The Ability Of Stimulants To Improve Mental Performance

The pressure to perform at peak mental capacity has never been higher. From demanding workplaces to fiercely competitive academic environments, individuals are constantly seeking an edge. This has led to a growing, and often controversial, interest in cognitive enhancement, particularly through the use of stimulants.
At the heart of this debate lies the question: Do stimulants truly improve mental performance, and at what cost? This article will delve into the science behind stimulant use for cognitive enhancement, exploring the potential benefits, risks, ethical considerations, and long-term implications. We will examine the perspectives of researchers, medical professionals, and individuals who have personal experience with these substances to provide a balanced and comprehensive overview of this complex issue.
The Science of Stimulants and the Brain
Stimulants, such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine (Adderall), work by increasing the levels of certain neurotransmitters in the brain, primarily dopamine and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters play crucial roles in attention, focus, motivation, and wakefulness.
By boosting these neurotransmitter levels, stimulants can enhance alertness and reduce fatigue. This can lead to improved concentration and a greater ability to focus on tasks, particularly those that require sustained attention. Studies have shown that stimulants can improve performance on cognitive tests, such as working memory and processing speed, in some individuals.
However, the effects of stimulants are not universal. Individual responses can vary significantly depending on factors such as genetics, pre-existing conditions, dosage, and the specific stimulant used.
Potential Benefits: Enhanced Performance and Focus
For individuals diagnosed with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), stimulants are a first-line treatment. They help to regulate neurotransmitter levels and improve focus, attention, and impulse control, leading to significant improvements in daily functioning.
Beyond ADHD, some individuals without the disorder use stimulants for cognitive enhancement, often referred to as "off-label" use. They might seek improved focus for studying, increased productivity at work, or enhanced creativity. The perceived benefits can include improved concentration, increased motivation, and a feeling of mental clarity.
Anecdotal evidence suggests that some professionals in high-pressure fields, such as finance and tech, use stimulants to maintain a competitive edge. However, these benefits must be weighed against the potential risks and ethical considerations.
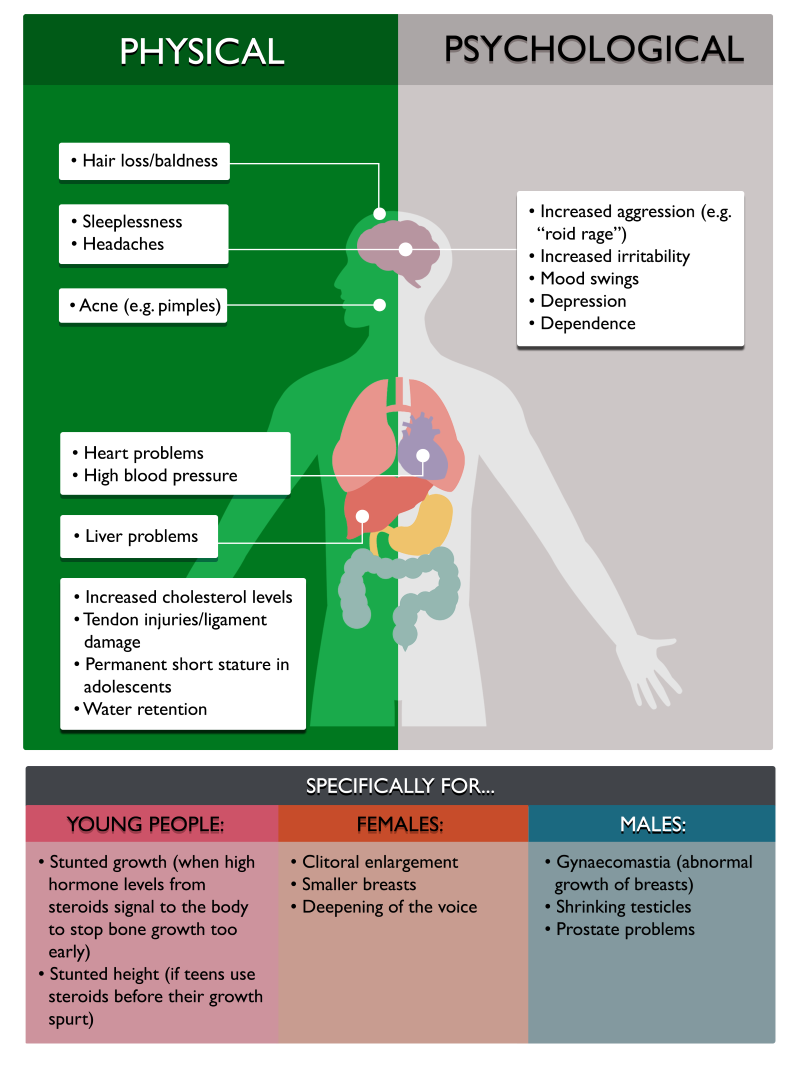
The Risks: Side Effects and Long-Term Consequences
Stimulants are not without their risks. Common side effects include insomnia, anxiety, decreased appetite, and increased heart rate and blood pressure.
More serious side effects, although rare, can include cardiovascular problems, psychiatric disturbances, and even sudden death. The long-term effects of stimulant use on the brain and body are still not fully understood, particularly in individuals without ADHD.
