Quality Of Information That Assures Users That Information

In an era defined by unprecedented access to information, the very fabric of trust is fraying. A deluge of misinformation, disinformation, and outright falsehoods threatens to erode public confidence in institutions, scientific findings, and even basic facts. The question is no longer just about the quantity of information available, but critically, about the quality of that information, and how users can be assured of its reliability.
This crisis of credibility demands urgent attention. This article will delve into the key factors that contribute to information quality, examining verification processes, source transparency, and the role of media literacy in empowering individuals to navigate the complex information landscape. By understanding these elements, we can begin to build a more resilient and trustworthy information ecosystem.
Defining Information Quality: A Multifaceted Approach
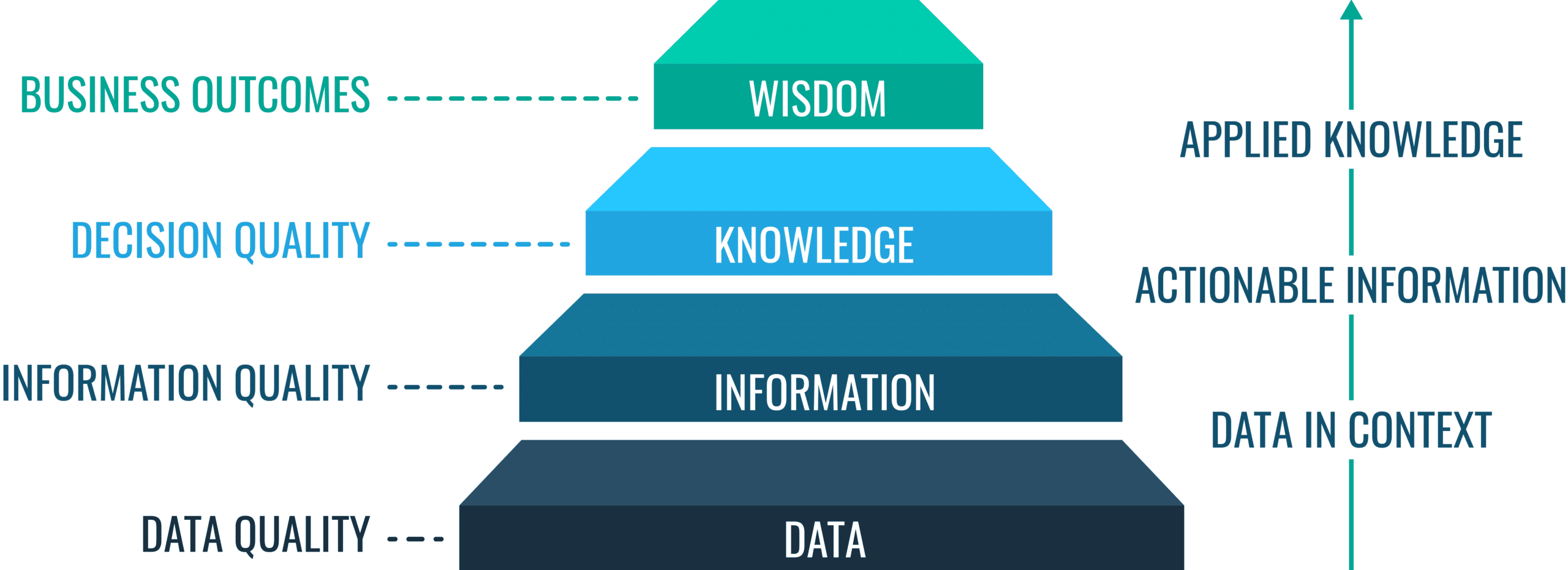
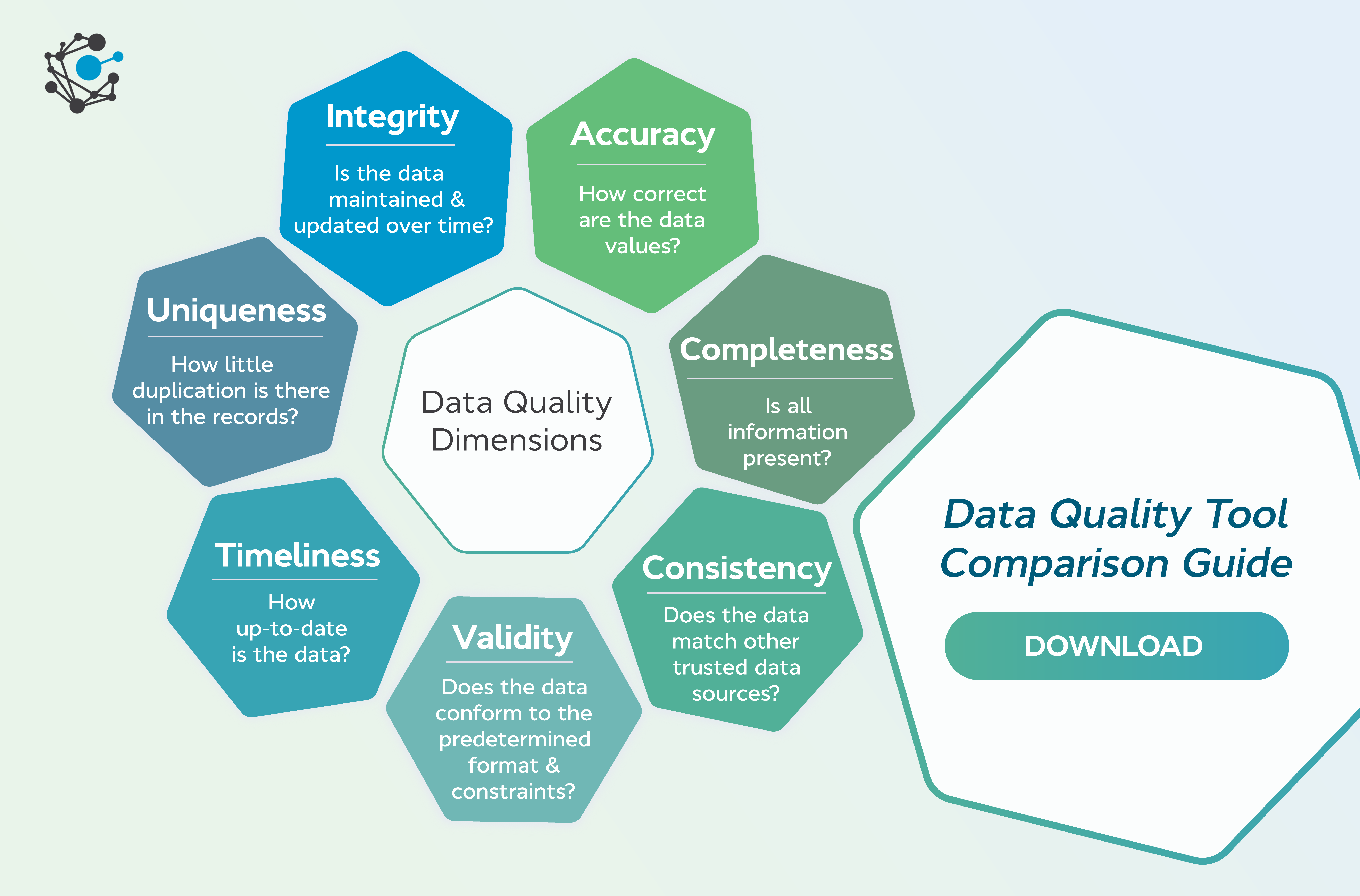
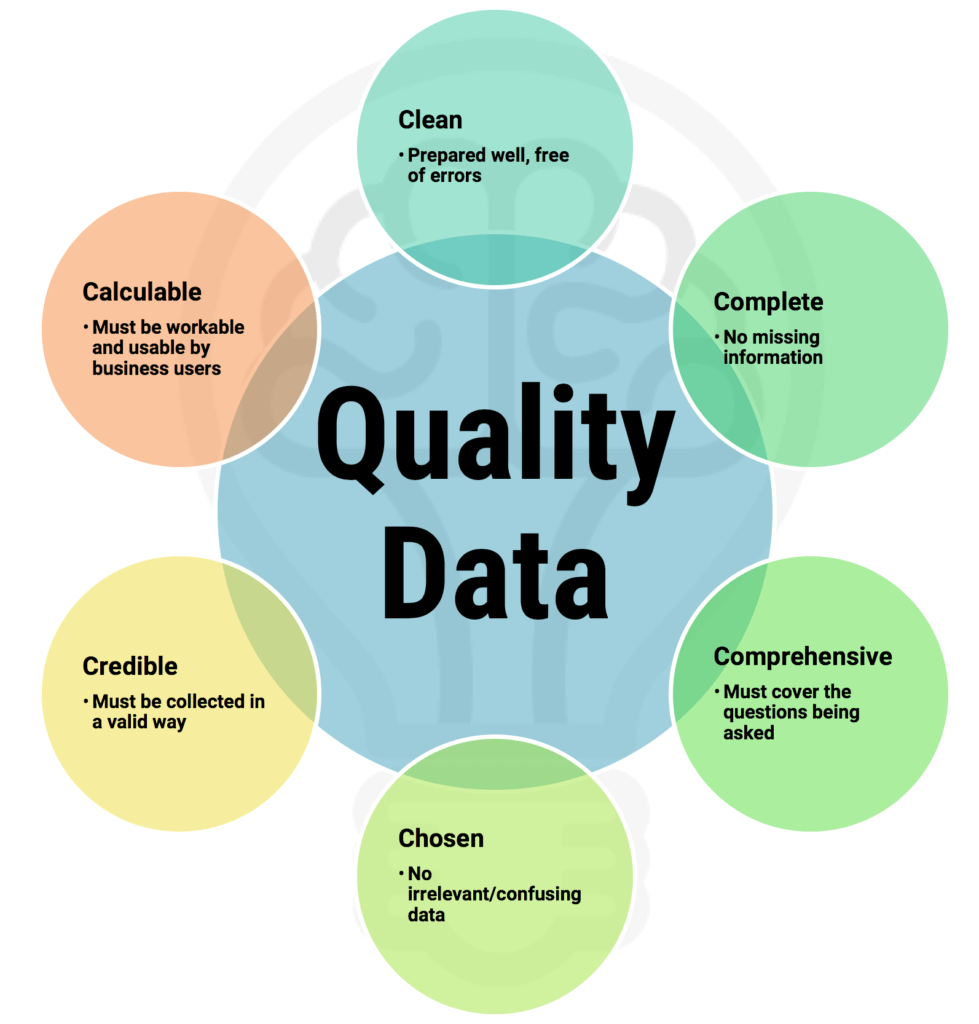
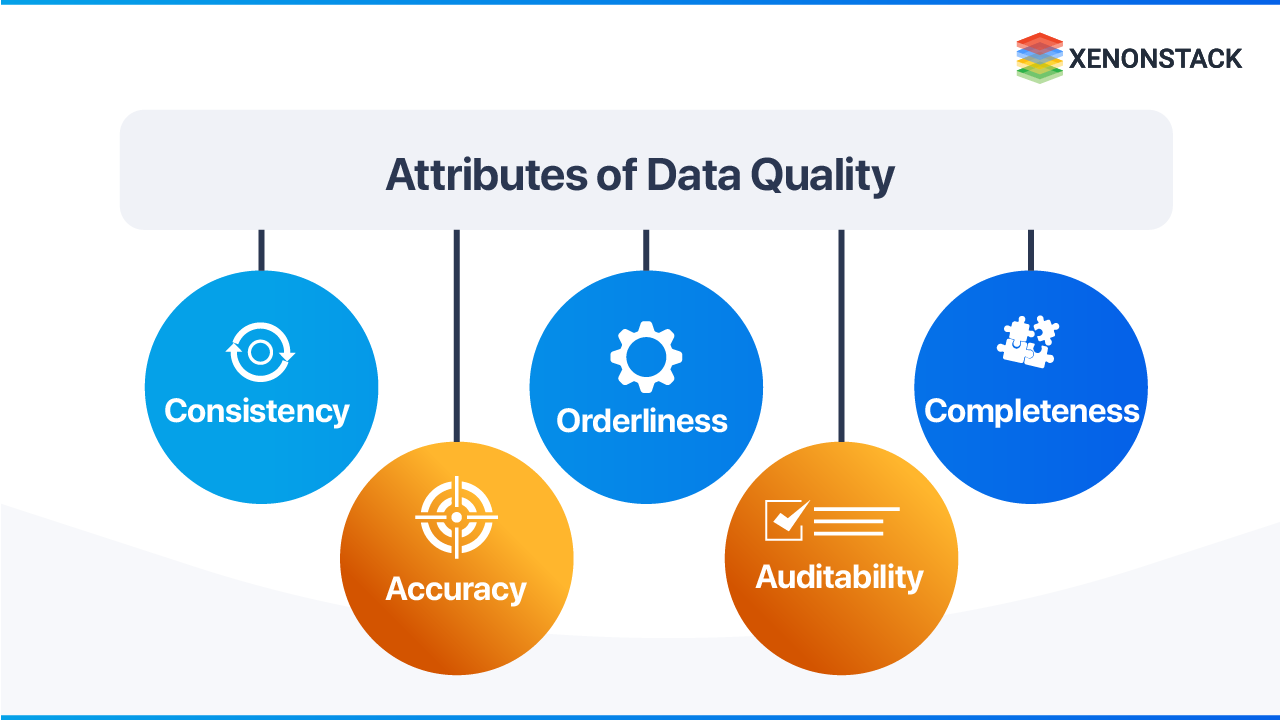
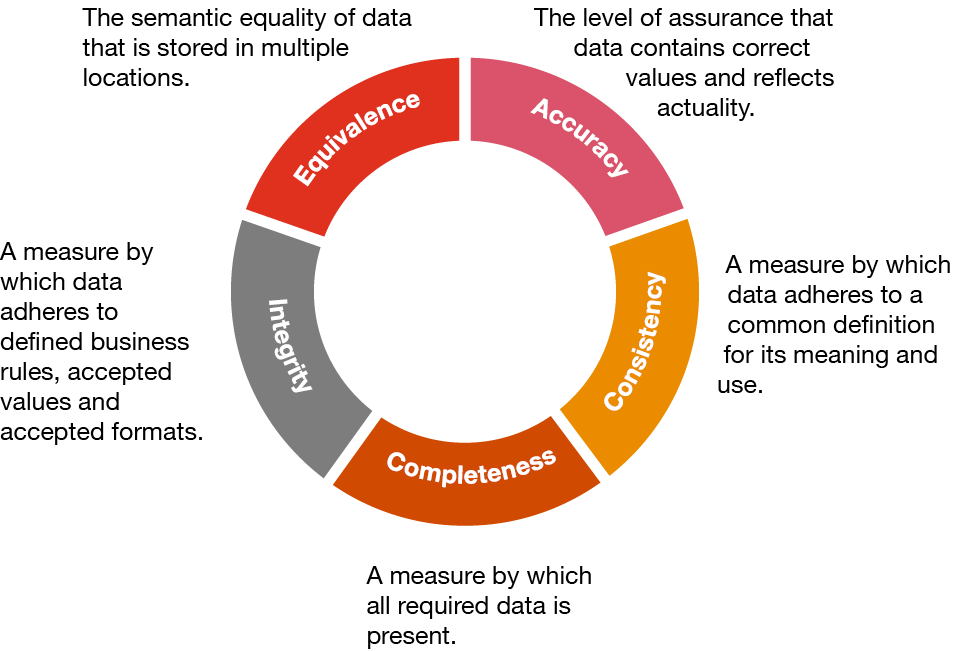
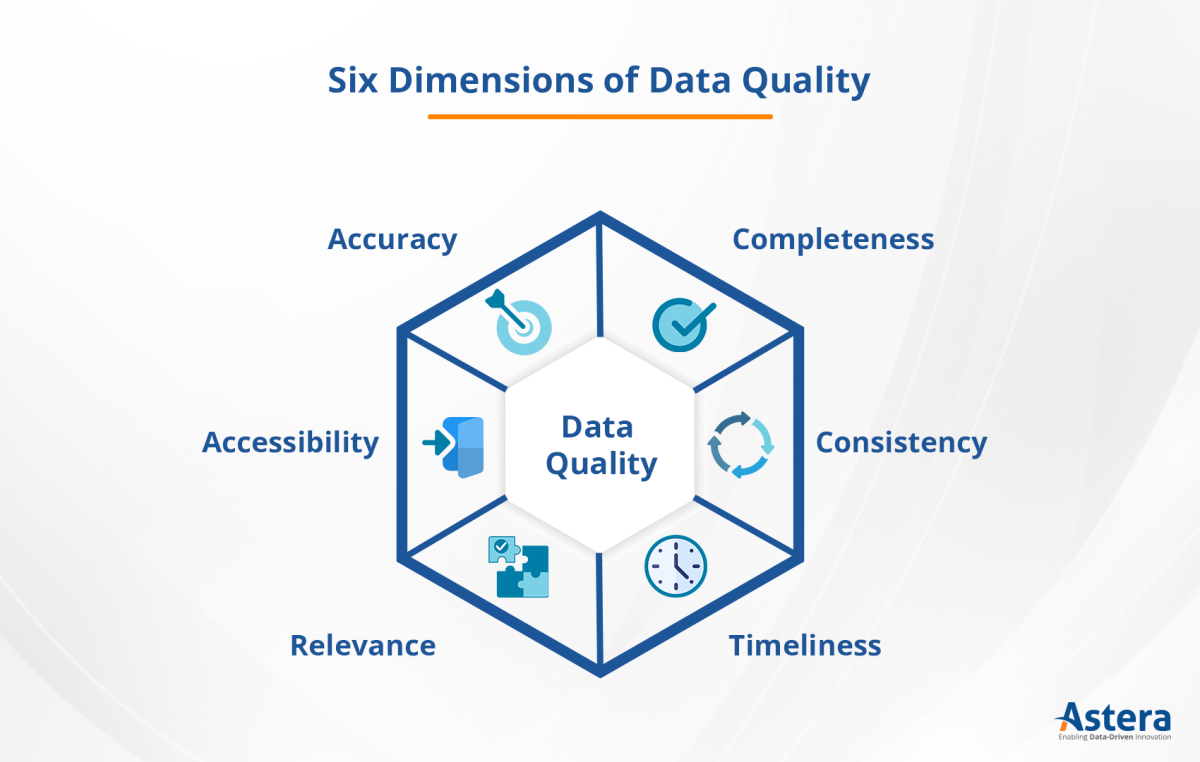
Information quality isn't a single, easily definable metric. Instead, it encompasses several crucial characteristics. These include accuracy, objectivity, currency, completeness, and relevance.
Accuracy refers to the factual correctness of the information presented, supported by evidence and verifiable sources. Objectivity ensures that information is presented without bias or undue influence, reflecting a neutral perspective. Currency requires information to be up-to-date and relevant to the present time, considering the rapidly evolving nature of many topics.
Completeness entails providing sufficient context and detail for users to understand the information fully. Finally, relevance ensures that the information is appropriate and applicable to the user's needs and search intent.
