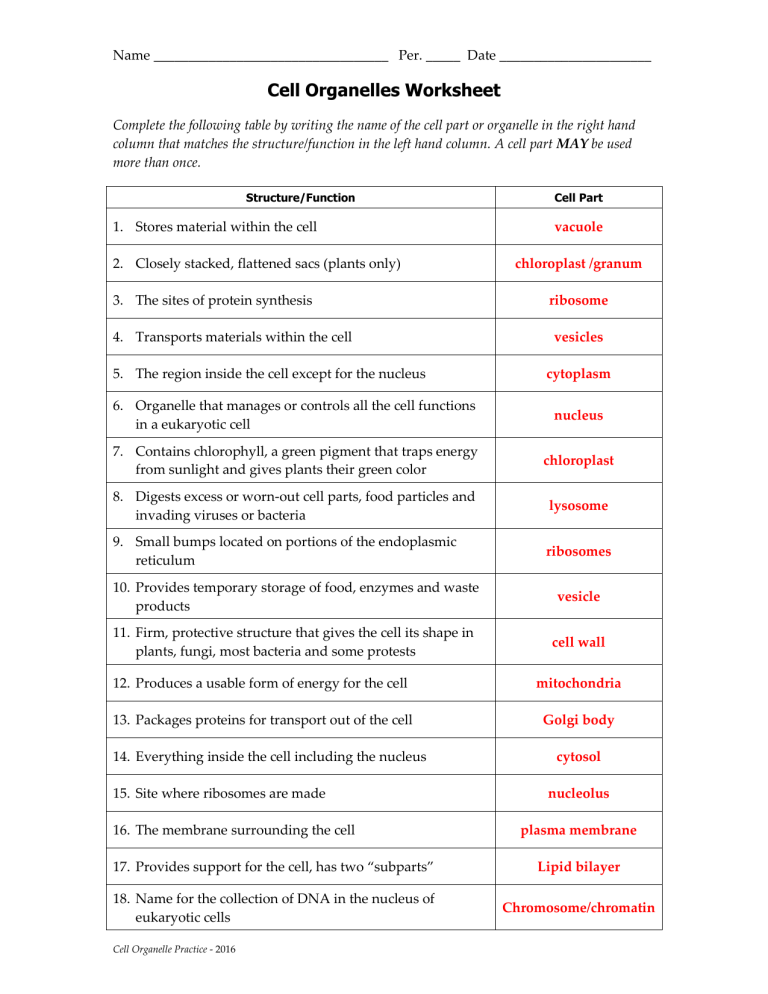
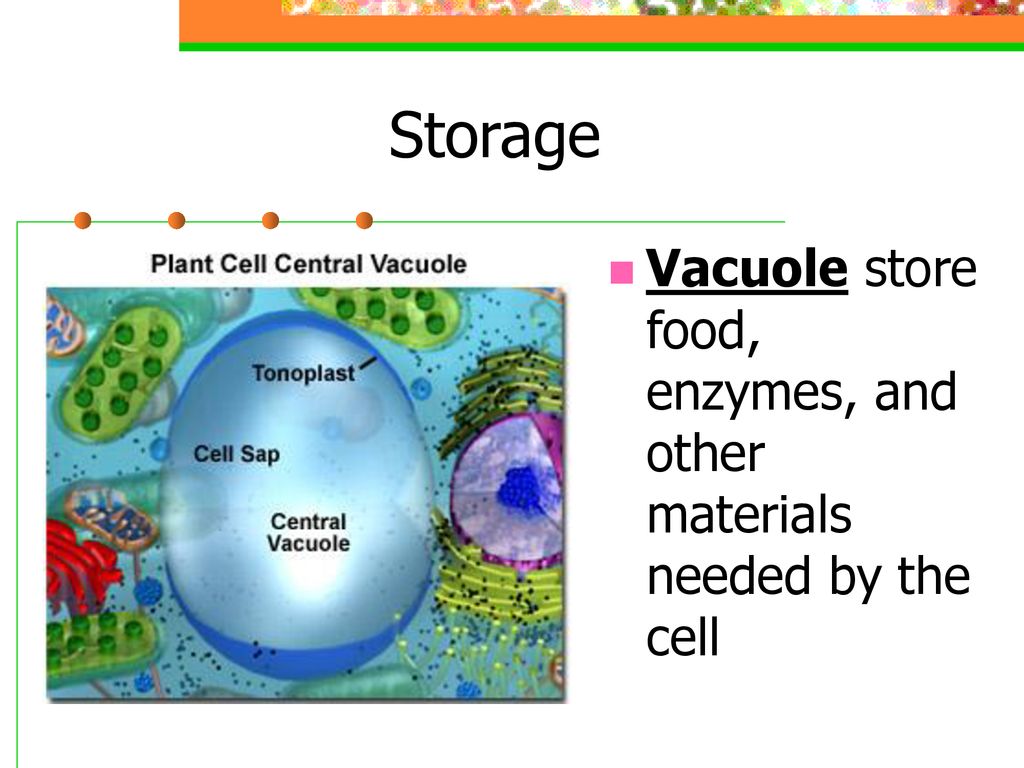
Provides Temporary Storage Of Food Enzymes And Waste Products

Cellular structures, often unseen powerhouses within our bodies, are the subject of renewed scientific interest as researchers delve deeper into the function and significance of organelles. Recent studies have illuminated the multifaceted role of a specific organelle, the vacuole, challenging previous assumptions about its relatively simple purpose within cells.
