Study Of All Aspects Of Diseases

A comprehensive, multi-faceted study aiming to understand diseases from their earliest molecular origins to their societal impacts is underway, promising to reshape how we approach prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. The project, spearheaded by a consortium of international research institutions, seeks to integrate biological, environmental, and behavioral data on an unprecedented scale.
This ambitious undertaking, known as the "Pan-Disease Atlas Initiative (PDAI)," aims to create a detailed map of disease processes across a wide range of conditions. It focuses on identifying common threads and unique variations, with the goal of developing more targeted and effective interventions. The initiative’s significance lies in its potential to move beyond treating symptoms to addressing the root causes of illness.
Unveiling the Pan-Disease Atlas Initiative
The PDAI brings together researchers from institutions like the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the World Health Organization (WHO), and leading universities across Europe and Asia. The project, officially launched in January 2024, is anticipated to run for at least ten years with ongoing data analysis and refinement.
The "who" includes a diverse team of geneticists, epidemiologists, data scientists, and clinicians. They are collaborating to collect and analyze data from diverse populations across various geographical locations. "What" is the creation of a comprehensive atlas detailing the molecular mechanisms, environmental factors, and behavioral influences that contribute to disease development and progression.
The "where" encompasses research sites and data collection centers worldwide. "When" refers to the ongoing data collection and analysis that began in early 2024. "Why" is to improve disease prevention and treatment through a deeper understanding of disease processes.
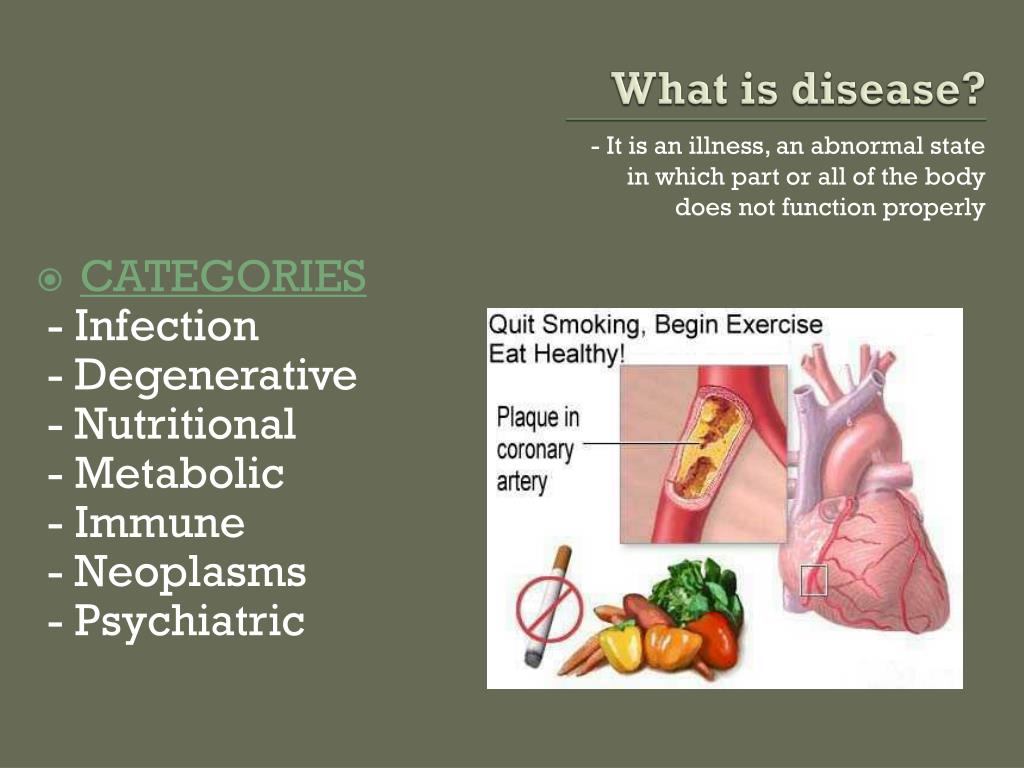
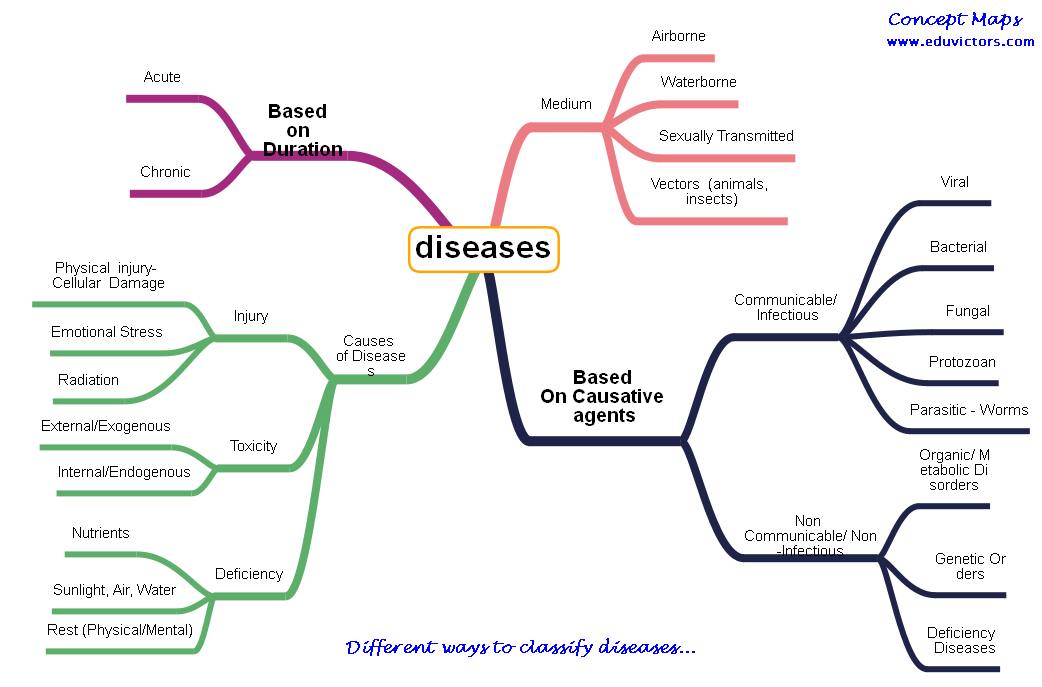
Key Components of the Study
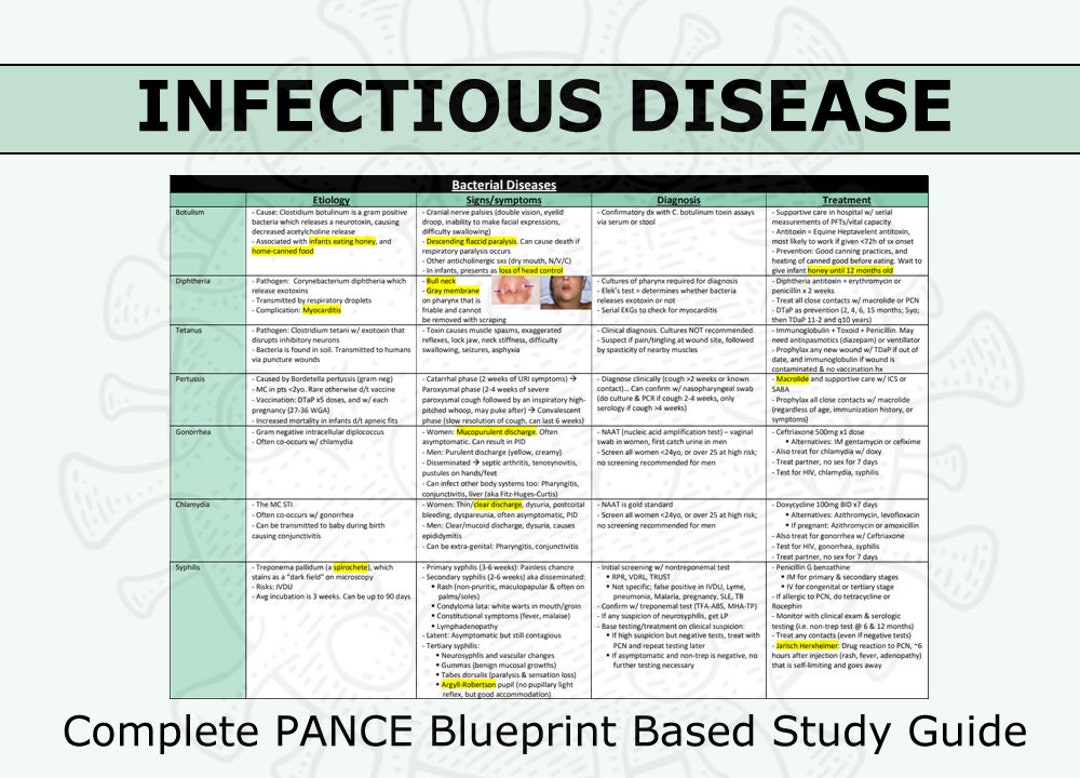
The PDAI employs a multi-pronged approach, integrating several key research areas. One crucial component is extensive genomic sequencing to identify genetic predispositions to various diseases. This involves analyzing DNA samples from thousands of individuals to pinpoint specific genes or mutations that increase disease risk.
