The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy Pdf

Imagine a bustling marketplace, vendors hawking their wares, customers haggling for the best prices, and new stalls popping up seemingly overnight. The air is thick with competition, a constant push and pull that determines who thrives and who fades away. This dynamic, though simplified, mirrors the complex forces at play in the business world, forces that savvy strategists must understand to navigate the ever-changing landscape.
At the heart of understanding this competitive environment lies a framework developed by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter. His "Five Forces" model, outlined in his seminal work "The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy," provides a powerful tool for analyzing industry attractiveness and developing sustainable competitive advantage. This framework, often accessed through a simple PDF, empowers businesses to understand the power dynamics that influence their profitability and strategic options.
The Five Forces framework isn't just an academic exercise; it's a practical guide for businesses of all sizes. Understanding these forces allows companies to make informed decisions about entering new markets, developing new products, and ultimately, achieving lasting success. It's about more than just reacting to the competition; it's about proactively shaping the competitive landscape to your advantage.
The Genesis of a Strategic Framework
The origins of the Five Forces model can be traced back to the late 1970s, a period of significant economic change and increasing global competition. Michael Porter, then a young professor at Harvard, sought to move beyond traditional economic models that focused primarily on industry structure. He recognized the need for a more comprehensive framework that considered a wider range of factors influencing industry profitability.
Published in the Harvard Business Review in 1979 and later expanded in his book "Competitive Strategy" (1980), the Five Forces framework quickly gained traction among academics and business practitioners alike. Its intuitive nature, coupled with its practical application, made it an indispensable tool for strategic analysis. The enduring popularity of the Five Forces, easily accessible through numerous PDF documents and resources, speaks volumes about its relevance in today's dynamic business environment.
The Five Forces Explained
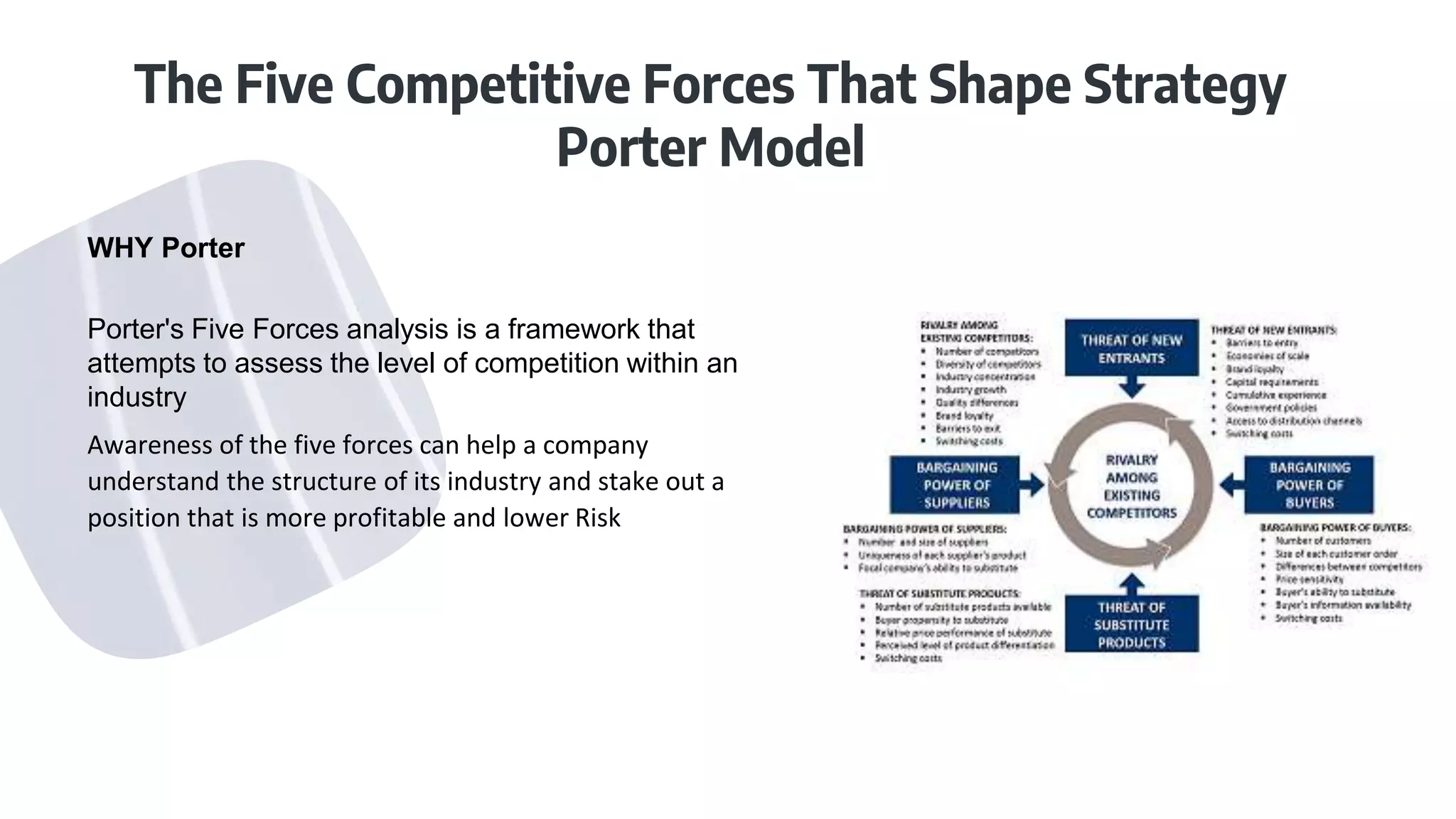
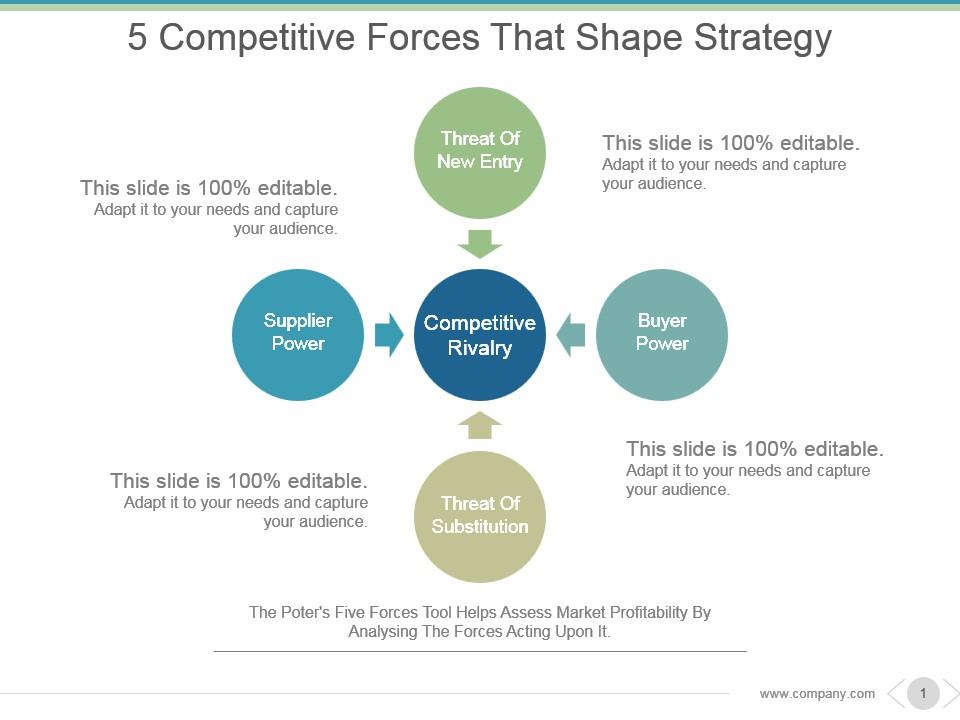
The Five Forces model examines five key competitive forces that collectively determine the intensity of competition and the attractiveness of an industry.
