Stem Cell Storage Cost In Usa

The promise of regenerative medicine, fueled by the potential of stem cells, has captivated the medical world and offered hope for treating previously incurable diseases. However, this promise comes with a significant price tag, particularly when considering the long-term storage of these precious cells. In the United States, the cost of stem cell storage presents a substantial barrier for many families, raising ethical and economic questions about accessibility and equitable access to potentially life-saving treatments.
This article delves into the complex landscape of stem cell storage costs in the U.S., examining the factors that contribute to these expenses, the varying pricing models employed by storage facilities, the ethical considerations surrounding affordability, and the potential future of stem cell storage and its impact on healthcare accessibility. Understanding these intricate aspects is crucial for patients, healthcare providers, and policymakers alike.
The Rising Costs of Hope: Factors Influencing Stem Cell Storage Prices
Several factors contribute to the high cost of stem cell storage in the United States. First and foremost, the process requires specialized equipment and highly trained personnel. This includes the collection, processing, and cryopreservation of stem cells, all of which demand meticulous attention to detail and adherence to stringent quality control standards.
The maintenance of these cells in a viable state for extended periods also contributes significantly to the overall expense. Cryopreservation, typically involving liquid nitrogen, demands continuous monitoring and backup systems to ensure the integrity of the samples. Any lapse in these procedures could render the stored stem cells unusable, highlighting the critical need for robust infrastructure and rigorous protocols.
Furthermore, regulatory compliance adds to the cost burden. Storage facilities must adhere to guidelines set by organizations like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and meet specific accreditation standards. This involves extensive documentation, quality audits, and ongoing training, all of which incur significant operational expenses.
