The First Step Toward Creating Content For Patients Is

A groundbreaking consensus on patient content creation has emerged, signaling a pivotal shift in healthcare communication. Experts finalized a foundational framework prioritizing accessibility and patient understanding, marking the first concrete step towards standardized, effective health information.
This initiative aims to bridge the communication gap between healthcare providers and patients, empowering individuals with the knowledge needed for informed decision-making. The lack of clear, understandable content has long been a barrier to effective healthcare, and this framework seeks to dismantle that barrier.
The Genesis of the Framework
The framework's development was spearheaded by the National Institute of Health (NIH) in collaboration with the American Medical Association (AMA) and several patient advocacy groups. After months of deliberation, the coalition, comprised of 30 key stakeholders, reached unanimous agreement.
The agreement occurred on October 26, 2023, during a closed-door meeting held at the NIH headquarters in Bethesda, Maryland. The primary goal was to establish minimum standards for all patient-facing content, regardless of its format or delivery method.
Key Components of the Framework
The framework emphasizes three core principles: simplicity, accuracy, and cultural sensitivity. All content must be written at a reading level accessible to the average adult, around the 6th to 8th grade level. This directly addresses concerns about complex medical jargon hindering patient comprehension.
Accuracy is paramount, requiring all information to be based on the latest evidence-based research. Content must undergo rigorous review by medical professionals to ensure its validity and reliability.
Cultural sensitivity is another crucial aspect, demanding that content be tailored to diverse audiences, considering language, ethnicity, and cultural beliefs. This includes providing materials in multiple languages and ensuring that visuals are representative of the patient population.
Who Will Be Impacted?
The new framework will impact a wide range of stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem. This includes hospitals, clinics, pharmaceutical companies, and health insurance providers.
Any organization that produces content intended for patients will be required to adhere to these standards. The NIH plans to provide resources and training to help organizations implement the framework effectively.
Patients themselves are the ultimate beneficiaries of this initiative. By receiving clear, accurate, and culturally sensitive information, they will be better equipped to manage their health and make informed decisions about their care.