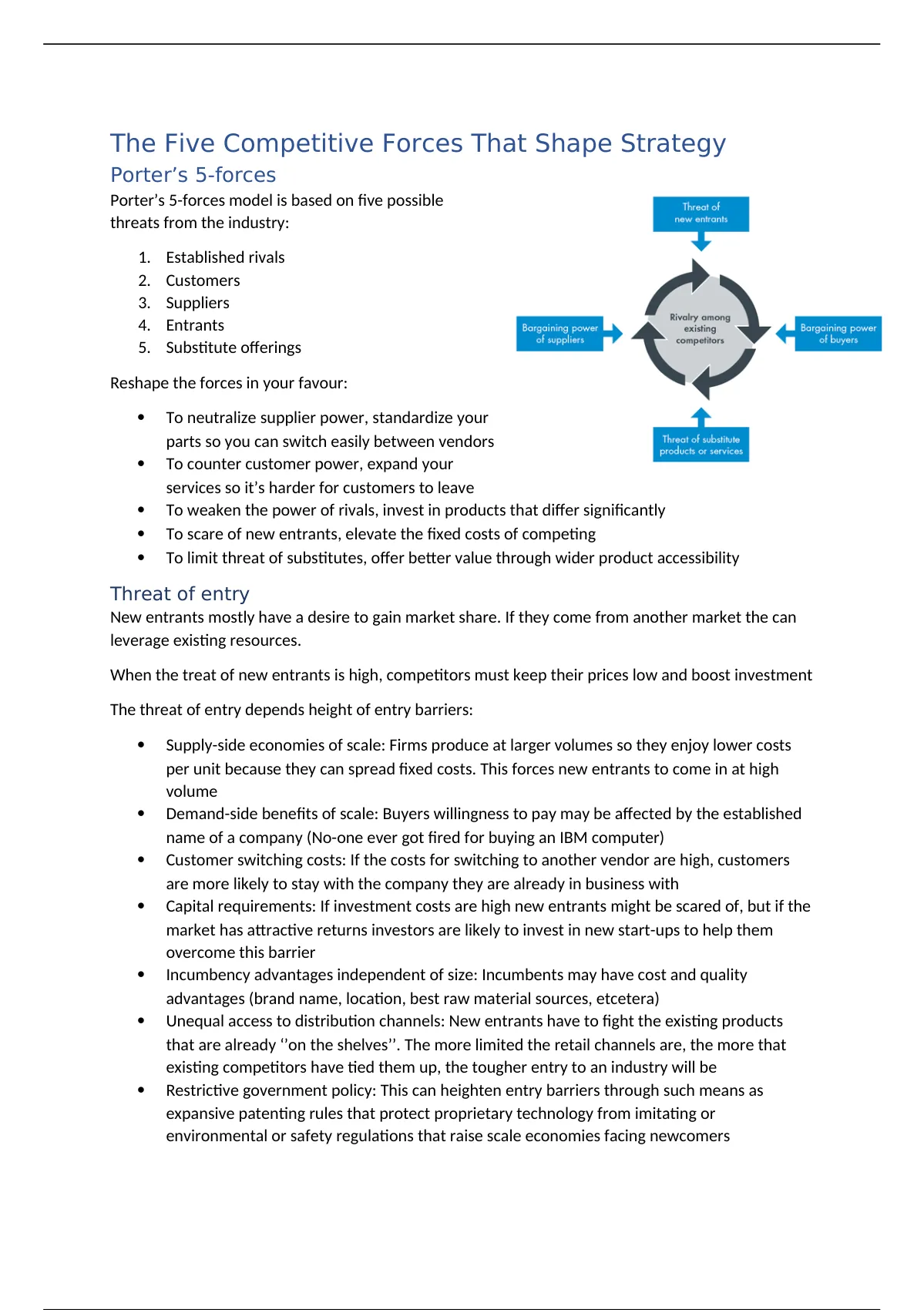
1. Threat of New Entrants
This force considers how easy or difficult it is for new companies to enter the industry. High barriers to entry, such as significant capital requirements, strong brand loyalty, or government regulations, reduce the threat of new entrants, making the industry more attractive. Conversely, low barriers to entry increase the threat, leading to increased competition and potentially lower profitability.
For example, the airline industry faces significant barriers to entry due to the high cost of aircraft, regulatory hurdles, and the need for established routes. This limits the number of new airlines that can effectively compete with existing players.