Furthermore, stimulants can be addictive. Prolonged use can lead to dependence, tolerance (requiring higher doses to achieve the same effect), and withdrawal symptoms upon cessation.
Ethical Considerations: Fairness and Equity
The use of stimulants for cognitive enhancement raises significant ethical questions. Is it fair for some individuals to gain an advantage through the use of drugs, while others do not?
The use of stimulants could exacerbate existing inequalities, potentially creating a two-tiered system where those with access to these drugs have a significant advantage in academic and professional settings.
"The potential for cognitive enhancement to exacerbate existing social inequalities is a serious concern," said Dr. Sarah Jones, a bioethicist at the University of California, Berkeley.
There are also concerns about coercion and pressure to use stimulants in highly competitive environments. Students may feel compelled to use stimulants to keep up with their peers, even if they are uncomfortable with the risks. "We need to have open and honest conversations about the potential downsides of cognitive enhancement," stated a recent report from the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
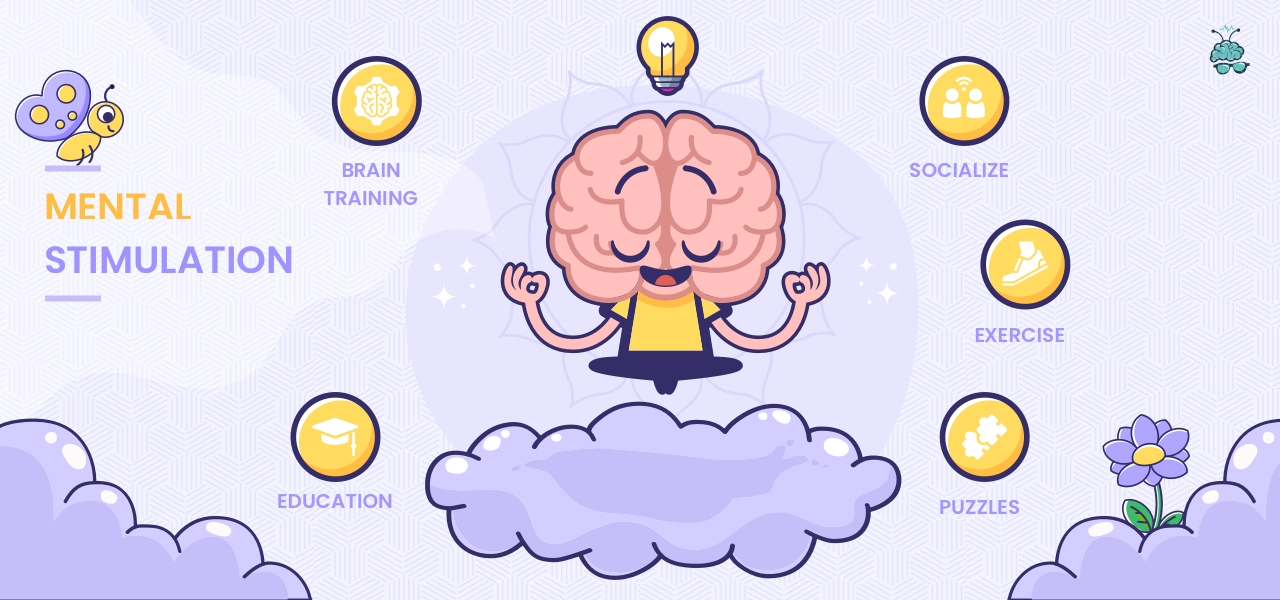
Alternatives to Stimulants: Non-Pharmacological Approaches
Fortunately, there are many non-pharmacological approaches to improving mental performance. These include regular exercise, a healthy diet, adequate sleep, and mindfulness practices.
Cognitive training exercises, such as brain games and puzzles, can also help to improve memory and attention. Mindfulness techniques, such as meditation, can reduce stress and improve focus. Prioritizing sleep is crucial for cognitive function. "Sleep deprivation can significantly impair cognitive performance," according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
These strategies offer a safer and more sustainable approach to cognitive enhancement, without the risks and ethical concerns associated with stimulants. Furthermore, they provide broad benefits for overall health and well-being.
Looking Ahead: Research and Regulation
More research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of stimulant use for cognitive enhancement. Studies should focus on the impact of stimulants on brain development, cardiovascular health, and mental well-being.
Regulations regarding the use of stimulants for cognitive enhancement are varied and often unclear. Some countries have stricter regulations than others, and enforcement can be challenging.
A balanced approach is needed, one that protects individuals from the potential risks of stimulant use while allowing for responsible access for those who genuinely need them. Education and awareness are crucial to ensure that individuals are making informed decisions about their health and well-being. Further investigation into the efficacy of non-pharmaceutical alternative is imperative.









.jpg)



.jpg)


