Positive Feedback Differs From Negative Feedback In That

Scientific understanding just took a leap forward. Researchers have clarified a key distinction between positive and negative feedback loops, impacting fields from climate modeling to biological systems analysis.
This clarification addresses a long-standing source of confusion in various scientific disciplines. The research pinpoints fundamental differences in how these feedback mechanisms operate and influence system stability, offering more precise predictive capabilities.
The Core Difference: Amplification vs. Stabilization
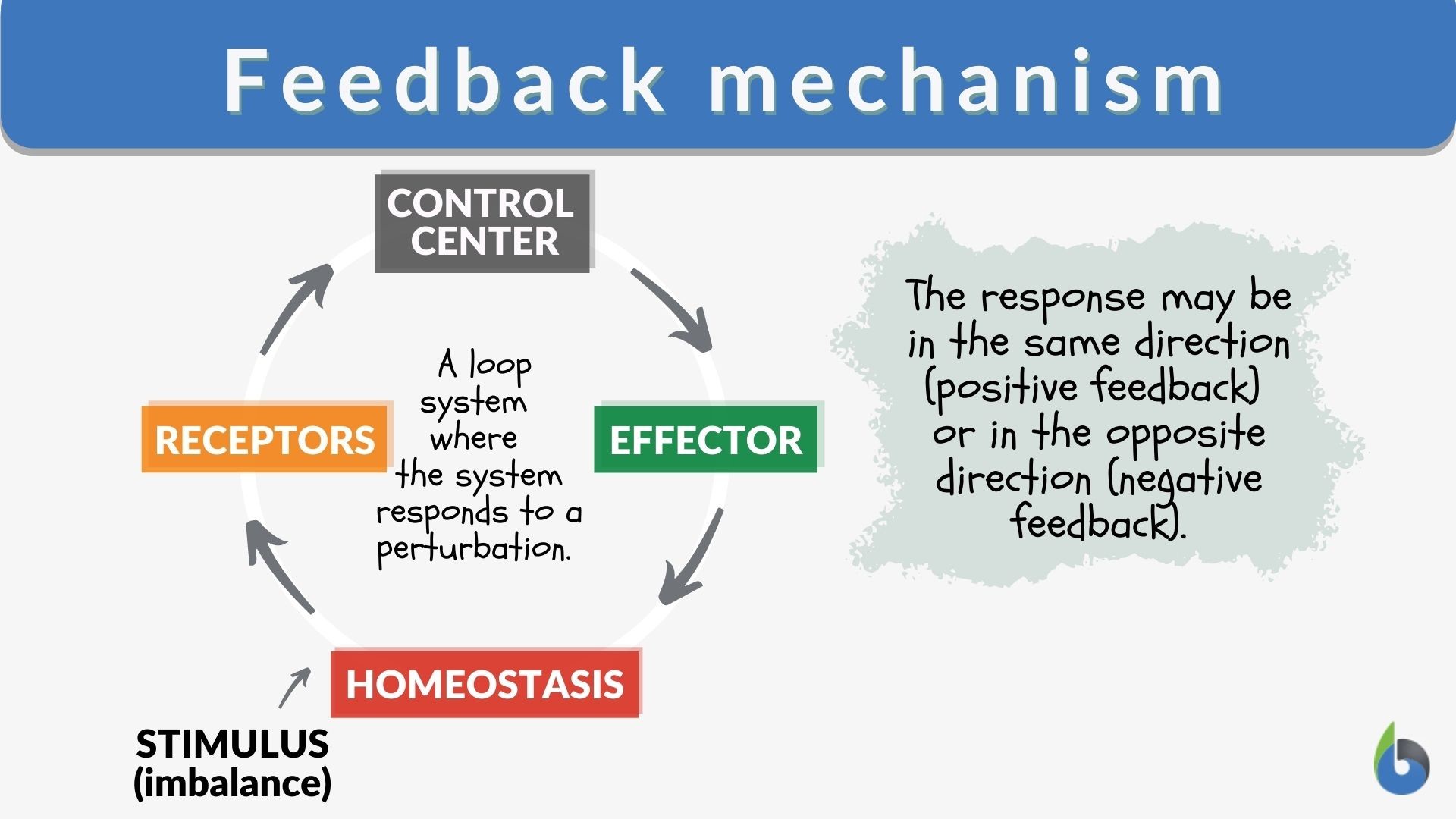
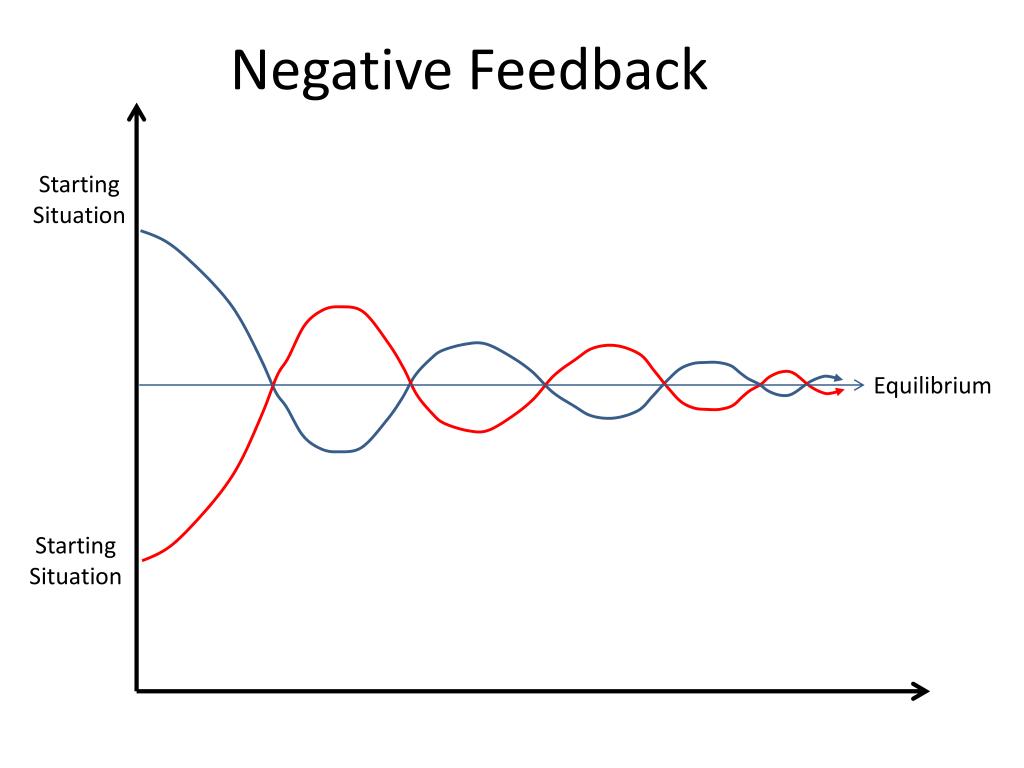
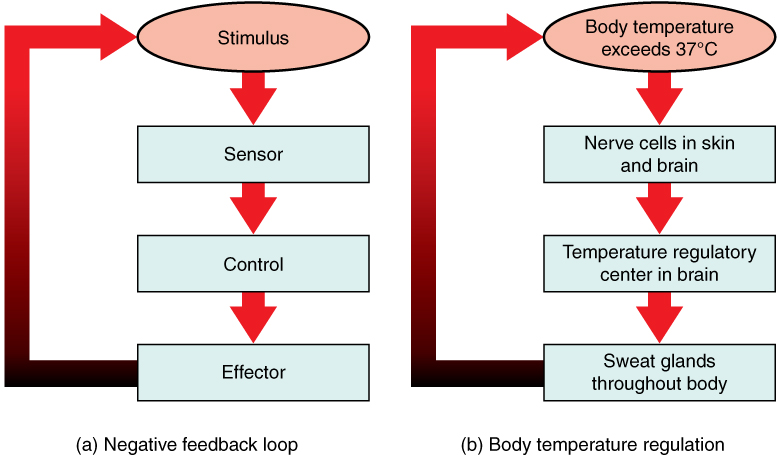
The crux of the matter lies in their opposing effects on system equilibrium. Negative feedback acts to dampen or counteract changes, pushing a system back towards its initial state.