The Role of Verification and Fact-Checking
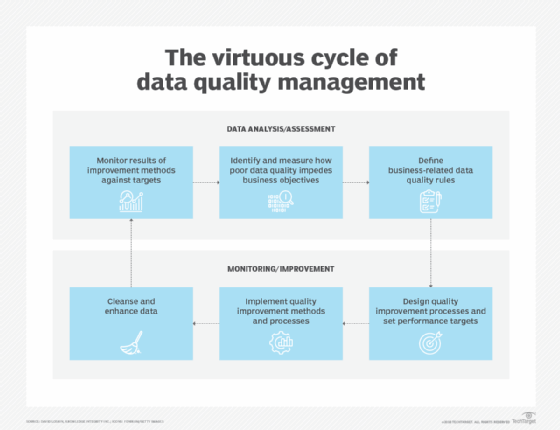
Verification and fact-checking are fundamental pillars of information quality. Professional journalists and reputable news organizations employ rigorous fact-checking processes to ensure the accuracy of their reporting.
This includes cross-referencing information with multiple sources, consulting with experts, and scrutinizing claims made by individuals or organizations. Organizations like PolitiFact and Snopes dedicate themselves entirely to fact-checking, providing detailed analyses of claims made in politics and public discourse.
These organizations use a systematic approach. They investigate the origins of claims, analyze the evidence supporting them, and assign a rating based on the accuracy of the information.
Source Transparency and Reputation
The credibility of information is inextricably linked to the source from which it originates. Reputable sources, such as established news organizations, academic institutions, and government agencies, adhere to journalistic ethics and rigorous standards of accuracy.
Users should be wary of anonymous sources or sources with a known bias or agenda. Checking the "About Us" section of a website can provide valuable insights into its mission, funding, and editorial policies. It's also helpful to investigate the author's credentials and expertise in the subject matter.
According to a recent report by the Pew Research Center, trust in news organizations varies significantly across different demographics and political affiliations. Understanding these biases is crucial for critically evaluating the information presented.
The Impact of Algorithms and Social Media
Algorithms play an increasingly significant role in shaping the information that users encounter online. Social media platforms, in particular, rely on algorithms to curate content based on user preferences, engagement metrics, and other factors.
This can create "filter bubbles" or "echo chambers" where users are primarily exposed to information that confirms their existing beliefs, reinforcing biases and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. This algorithmic curation can lead to the spread of misinformation and the polarization of opinions.
Furthermore, the ease with which misinformation can be disseminated on social media platforms poses a significant challenge. Bot networks and malicious actors can amplify false narratives, making it difficult for users to distinguish between credible and unreliable information.
Empowering Users Through Media Literacy
Media literacy is the ability to access, analyze, evaluate, and create media in a variety of forms. It is a crucial skill for navigating the complex information landscape and discerning credible information from misinformation.
Media literacy education should equip individuals with the tools to critically evaluate sources, identify biases, and understand the motivations behind the creation and dissemination of information. This includes teaching individuals how to identify common disinformation tactics, such as emotionally charged language, false headlines, and manipulated images.
Organizations like the National Association for Media Literacy Education (NAMLE) provide resources and training programs to promote media literacy skills. They emphasize the importance of teaching critical thinking and empowering individuals to be active and informed consumers of information.
The Role of Technology in Combating Misinformation
Technology can also play a role in combating misinformation. Artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to detect and flag potentially false or misleading content, helping to prevent its widespread dissemination.
Fact-checking organizations are increasingly using AI to automate the process of identifying and verifying claims. Blockchain technology can also be used to create a more transparent and secure information ecosystem, making it more difficult to tamper with or falsify data.
However, it's important to recognize that technology is not a silver bullet. AI algorithms can be biased and can inadvertently censor legitimate content. A human-centered approach to combating misinformation is essential, focusing on empowering individuals to critically evaluate information and make informed decisions.
Moving Forward: Building a More Trustworthy Information Ecosystem
Addressing the crisis of information quality requires a multi-faceted approach involving governments, media organizations, technology companies, and individuals. Governments can play a role in promoting media literacy education and regulating online platforms to prevent the spread of misinformation.
Media organizations must adhere to journalistic ethics and invest in rigorous fact-checking processes. Technology companies should prioritize transparency and accountability in their algorithms, working to reduce the spread of misinformation and promote credible content.
Ultimately, it is up to each individual to cultivate critical thinking skills and be a responsible consumer of information. By demanding quality and holding sources accountable, we can collectively build a more trustworthy and resilient information ecosystem for the future.