Open-market Operations Consist Of The Buying And Selling Of

Imagine a bustling marketplace, but instead of fruits and vegetables, the items traded are government securities. It's a place where the fate of interest rates and the overall economy hangs in the balance, all orchestrated with the precision of a seasoned conductor leading an orchestra. Welcome to the world of open-market operations, a critical tool used by central banks to steer the economic ship.
At its heart, open-market operations consist of the buying and selling of government securities in the open market by a central bank, like the Federal Reserve in the United States. This seemingly simple action has profound implications, influencing short-term interest rates and the availability of credit, ultimately shaping economic growth and inflation.
The Nuts and Bolts of Open-Market Operations
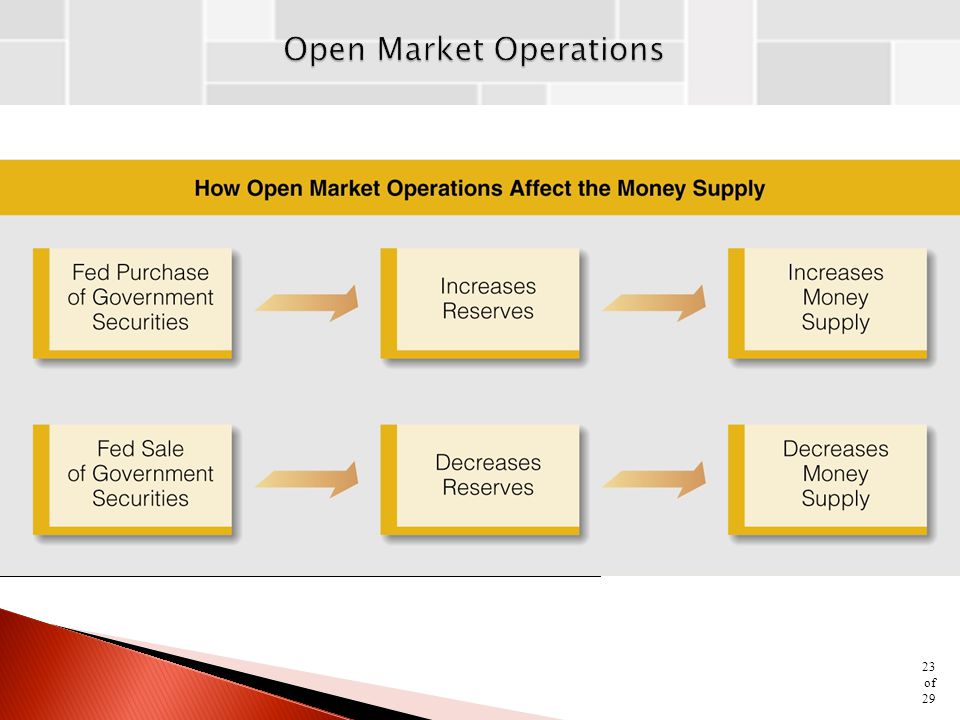
To truly understand the power of open-market operations, it's essential to delve into the mechanics. When the central bank buys government securities (like Treasury bonds) from commercial banks and other institutions, it injects money into the banking system.
This increases the reserves available to banks, allowing them to lend more money to businesses and consumers. Conversely, when the central bank sells government securities, it drains money from the banking system, reducing reserves and limiting lending capacity.
This ebb and flow of liquidity directly impacts the federal funds rate, the target rate the Federal Reserve aims to control. By manipulating the supply of reserves, the Fed can nudge the federal funds rate up or down, influencing a ripple effect throughout the economy.
A Historical Perspective
The use of open-market operations as a primary monetary policy tool evolved over time. Prior to the 1920s, central banks often relied on other methods, such as directly setting interest rates or changing reserve requirements.
However, the flexibility and precision offered by open-market operations gradually made it the preferred method. The Great Depression highlighted the need for more active and responsive monetary policy, solidifying the role of open-market operations in economic management.
According to "Purposes and Functions" from the Federal Reserve, open market operations became the primary tool to regulate the money supply in the latter half of the twentieth century.
Why Are Open-Market Operations So Important?
The impact of open-market operations extends far beyond the financial markets. By influencing interest rates and credit conditions, these operations play a crucial role in managing economic growth, inflation, and employment.
When the economy is slowing down, the central bank can lower interest rates by buying government securities. This encourages borrowing and investment, stimulating economic activity and creating jobs.
Conversely, when inflation is rising too rapidly, the central bank can raise interest rates by selling government securities. This dampens demand, helping to control price increases and maintain economic stability.
Responding to Economic Challenges
The effectiveness of open-market operations has been particularly evident during times of economic crisis. During the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve aggressively used open-market operations to inject liquidity into the financial system and prevent a complete collapse of the banking sector.
They purchased massive amounts of government securities and mortgage-backed securities, providing crucial support to struggling institutions and helping to stabilize the economy. This unconventional use of open-market operations, known as quantitative easing, demonstrated the flexibility and adaptability of this policy tool.
More recently, during the COVID-19 pandemic, open-market operations were once again deployed to support the economy. The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates to near zero and purchased trillions of dollars in government securities to ensure that credit remained available to businesses and households.
The Human Impact
The seemingly abstract world of open-market operations has a tangible impact on everyday lives. Lower interest rates can make it more affordable to buy a home, start a business, or finance education.
Stable prices can help protect the purchasing power of savings and wages, ensuring that families can afford essential goods and services. Strong economic growth can create job opportunities and raise living standards.
While the effects of open-market operations are often indirect, they play a critical role in creating a stable and prosperous economic environment for individuals and communities.
Limitations and Considerations
Despite their effectiveness, open-market operations are not a perfect solution. Their impact can be difficult to predict with precision, and there can be lags between the implementation of a policy and its effects on the economy.
Moreover, open-market operations can be less effective when interest rates are already near zero, as was the case during the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis. In such situations, central banks may need to resort to other unconventional measures to stimulate the economy.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of open-market operations can be influenced by factors beyond the control of the central bank, such as global economic conditions and consumer confidence.
Looking Ahead
As the global economy continues to evolve, open-market operations will likely remain a vital tool for central banks. However, the specific strategies and tactics used may need to adapt to new challenges and opportunities.
The rise of digital currencies, for example, could potentially impact the effectiveness of traditional open-market operations. Central banks may need to explore new ways to manage liquidity and influence interest rates in a digital age.
Ongoing research and analysis will be crucial to ensure that open-market operations remain an effective instrument for promoting economic stability and prosperity. Continued reliance on data and evolving to meet the demands of a new economy is paramount.
A Continuing Conversation
The world of economics is constantly evolving, and understanding the nuances of tools like open-market operations is crucial for informed citizenship. Whether you're a seasoned investor or simply curious about how the economy works, exploring these concepts empowers you to engage in meaningful conversations about the future.
As we navigate an increasingly complex financial landscape, staying informed and asking questions is more important than ever. By embracing knowledge and critical thinking, we can all contribute to building a more stable and prosperous future for ourselves and generations to come.
In conclusion, open-market operations, with their elegant simplicity, remain a powerful force in shaping the economic landscape. The constant buying and selling of government securities serves as a testament to the careful balance required to foster growth and stability in an ever-changing world.