A Patchwork of Pricing Models: Navigating the Storage Landscape
The pricing structures for stem cell storage vary considerably across different facilities in the U.S. Some companies offer a one-time upfront payment that covers processing and an initial period of storage, followed by annual or recurring storage fees. Others employ a subscription-based model, where customers pay a monthly or annual fee for ongoing storage services.
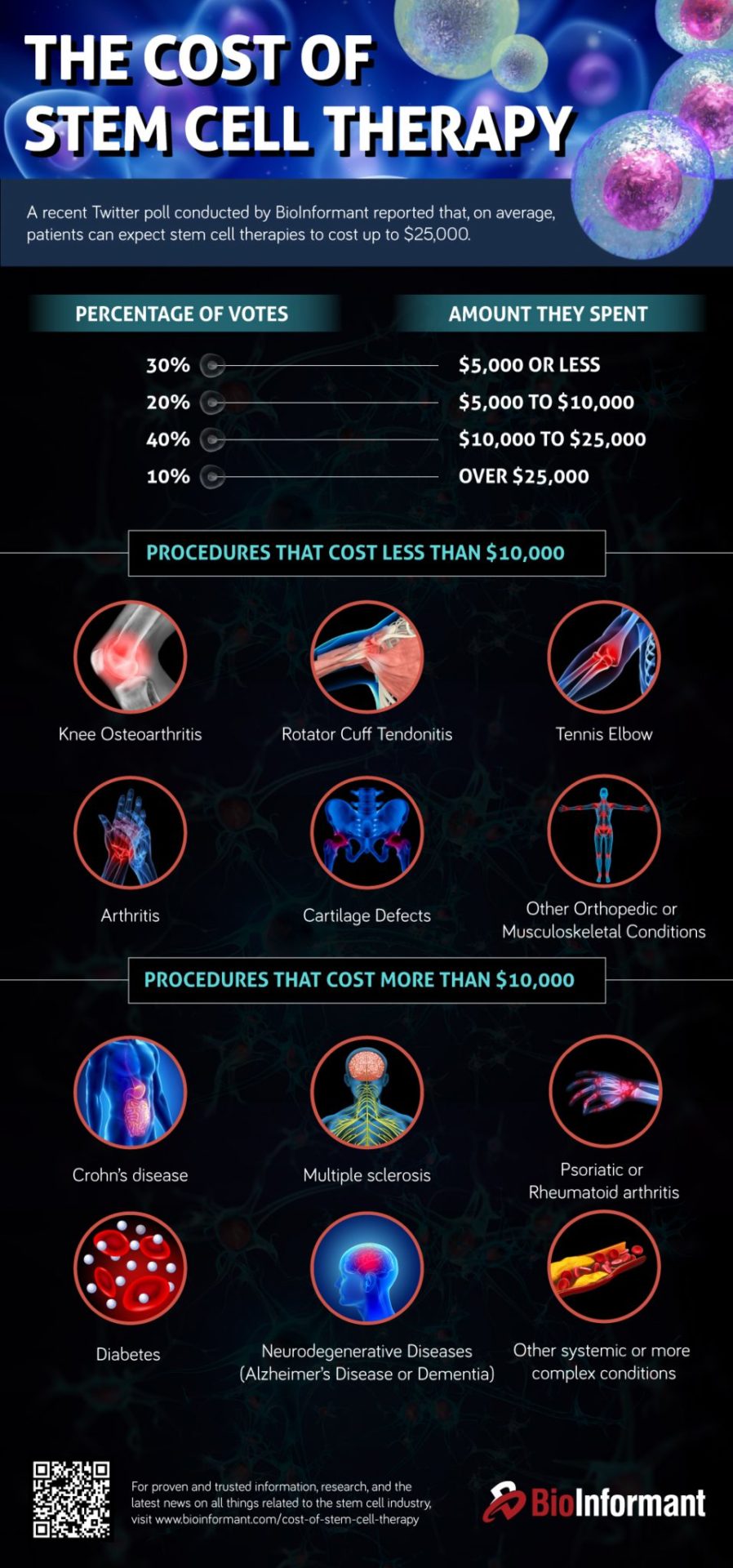
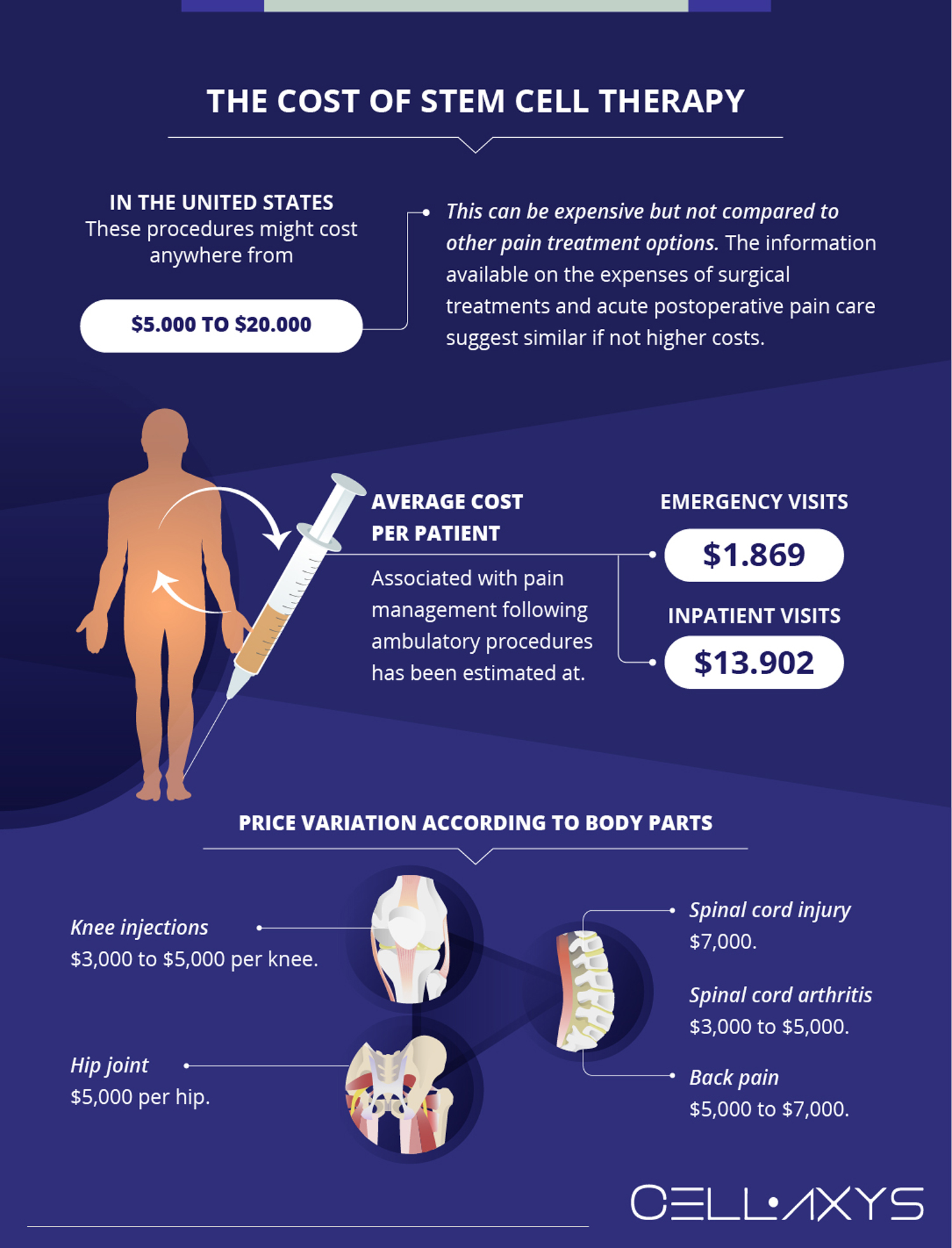
These prices can range from several hundred dollars to several thousand dollars for the initial processing and first year of storage. Annual storage fees typically range from $100 to $300 per year. The overall cost depends on the type of stem cells being stored (e.g., cord blood, bone marrow, or adipose tissue), the duration of storage, and any additional services offered, such as genetic testing or sample transportation.
It's important to note that pricing transparency can be a challenge in this industry. Some facilities may not fully disclose all potential costs upfront, leading to unexpected expenses down the line. Careful comparison shopping and thorough review of contracts are essential for consumers to make informed decisions.
Ethical Considerations: Accessibility and Equity
The high cost of stem cell storage raises serious ethical concerns regarding accessibility and equity. For families with limited financial resources, the option of storing stem cells may be simply unattainable. This creates a disparity where access to potentially life-saving treatments is disproportionately available to those who can afford it.
Critics argue that this situation exacerbates existing healthcare inequalities and undermines the principles of equitable access to medical advancements. The argument rests on the premise that while stem cell therapies are not yet widely available, their potential future applications warrant ensuring broad access to storage, regardless of socioeconomic status.
