Stage 4 Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer Life Expectancy
The afternoon sun cast long shadows across the hospital waiting room, illuminating dust motes dancing in the air. A gentle hum filled the space, a symphony of quiet anxieties and hopeful whispers. Sarah clutched her husband David's hand, the warmth a comforting anchor in a sea of uncertainty. They were here to discuss the next steps, the path forward after David’s diagnosis: stage 4 neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer.
Understanding the prognosis for stage 4 neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer, particularly life expectancy, is crucial for patients and their families. While statistics offer a general framework, individual experiences vary widely based on factors like tumor type, treatment response, and overall health. This article aims to provide a compassionate and informed overview of stage 4 neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer life expectancy, emphasizing the importance of personalized care and ongoing research.
Understanding Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer
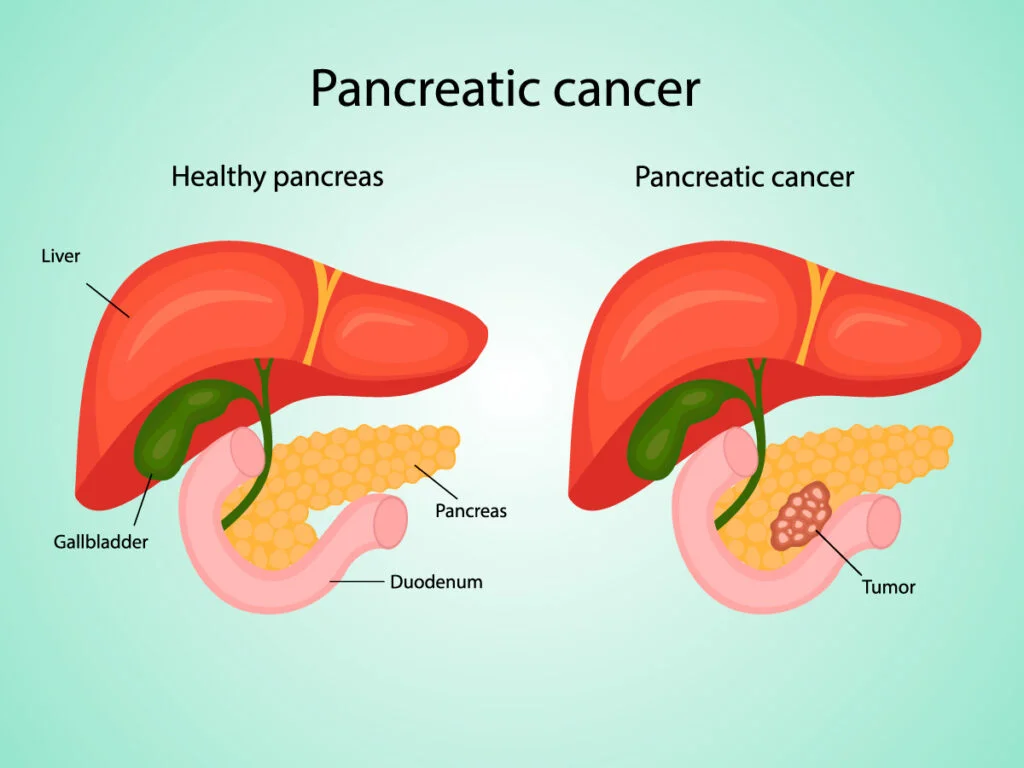
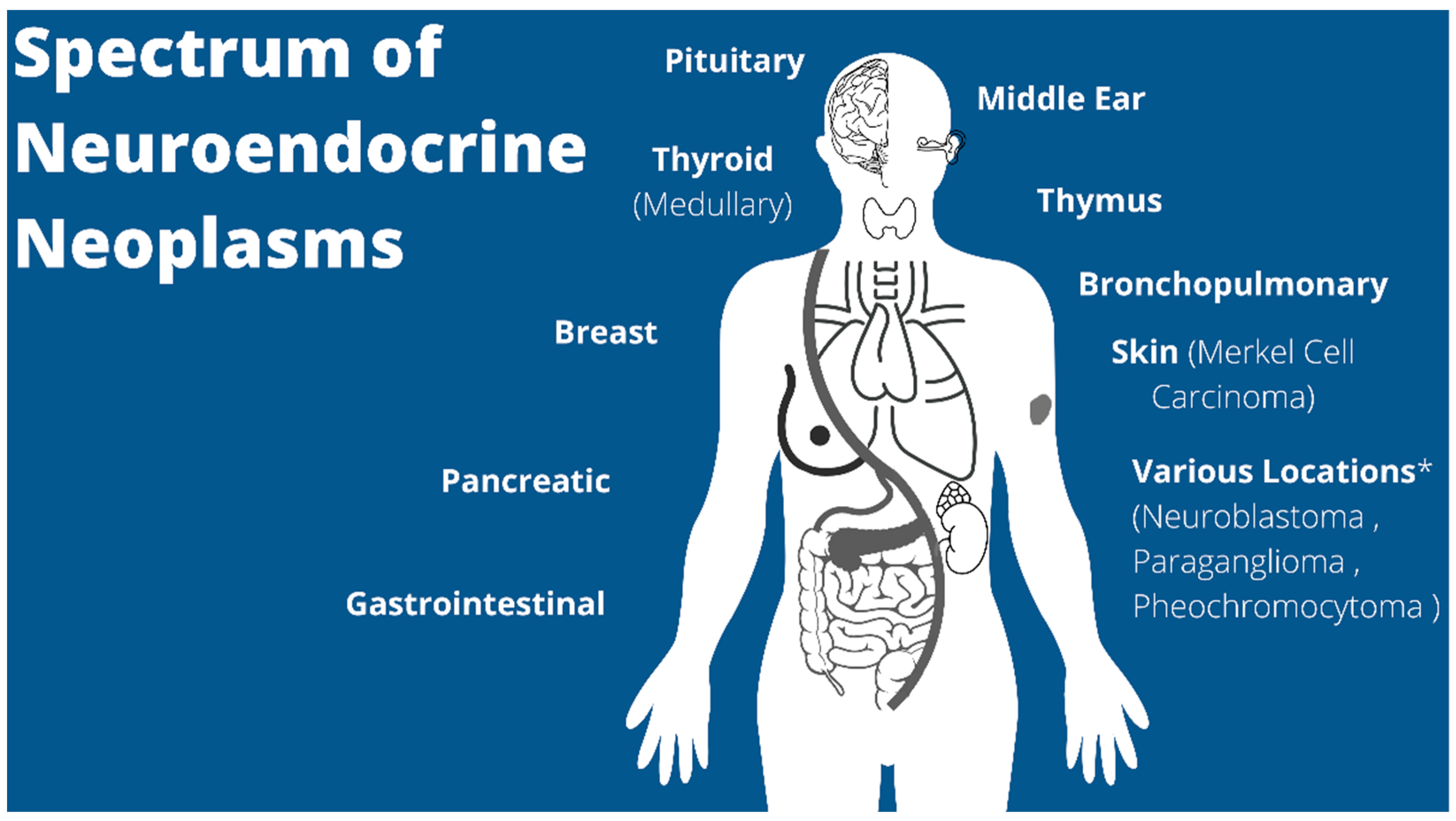
Pancreatic cancer isn’t a singular disease. Neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are a distinct type, arising from specialized cells in the pancreas responsible for producing hormones.
These hormones regulate various bodily functions. Unlike the more common adenocarcinoma, NETs tend to grow slower and often have a better prognosis.
However, when NETs reach stage 4, it signifies that the cancer has spread to distant sites, such as the liver, lungs, or bones.
Diagnosis and Staging
Diagnosing pancreatic NETs often involves a combination of imaging techniques, such as CT scans, MRI, and PET scans. Biopsies are essential to confirm the diagnosis and determine the specific type of NET.
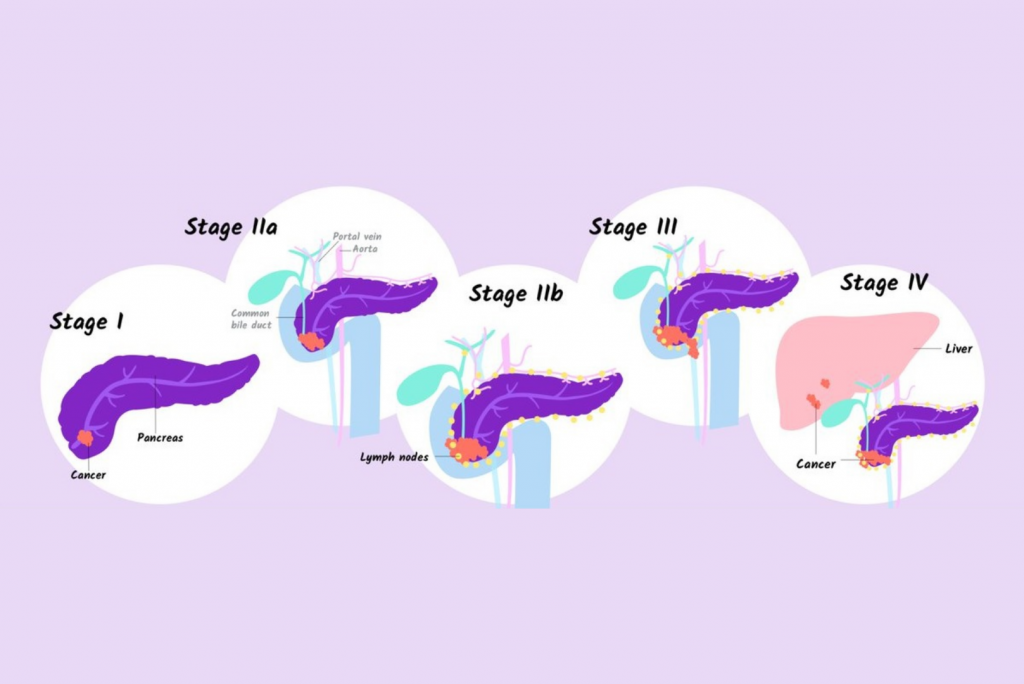
Staging, according to the American Cancer Society, assesses the extent of the cancer's spread, with stage 4 indicating distant metastasis.