The Importance of Plain Language
A key element of the framework is the use of plain language. This means avoiding jargon, using simple sentence structures, and defining technical terms clearly.
Studies have shown that patients are more likely to understand and remember information presented in plain language. This leads to better adherence to treatment plans and improved health outcomes. According to a 2022 study by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ), patients who receive information in plain language are 26% more likely to follow their doctor's instructions.
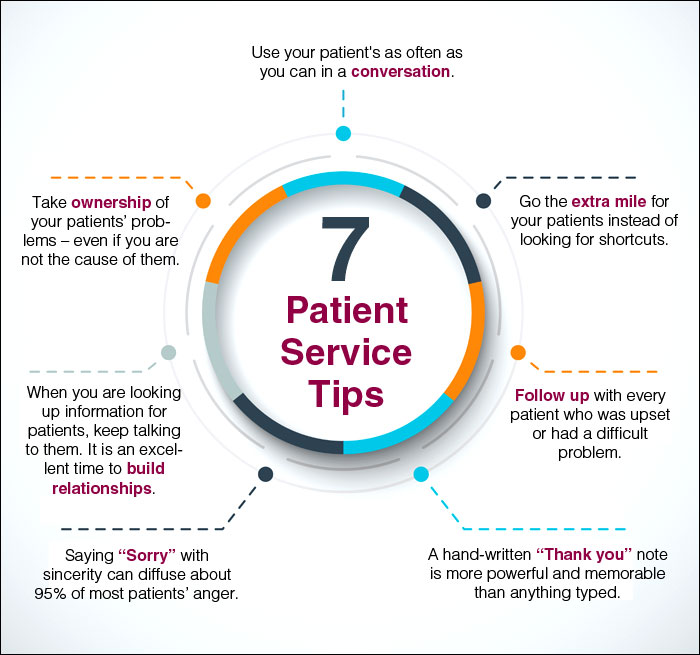
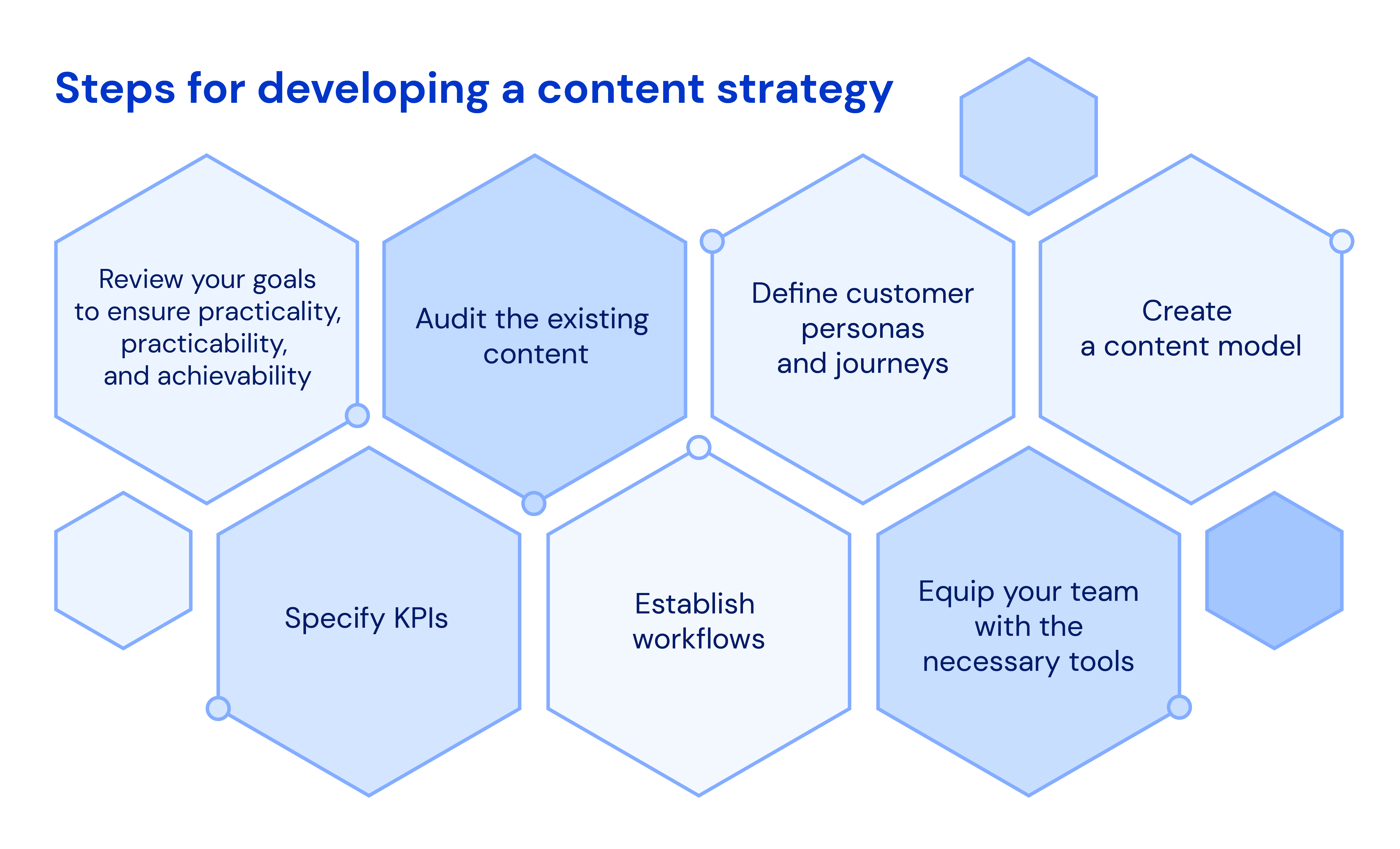
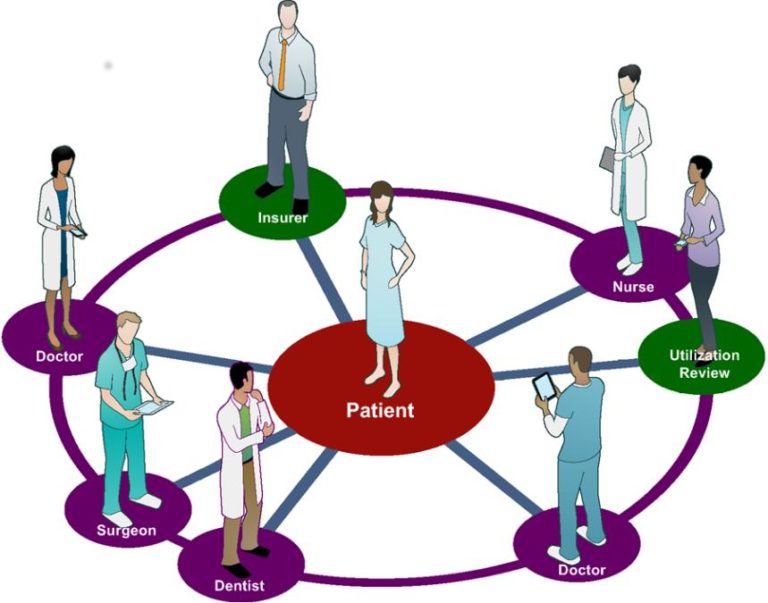
The framework also encourages the use of visual aids, such as diagrams and illustrations, to enhance understanding. These visuals can help to break down complex concepts and make them more accessible to patients.
Implementation and Enforcement
The framework is not legally binding, but the NIH and AMA are strongly encouraging all healthcare organizations to adopt it voluntarily. Several major hospital systems have already pledged to implement the framework across their institutions.
The NIH is also working with accreditation bodies to incorporate the framework into their standards. This would create a stronger incentive for organizations to comply.
Long-term enforcement strategies are still under discussion. However, the NIH intends to monitor the implementation of the framework and track its impact on patient outcomes.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the widespread support for the framework, some challenges remain. One challenge is ensuring that all healthcare professionals are trained in plain language communication.
Another challenge is adapting the framework to different types of content, such as websites, mobile apps, and social media posts. The NIH is developing specific guidelines for each of these formats.
Future directions include exploring the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to generate patient-friendly content. AI could be used to automatically translate complex medical jargon into plain language.
Next Steps
The NIH will release a comprehensive implementation guide by November 15, 2023. This guide will provide detailed instructions on how to adopt the framework.
The AMA will host a series of webinars to train healthcare professionals on plain language communication. These webinars will be available to all healthcare providers, regardless of their affiliation.
Ongoing monitoring and evaluation will be crucial to ensure the framework's effectiveness. The NIH plans to conduct regular surveys to assess patient understanding and satisfaction with healthcare information.