Once The Estimated Depreciation Expense For An Asset Is Calculated:
Businesses nationwide face critical accounting adjustments following a recent IRS directive regarding depreciation expense calculations. Errors could lead to substantial financial penalties and restatements.
This urgent notification addresses the necessary steps companies must take after calculating the estimated depreciation expense for an asset. Incorrect handling can trigger audits and legal repercussions.
Depreciation Expense Calculation: Post-Calculation Procedures
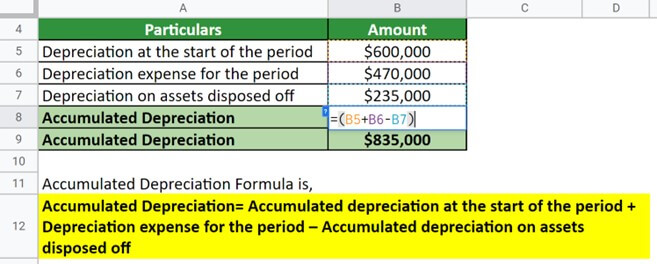
Once the estimated depreciation expense for an asset is calculated, it must be accurately recorded in the company's financial statements. This typically involves debiting the depreciation expense account and crediting the accumulated depreciation account.
The IRS mandates that companies maintain detailed records supporting their depreciation calculations. These records should include the asset's cost, estimated salvage value, useful life, and the depreciation method used.
Impact on Financial Statements
Depreciation expense directly impacts the company's income statement, reducing net income. Accumulated depreciation, on the other hand, affects the balance sheet by reducing the asset's book value.