2. Bargaining Power of Suppliers
This force examines the ability of suppliers to drive up prices. Suppliers have strong bargaining power when there are few substitutes for their products, when the industry is not a significant customer for the supplier group, or when suppliers threaten to integrate forward into the industry. A PDF overview of the forces will usually contain a matrix to analyze supplier power.
Consider the relationship between Intel and computer manufacturers. Intel, as a major supplier of processors, wields considerable power due to its dominant market share and the limited number of viable alternatives. This allows Intel to command premium prices.
3. Bargaining Power of Buyers
This force assesses the ability of customers to drive down prices. Buyers have strong bargaining power when there are many suppliers, when the products are standardized, or when buyers can easily switch to alternative products. This is usually explained in detail in any PDF outlining the Five Forces.
The retail industry is a prime example, where large retailers like Walmart can exert significant pressure on suppliers due to their massive purchasing volume and the availability of alternative suppliers. This forces suppliers to accept lower prices and tighter margins.
4. Threat of Substitute Products or Services
This force considers the availability of alternative products or services that can satisfy the same customer need. A strong threat of substitutes limits the price that companies can charge and reduces industry profitability. Identifying potential substitutes is crucial for strategic planning, often highlighted in PDF guides on the framework.
For instance, the rise of video streaming services like Netflix and Hulu has posed a significant threat to traditional cable television providers. Consumers can now access a vast library of content at a lower price, leading to a decline in cable subscriptions.
5. Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
This force examines the intensity of competition among existing players in the industry. High rivalry can lead to price wars, increased marketing spending, and reduced profitability. Factors contributing to high rivalry include a large number of competitors, slow industry growth, and high exit barriers. A comprehensive understanding of these factors, often illustrated in PDF diagrams, is essential for strategic decision-making.
The soft drink industry, dominated by Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, is characterized by intense rivalry. The two companies engage in constant marketing battles, price promotions, and product innovation to gain market share, resulting in a highly competitive landscape.
Applying the Five Forces: A Strategic Imperative
By analyzing each of these five forces, businesses can gain a clear understanding of the competitive dynamics within their industry. This understanding allows them to identify opportunities to improve their competitive position and increase profitability. A thorough PDF analysis of the Five Forces model offers insights into how to leverage these factors.