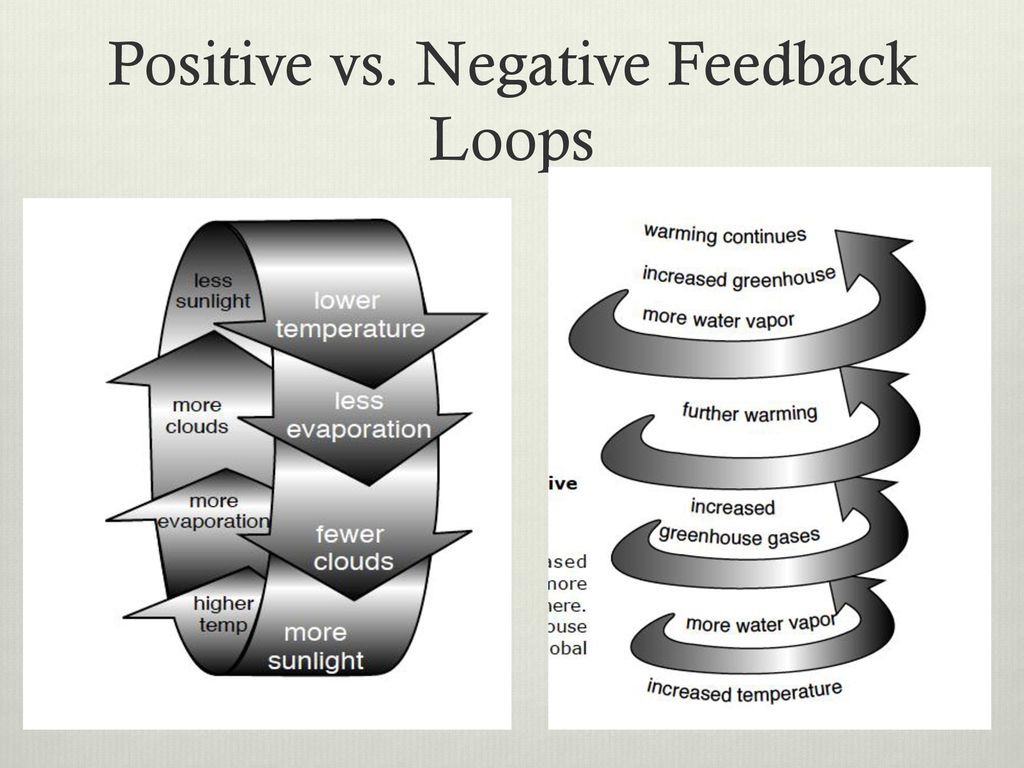
Conversely, positive feedback amplifies changes, driving a system away from its equilibrium. This amplification can lead to rapid and dramatic shifts in system behavior.
Understanding Negative Feedback
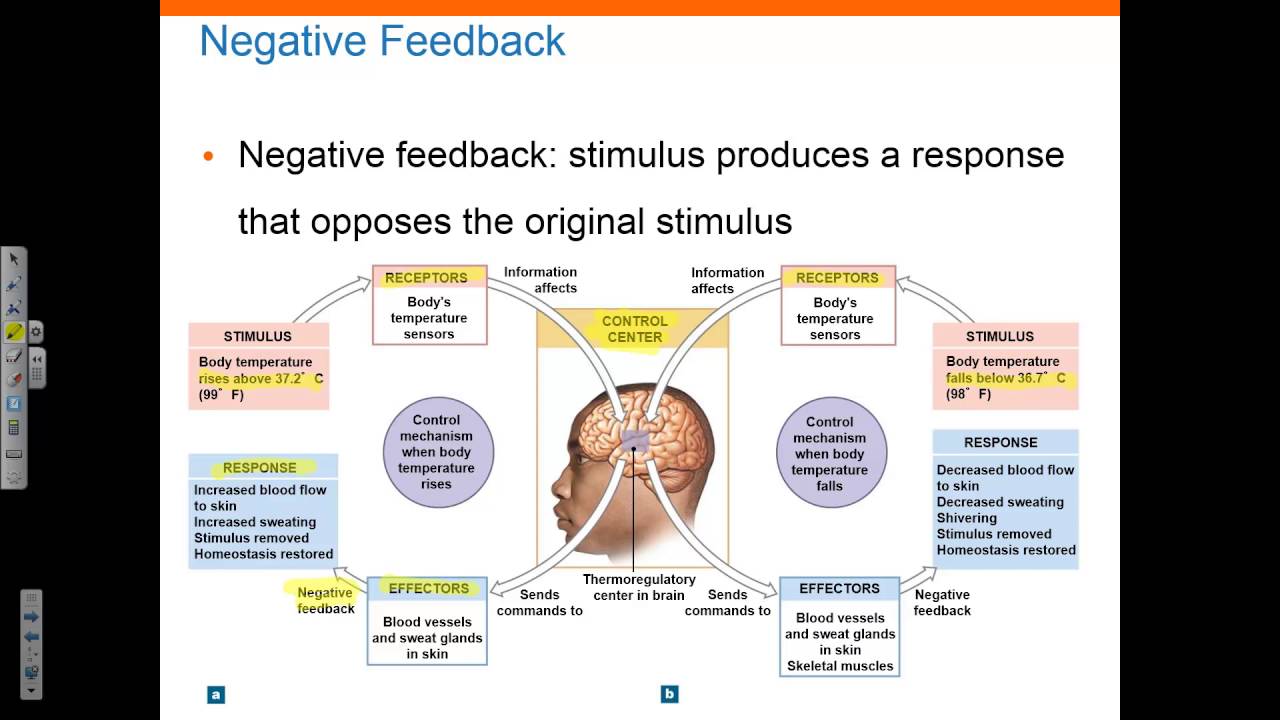
Imagine a thermostat controlling room temperature. If the temperature rises above the set point, the thermostat activates the air conditioner, cooling the room down – a clear example of negative feedback in action.