Furthermore, the marketing practices of some stem cell storage companies have come under scrutiny. Concerns have been raised about aggressive advertising tactics that may prey on parents' anxieties and promote the storage of stem cells without providing clear evidence of their clinical utility. This raises questions about informed consent and whether families are making fully informed decisions based on scientific evidence.
The Future of Stem Cell Storage: Technology, Policy, and Accessibility
The future of stem cell storage hinges on advancements in technology, policy changes, and evolving perceptions of clinical utility. Ongoing research into more efficient and cost-effective cryopreservation techniques could potentially lower storage costs. Automation and improved quality control systems could also contribute to reducing operational expenses.
Policy initiatives aimed at increasing accessibility could play a significant role. Government subsidies or tax incentives for stem cell storage could help to alleviate the financial burden on families. Increased transparency in pricing and stricter regulations on marketing practices could also protect consumers from deceptive practices.
Ultimately, the widespread adoption of stem cell therapies will depend on robust clinical trials that demonstrate their safety and efficacy. As more stem cell-based treatments become established, the demand for stem cell storage is likely to increase, potentially driving down costs due to economies of scale. A balanced approach that combines technological innovation, ethical considerations, and policy interventions is crucial to ensuring that the promise of stem cell therapy is accessible to all who could benefit.
The evolving landscape of stem cell storage demands a continued dialogue between researchers, policymakers, and the public to ensure that these promising medical advancements are used responsibly and equitably. The challenge lies in bridging the gap between scientific potential and practical accessibility, making the hope of regenerative medicine a reality for all.