The stage is crucial for informing treatment decisions and providing a general understanding of the expected outcome.
Stage 4: What Does it Mean for Life Expectancy?
The term "life expectancy" can be daunting. It represents the average length of time a group of people with a similar condition is expected to live.
However, it's vital to remember that these are just averages. Every individual's journey with cancer is unique.
Factors like the grade of the tumor (how quickly it grows), the extent of metastasis, and the patient's overall health significantly influence survival.
According to the Cancer.Net, the 5-year survival rate for stage 4 pancreatic NETs is approximately 30-40%. This means that 30-40% of people diagnosed with stage 4 NETs are still alive five years after their diagnosis.
These numbers are based on historical data and may not reflect the impact of newer treatments and advancements in cancer care.
The actual survival time can vary greatly. Some individuals may live for several years, while others may have a shorter life expectancy.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
Several key factors play a crucial role in determining the life expectancy of individuals with stage 4 neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer.
Tumor Grade: The grade reflects how quickly the cancer cells are dividing and growing. Lower-grade tumors generally have a better prognosis than high-grade tumors.
Well-differentiated tumors (lower grade) tend to be less aggressive. Poorly differentiated tumors (higher grade) are more aggressive and often associated with a poorer outcome.
Extent of Metastasis: The location and extent of the cancer's spread affect survival. Limited metastasis to a single organ may have a better prognosis than widespread metastasis to multiple sites.
The liver is a common site of metastasis for pancreatic NETs. The burden of disease in the liver can significantly impact overall health and life expectancy.
Treatment Response: How well the cancer responds to treatment is a significant determinant of survival. Individuals who respond well to therapy may experience longer remission and improved quality of life.
Treatment options include surgery (if feasible), targeted therapies, chemotherapy, and peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT). The choice of treatment depends on the tumor type, location, and stage, as well as the patient's overall health.
Overall Health: A patient's general health status, including age, other medical conditions, and lifestyle factors, can influence their ability to tolerate treatment and their overall survival.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can improve overall well-being and potentially enhance treatment outcomes.
Treatment Options and Advancements
The landscape of pancreatic NET treatment is continuously evolving. A multidisciplinary approach, involving oncologists, surgeons, endocrinologists, and other specialists, is often recommended.
The primary goal of treatment is to control tumor growth, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life.
Newer targeted therapies and immunotherapies are showing promise in treating advanced NETs.
Surgery: If possible, surgical removal of the primary tumor and any localized metastases can significantly improve survival. However, surgery may not be feasible if the cancer has spread extensively.
Targeted Therapies: These drugs target specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth and survival. Examples include everolimus and sunitinib.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy may be used to shrink tumors and slow their growth. It is often used for high-grade NETs or when other treatments are not effective.
Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT): This therapy involves injecting a radioactive substance that targets specific receptors on NET cells. It can effectively shrink tumors and improve symptoms.
Research is ongoing to develop even more effective treatments for stage 4 pancreatic NETs. Clinical trials offer patients access to cutting-edge therapies that may not be widely available.
Participating in a clinical trial can contribute to advancing our understanding of the disease and improving future treatment options.
Living with Stage 4 Neuroendocrine Pancreatic Cancer
A diagnosis of stage 4 cancer can be emotionally overwhelming. It's essential to prioritize mental and emotional well-being alongside physical health.
Support groups, counseling, and open communication with loved ones can provide invaluable support during this challenging time.
Focusing on quality of life, managing symptoms, and pursuing meaningful activities can help individuals live as fully as possible.
Managing symptoms such as pain, fatigue, and nausea is crucial for maintaining comfort and well-being. Palliative care specialists can provide expert assistance in managing these symptoms.
Open and honest communication with the healthcare team is essential. Patients should feel comfortable asking questions and expressing their concerns.
Maintaining a sense of hope and focusing on positive aspects of life can help individuals cope with the challenges of living with cancer.
Hope and the Future
While stage 4 neuroendocrine pancreatic cancer presents significant challenges, it's important to remember that hope remains. Medical advancements are constantly improving treatment options and extending survival for many individuals.
The journey with cancer is a marathon, not a sprint. Focusing on each day, celebrating small victories, and seeking support from loved ones and healthcare professionals can help individuals navigate this challenging path with resilience and grace.
David squeezed Sarah's hand, a silent acknowledgment of the road ahead. They knew it wouldn't be easy, but they were ready to face it together, armed with knowledge, hope, and unwavering love.