Should Berberine Be Taken In The Morning Or At Night

The optimal timing of berberine supplementation – morning versus night – is sparking debate among health professionals and users alike. Research indicates the timing can impact its effectiveness, particularly regarding blood sugar control and potential side effects.
Berberine: A Powerful Compound
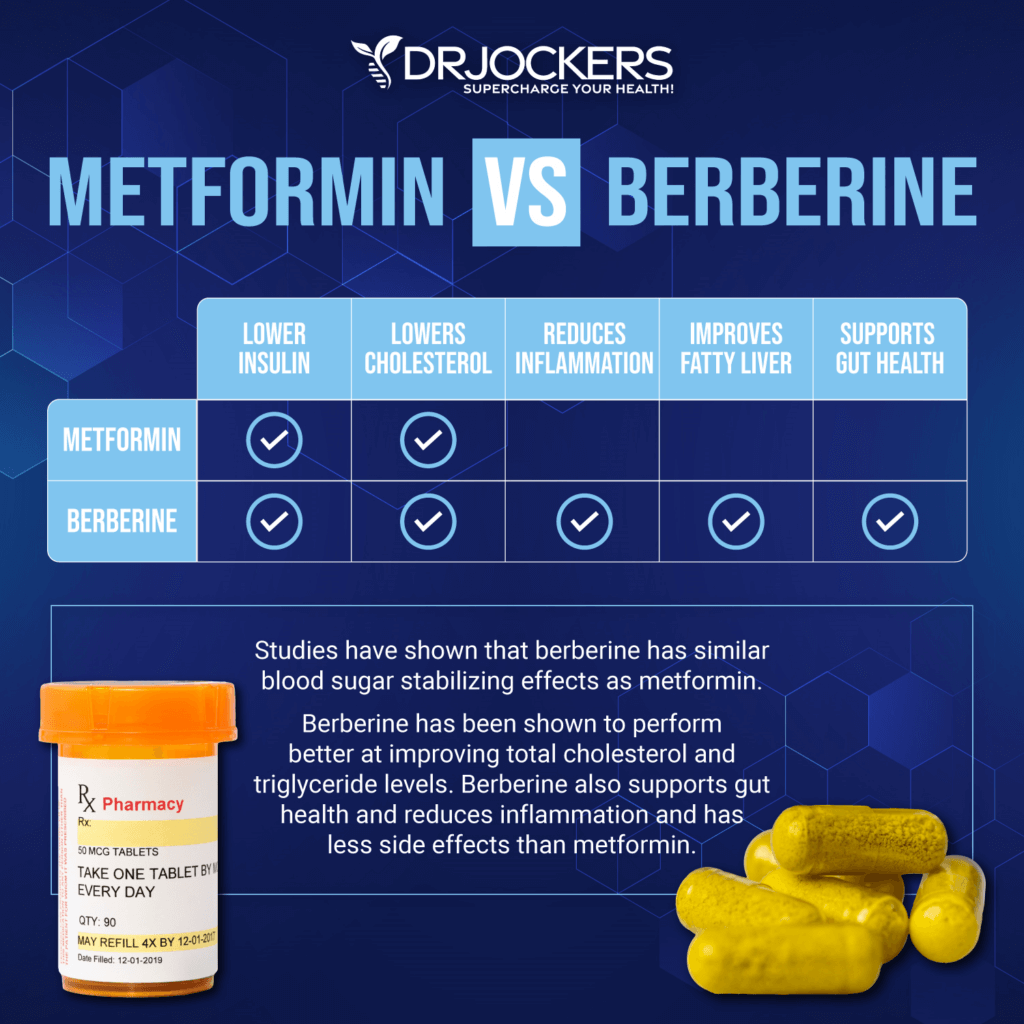
Berberine, a natural alkaloid found in plants like goldenseal and barberry, is increasingly popular for its potential health benefits. These benefits include blood sugar regulation, cholesterol management, and antimicrobial properties. However, maximizing these benefits requires understanding the best time to take it.
The Morning Argument
Many experts suggest taking berberine in the morning, particularly before meals. This timing aligns with the body's natural circadian rhythm and insulin sensitivity. Improved glucose disposal is observed when berberine is taken before breakfast.
A study published in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology showed that berberine taken in the morning resulted in better postprandial glucose control. Participants taking berberine before breakfast exhibited a more stable blood sugar response after eating. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals managing type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
Furthermore, some users report experiencing increased energy levels when taking berberine in the morning. This may be due to its impact on cellular energy production and mitochondrial function.
The Nighttime Approach
Conversely, some research suggests that taking berberine at night may offer distinct advantages. This timing can potentially optimize lipid metabolism and promote better sleep quality.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism found that taking berberine before bed significantly improved lipid profiles in participants with dyslipidemia. LDL cholesterol levels decreased more substantially in those taking berberine at night. This could be related to the liver's increased activity in processing fats during sleep.
Additionally, some individuals find that taking berberine at night minimizes potential gastrointestinal side effects. Taking it with dinner may help to mitigate digestive discomfort.
Dosage and Side Effects: Key Considerations
The typical dosage of berberine ranges from 500mg to 1500mg per day, usually divided into two or three doses. Starting with a lower dose and gradually increasing it can help minimize side effects.
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain. These side effects are often mild and temporary, but can be more pronounced in some individuals.
Berberine can interact with certain medications, including those for diabetes, blood pressure, and heart conditions. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting berberine, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking prescription medications.
Expert Opinions and Research Findings
Dr. Emily Carter, a leading endocrinologist, emphasizes the importance of individualizing berberine timing. "The optimal time to take berberine depends on individual health goals and how the body responds to it," she explains. "Some people find that morning works best for blood sugar control, while others prefer nighttime for lipid management."
A meta-analysis published in PLoS One examined multiple studies on berberine and its effects on metabolic parameters. The analysis concluded that berberine is effective in improving blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure. However, it did not specifically address the optimal timing of administration.
"More research is needed to definitively determine the best time to take berberine,"states Dr. David Lee, a researcher specializing in natural supplements.
"Current evidence suggests that both morning and nighttime administration can be beneficial, depending on the specific health goals."
Who should take Berberine?
Individuals with insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, high cholesterol, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) may find berberine beneficial.
However, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation to assess suitability and potential interactions. It is also important to consider if you are currently taking prescription medication.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should avoid taking berberine due to potential risks.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research
Researchers are currently conducting further studies to investigate the optimal timing of berberine administration. These studies aim to provide more definitive guidance on how to maximize its benefits and minimize side effects.
In the meantime, individuals considering berberine should consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate timing and dosage based on their individual needs and health goals. Monitoring blood sugar levels, lipid profiles, and any potential side effects is crucial when starting berberine supplementation.
Pay close attention to how you feel and notice if morning or night works best for you. Adjustments to berberine supplementation should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.