Failure to accurately reflect depreciation can distort a company's profitability and asset valuation. This misrepresentation can have serious consequences for investors and stakeholders.
According to a recent SEC filing, "Material misstatements related to depreciation expense can trigger regulatory scrutiny and potential legal action."
Choosing the Right Depreciation Method
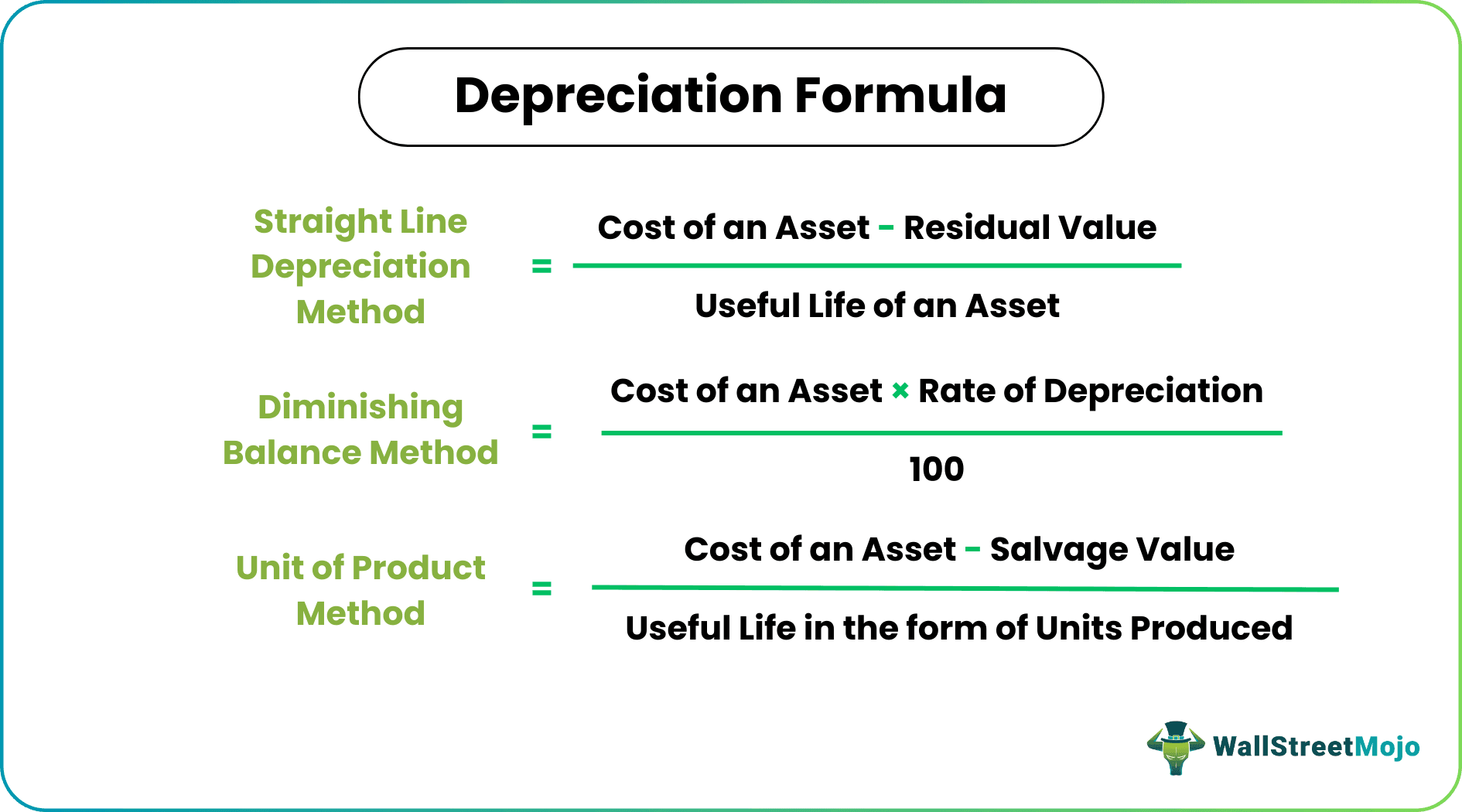
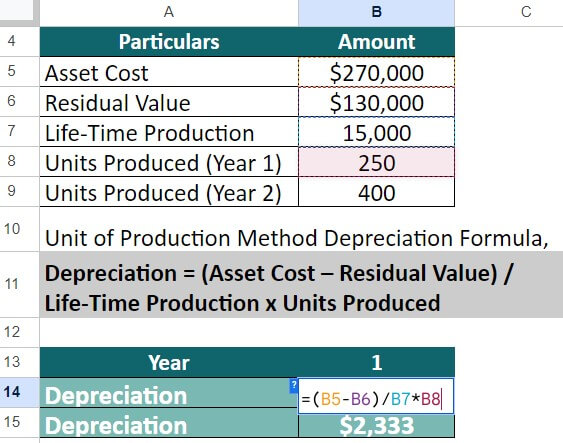
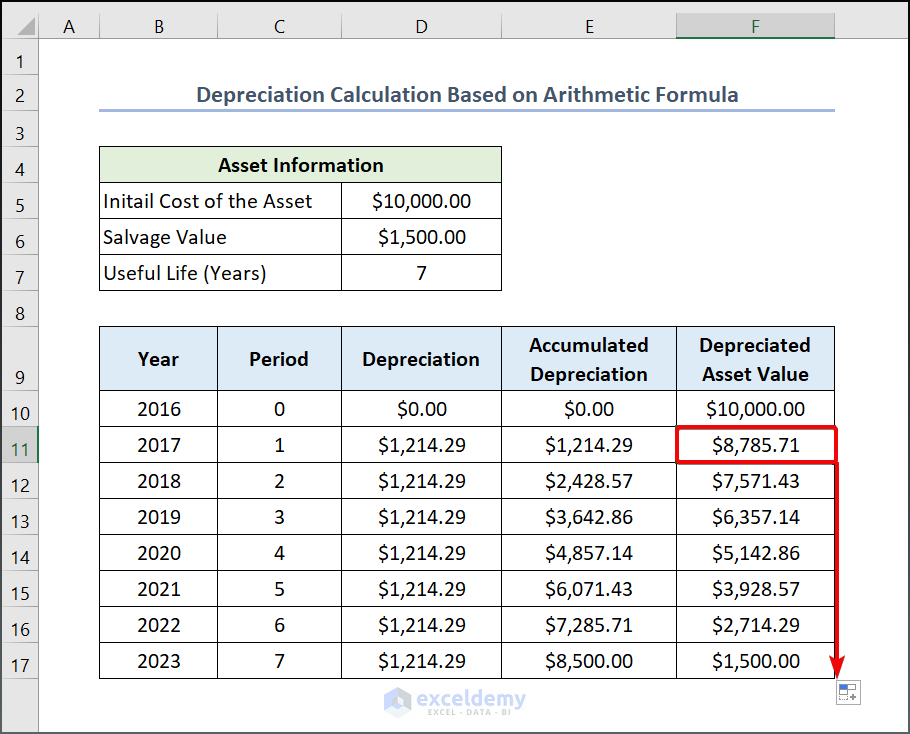
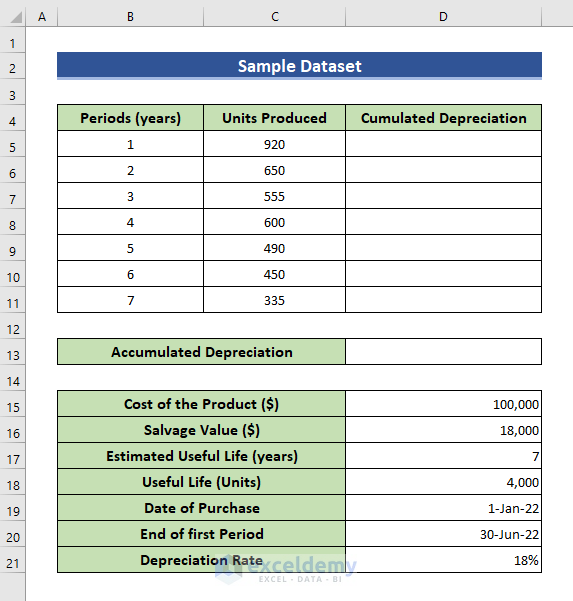
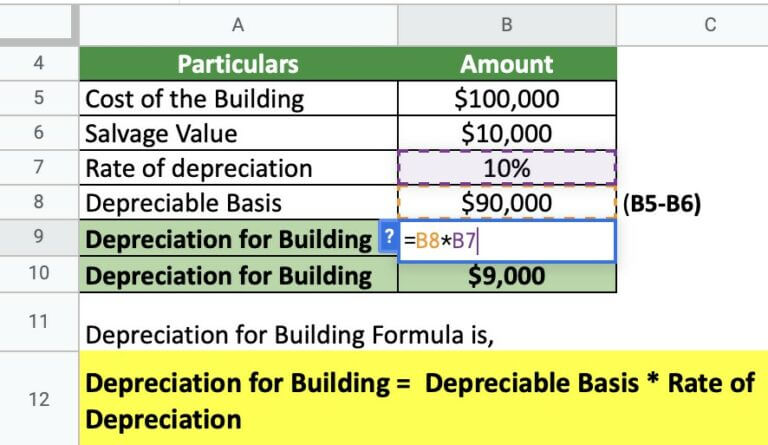
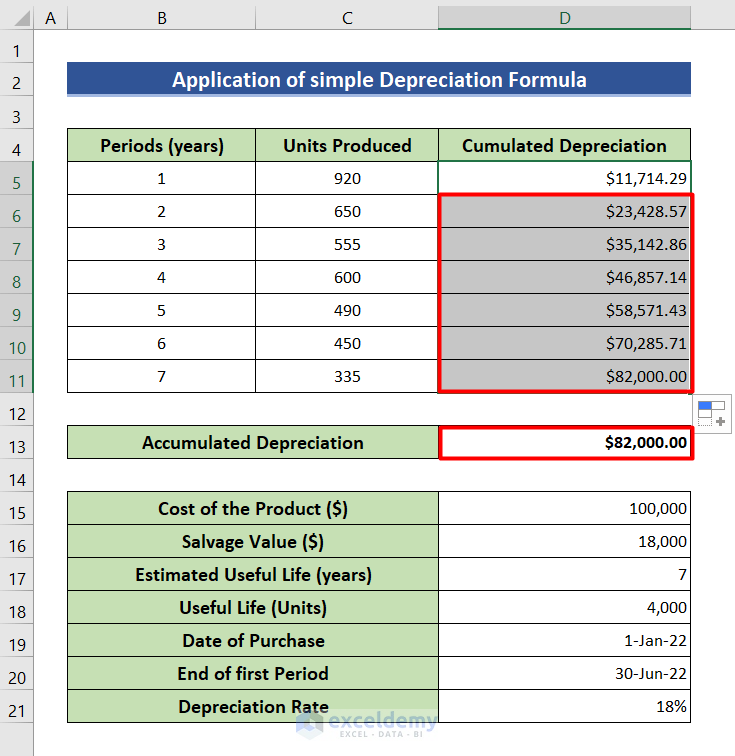
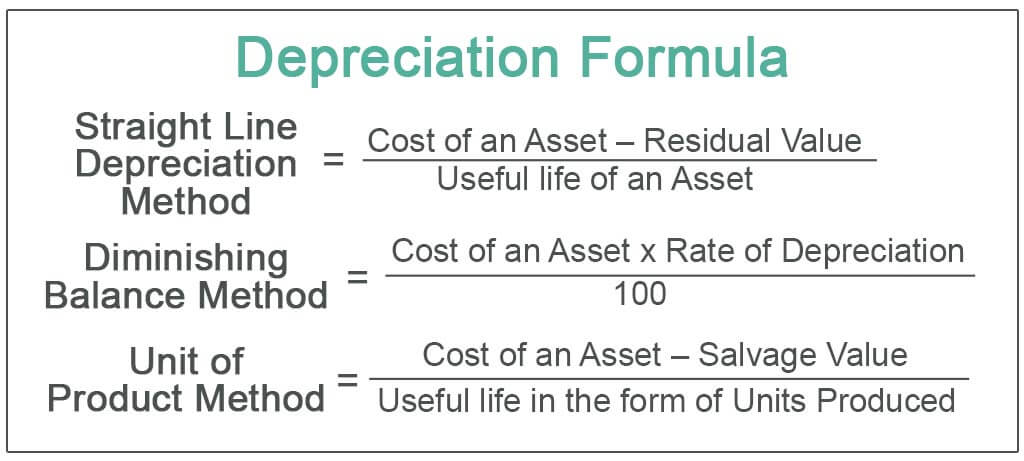
Selecting the appropriate depreciation method is crucial. Common methods include straight-line, declining balance, and units of production.
The chosen method should reflect the pattern in which the asset's economic benefits are consumed. Incorrect method selection can lead to inaccuracies and compliance issues.
Expert Tip: Consult with a qualified accountant or tax advisor to determine the most suitable depreciation method for your assets.
Common Errors and Pitfalls
One common error is failing to update depreciation calculations when there are changes in the asset's useful life or salvage value. Such updates are essential for maintaining accuracy.