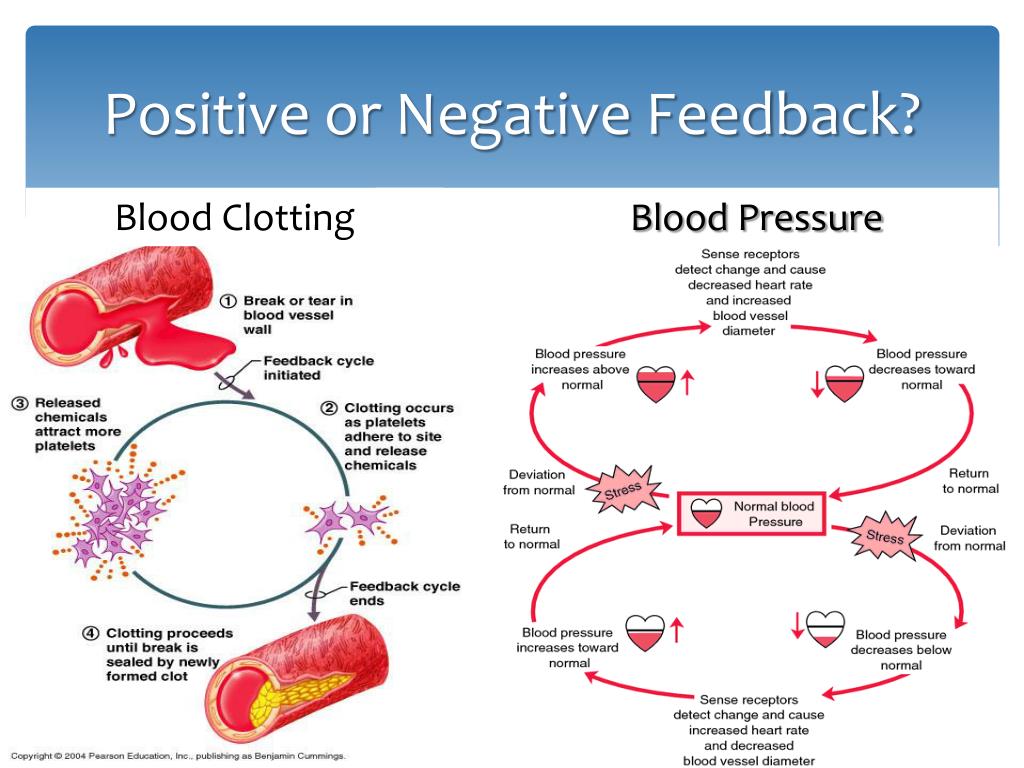
Biological systems also heavily rely on negative feedback. For instance, the regulation of blood glucose levels involves negative feedback loops to maintain stability.
The body releases insulin when blood sugar is high, which helps bring the levels back to normal. When levels are low, the body will use glucagon to raise the sugar levels to homeostasis.
Positive Feedback's Role
Childbirth provides a striking example of positive feedback. The release of oxytocin during labor stimulates uterine contractions, which in turn trigger the release of more oxytocin.
This cycle intensifies contractions until delivery occurs. Although crucial in specific instances, unchecked positive feedback can lead to instability and runaway effects.
Another example of positive feedback is the melting of arctic ice. As ice melts, it exposes darker ocean water, which absorbs more sunlight and warms the planet, causing even more ice to melt.
Implications Across Disciplines
This refined understanding has major implications for climate science. Accurate climate models hinge on precisely representing feedback mechanisms, both positive and negative.
Inaccurate representation can lead to flawed predictions about future climate change. Researchers and policymakers rely on this kind of modeling to make more effective decisions.
In biology, understanding these feedbacks is crucial for drug development. Modulating feedback loops can be a target to treat diseases or enhance therapeutic effects.
Examples in Economics
Economic systems are rife with both positive and negative feedback loops. A stock market bubble can be seen as a positive feedback loop.
Rising prices attract more investors, driving prices even higher, until the bubble eventually bursts. Negative feedback in economics can involve government intervention to stabilize the economy.
Tax policies and interest rate adjustments can act as negative feedback mechanisms to prevent runaway inflation or recession.
The Research Behind the Clarification
The study, published in "The Journal of System Dynamics," highlights a mathematical framework that distinguishes between the two types of feedback. The model provides a set of equations that demonstrate how each influences the system.
Dr. Anya Sharma, lead author of the study, emphasized the importance of this distinction: "Recognizing the fundamental differences between these loops is critical for accurately modeling complex systems."
Dr. Sharma says this distinction will help improve future analysis.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research
Researchers are now focusing on developing more sophisticated models that incorporate both positive and negative feedback. These models will be used to forecast the long-term effects of change in various systems.
Further investigation is also being directed towards identifying novel feedback mechanisms in biological systems. This pursuit could open new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
The scientific community is urged to adopt this refined understanding to improve accuracy in analysis and modeling efforts. The implications of improved scientific models will impact people everywhere.