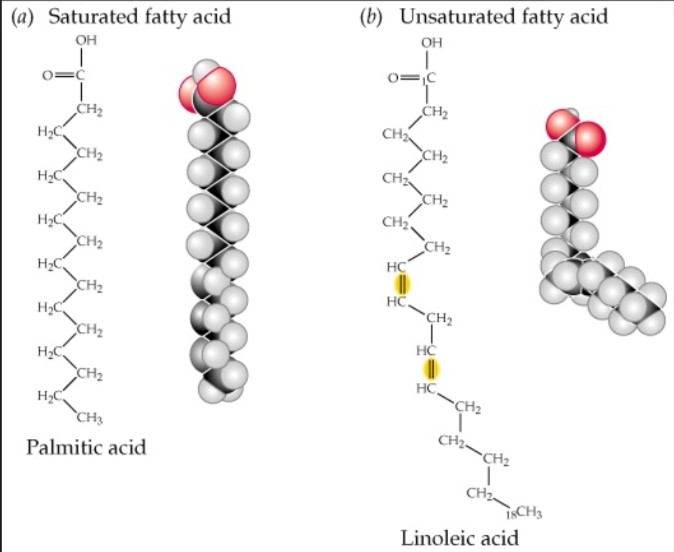
Saturated fatty acids contain only single bonds between carbon atoms in the hydrocarbon chain. This allows them to pack tightly together, making them solid at room temperature (e.g., butter, lard).
Unsaturated fatty acids, on the other hand, contain one or more double bonds. These double bonds create kinks in the chain, preventing tight packing and resulting in liquids at room temperature (e.g., olive oil, sunflower oil).
Monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs) have one double bond, while polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) have multiple double bonds.
The Significance of Chain Length ('n' Value)
The 'n' value in the formula directly correlates to the length of the fatty acid. Common fatty acids range from 4 to 28 carbon atoms in length.
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), typically with fewer than six carbon atoms, are produced by gut bacteria during fermentation. They play a vital role in gut health.
Long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs) are more common in the diet and are essential for energy storage and cell membrane structure. The specific 'n' value dictates their physical and chemical properties.
Where and When Was This Determined?
While the core formula has been established for decades through extensive research, advancements in analytical techniques like mass spectrometry and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) have refined our understanding. These techniques confirm the structure and allow for precise determination of fatty acid composition in complex samples.
Research institutions worldwide, including leading universities and pharmaceutical companies, contribute to this ongoing process. Data is continuously gathered and validated through peer-reviewed publications.
These determinations are ongoing as new fatty acids are discovered and characterized. The core principle of CH3(CH2)nCOOH, however, remains the foundation.
Impact on Health and Industry
Understanding the fatty acid formula allows scientists to design targeted therapies for diseases like cardiovascular disease and obesity. It also aids in developing functional foods with specific health benefits.
In industry, this knowledge is crucial for producing biofuels, lubricants, and various chemical products. Modified fatty acids are increasingly used in sustainable materials.
This foundational formula empowers research into the role of different fatty acids in human health and their potential applications across diverse fields.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research
Current research focuses on identifying novel fatty acids and understanding their specific roles in complex biological systems. Scientists are exploring the impact of dietary fatty acids on gene expression and disease risk.
Future endeavors include developing more sophisticated analytical techniques to characterize fatty acid isomers and understand their subtle differences in biological activity. The ultimate goal is to harness the power of fatty acids for improved health and sustainable technologies.
Ongoing analysis of how variations in the basic CH3(CH2)nCOOH structure affect biological pathways will continue to drive innovation in the years to come. Stay tuned for further updates as this vital area of research evolves.