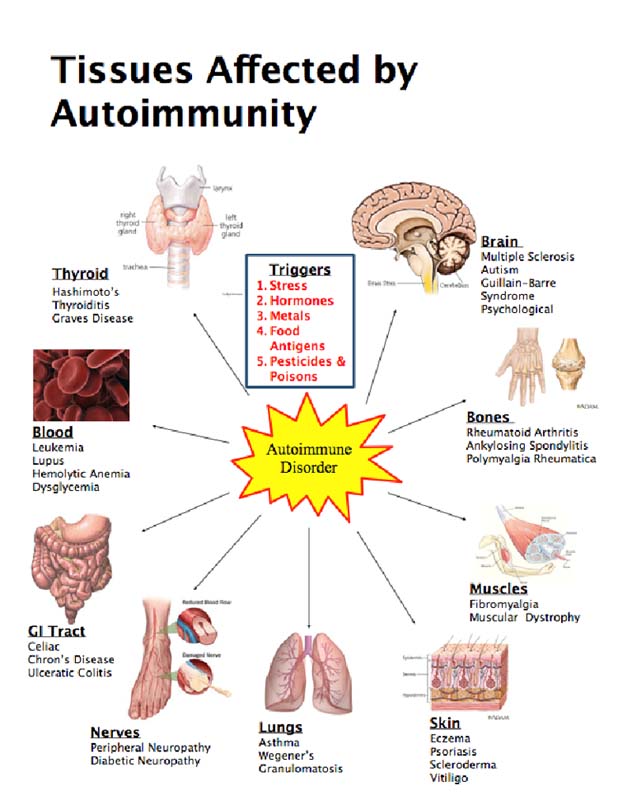
Another critical area is the investigation of environmental factors. Researchers are examining the impact of pollution, diet, lifestyle, and other environmental exposures on disease incidence and severity. They hope to reveal interactions between genes and the environment to clarify disease onset.
Behavioral studies are also included, focusing on how individual behaviors, such as smoking, exercise, and stress management, contribute to disease. This includes analyzing behavioral patterns and their correlation with disease development to inform public health initiatives.
Data Integration and Analysis
A key challenge is integrating and analyzing the vast amounts of data collected. To tackle this, the PDAI utilizes advanced computational methods and artificial intelligence. These tools help identify patterns, relationships, and potential targets for therapeutic intervention that might otherwise be missed.
The initiative also emphasizes data sharing and collaboration among researchers. A centralized database will be established to facilitate the exchange of information and accelerate the pace of discovery. This open-access approach aims to maximize the impact of the research and ensure that findings are widely disseminated.
Potential Impact and Future Directions
The PDAI has the potential to revolutionize our understanding of diseases and transform healthcare. By identifying common disease pathways, researchers hope to develop broad-spectrum therapies that can target multiple conditions simultaneously. The project also holds promise for personalized medicine, where treatment strategies are tailored to an individual's unique genetic and environmental profile.
"This initiative represents a paradigm shift in how we approach disease research," said Dr. Emily Carter, lead investigator for the PDAI at the NIH. "By integrating data across multiple disciplines, we can gain a holistic understanding of disease processes and develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies."
The PDAI is also committed to addressing health disparities. By including diverse populations in the study, researchers aim to identify genetic and environmental factors that contribute to differences in disease rates among various groups. This knowledge can then be used to develop targeted interventions to reduce health inequities.
A Human-Interest Angle
Consider the story of Maria Rodriguez, a participant in the PDAI. Her family has a history of diabetes and heart disease. She hopes the study will uncover the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to these conditions, leading to better prevention strategies for her children.
Maria's participation, and that of countless others, underscores the importance of this research and the potential for real-world impact on individuals and families affected by disease. Her contribution highlights the human dimension of this large-scale scientific endeavor.
The PDAI is more than just a scientific endeavor; it's a testament to the power of collaboration and innovation. By bringing together experts from around the world and harnessing the latest technologies, this initiative is poised to make significant strides in our fight against disease and improve the health and well-being of people everywhere.