Another pitfall is neglecting to properly document the rationale behind the chosen depreciation method and its application. Thorough documentation is crucial for defending against potential audits.
Ignoring the impact of impairments on asset value can also lead to misstated depreciation expense. Impairments should be recognized and factored into future calculations.
Software and Tools for Depreciation Calculation
Several software and online tools can streamline the depreciation calculation process. These tools automate calculations and help ensure accuracy.
Popular options include QuickBooks, Sage Intacct, and specialized fixed asset management software. Using these tools can reduce the risk of errors and improve efficiency.
When selecting software, ensure that it complies with relevant accounting standards and tax regulations. Compatibility with your existing financial systems is also important.
Auditing and Compliance Considerations
Depreciation expense is often a target area during audits. Auditors will scrutinize the company's depreciation policies, calculations, and documentation.
Maintaining accurate and complete records is essential for demonstrating compliance with accounting standards and tax laws. Proactive compliance measures can prevent costly penalties and legal issues.
Companies should regularly review their depreciation practices to identify and correct any potential errors. Internal controls can help ensure ongoing compliance.
Real-World Examples of Depreciation Errors
In 2022, XYZ Corporation was fined $5 million by the IRS for misstating depreciation expense related to its manufacturing equipment. The error stemmed from an incorrect application of the declining balance method.
ABC Company faced a shareholder lawsuit after it was discovered that the company had overstated its net income by understating depreciation expense. The lawsuit alleged that the company had misled investors about its financial performance.
These examples highlight the significant financial and legal risks associated with incorrect depreciation calculations.
Next Steps and Ongoing Developments
Companies should immediately review their current depreciation policies and procedures. Correct any identified errors and ensure that all calculations are accurate and well-documented.
Stay informed about changes in accounting standards and tax regulations related to depreciation. Consult with qualified professionals to ensure ongoing compliance.
The IRS is expected to release further guidance on depreciation calculations in the coming months. Monitor these developments and adjust your practices accordingly.