Vacuoles, primarily known for their storage capabilities, are now understood to be dynamic components actively involved in numerous cellular processes. This discovery has potentially significant implications for understanding and treating various diseases, as well as for developing new biotechnological applications.
The Multifaceted Role of Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles present in all plant cells, as well as fungal, and some animal and bacterial cells. Traditionally, they have been described as storage compartments within the cell, primarily responsible for holding water, nutrients, and waste products. However, recent research is highlighting a more complex picture.
Dr. Emily Carter, a lead researcher at the Institute for Cellular Biology, explains: "We are finding that vacuoles are far more than just passive storage units. They are actively involved in maintaining cellular homeostasis, regulating pH, and even participating in degradation processes."
Temporary Storage of Food Enzymes
One of the key functions of vacuoles is the temporary storage of food enzymes. These enzymes, crucial for breaking down complex molecules into usable energy, are often synthesized and stored within the vacuole until needed by the cell. This storage mechanism prevents premature activation of enzymes that could damage other cellular components.
The enzymes are transported to the vacuole via specific transport proteins embedded in the vacuolar membrane. These proteins act as gatekeepers, ensuring that only the correct enzymes are delivered and stored safely.
When the cell requires energy, signals are sent to the vacuole, triggering the release of the stored enzymes. These enzymes then move to the appropriate cellular locations to initiate the breakdown of complex molecules.
Waste Product Management
In addition to storing food enzymes, vacuoles also play a critical role in the management of waste products within the cell. Toxic substances and byproducts of cellular metabolism are sequestered within the vacuole, preventing them from interfering with normal cellular functions.
This sequestration process is essential for maintaining a healthy cellular environment. Without vacuoles, the accumulation of waste products could lead to cellular damage and even cell death.
Furthermore, vacuoles can also participate in the degradation of waste products. They contain a variety of enzymes capable of breaking down complex waste molecules into smaller, less toxic compounds.
Significance and Potential Impact
The renewed understanding of vacuole function has potentially far-reaching implications. By gaining a deeper insight into how vacuoles regulate cellular processes, researchers are developing new strategies for treating diseases related to cellular dysfunction.
For instance, in some diseases, the vacuolar transport system is disrupted, leading to the accumulation of toxic substances within the cell. Understanding the mechanisms behind this disruption could pave the way for new therapeutic interventions.
Dr. Carter states that, "Targeting vacuolar function could be a promising approach for treating a wide range of diseases, including neurodegenerative disorders and certain types of cancer."
The enhanced knowledge of vacuole function also opens up new possibilities in biotechnology. Vacuoles could be engineered to produce valuable substances, such as pharmaceuticals or biofuels.
By manipulating the vacuolar transport system, scientists could potentially create cells that act as miniature factories, producing desired products in a controlled and efficient manner.
Human Interest Angle
Beyond the scientific and technological implications, the study of vacuoles also provides a fascinating glimpse into the complexity and elegance of cellular biology. These tiny organelles, often overlooked, are essential for the life and health of all organisms.
A local high school student, Sarah Johnson, participating in a summer research program at the Institute for Cellular Biology, shared her enthusiasm: "I never realized how important vacuoles were. It's amazing to think that these little compartments inside our cells are constantly working to keep us alive and healthy."
Her involvement highlights the importance of engaging young scientists in cutting-edge research. This inspires future generations to pursue careers in science and contribute to advancing our understanding of the natural world.
Conclusion
The re-evaluation of vacuole function represents a significant step forward in our understanding of cellular biology. Vacuoles are not just simple storage compartments; they are dynamic and essential organelles actively involved in numerous cellular processes.
Further research into vacuolar function promises to unlock new insights into the causes of diseases and lead to the development of novel therapeutic and biotechnological applications. The ongoing exploration of these unseen cellular structures holds great potential for improving human health and advancing scientific knowledge.