For example, a company might choose to focus on differentiating its products to reduce the threat of substitutes. Alternatively, it might seek to build stronger relationships with suppliers to secure preferential pricing and ensure a reliable supply chain. The key is to develop a strategy that leverages the company's strengths to mitigate the impact of the competitive forces.
The Five Forces framework also plays a crucial role in evaluating the attractiveness of different industries. By assessing the strength of each force, companies can determine whether an industry offers the potential for long-term profitability. This information can inform decisions about entering new markets, exiting existing markets, and allocating resources strategically.
Beyond the Framework: Adaptability and Evolution
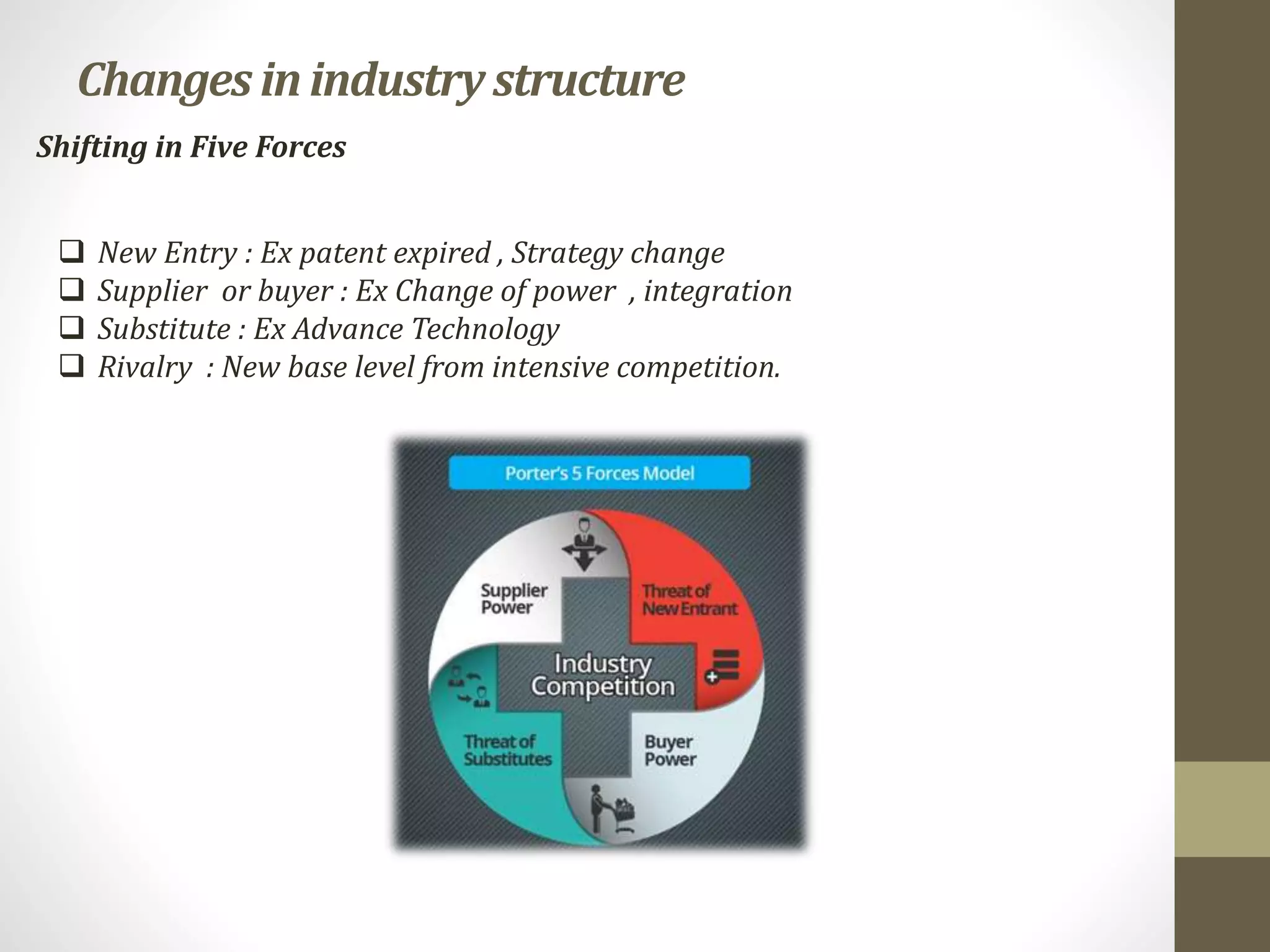
While the Five Forces model remains a powerful tool for strategic analysis, it's important to recognize that the business environment is constantly evolving. New technologies, changing consumer preferences, and globalization are all reshaping the competitive landscape. A static approach is insufficient; continuous monitoring of market dynamics is critical.
Some critics argue that the Five Forces model is too static and does not adequately account for disruptive innovation or the role of government regulation. However, Michael Porter himself has acknowledged these limitations and emphasized the need for a dynamic and adaptable approach to strategic analysis. Integrating factors like technological disruption and regulatory changes can enrich the Five Forces analysis.
The availability of the "The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy PDF" serves as a readily accessible resource. It enables managers and students alike to engage with the framework and adapt it to their specific contexts. This active engagement ensures that the Five Forces model remains relevant and valuable in today's complex business world.
A Lasting Legacy
The Five Forces framework, as detailed in countless PDF documents and academic papers, continues to be a cornerstone of strategic management. It provides a valuable framework for understanding the competitive dynamics of an industry and developing strategies for achieving sustainable competitive advantage. Its simplicity and applicability have made it a favorite among business leaders and academics alike.
Perhaps the greatest testament to the Five Forces model is its enduring relevance. In a world of constant change, the fundamental principles of competition remain the same. By understanding these principles, businesses can navigate the challenges and opportunities of the marketplace and create lasting value. It is not just about the PDF, but about the power of the insights it provides.
The framework encourages a proactive approach to strategy, prompting businesses to anticipate future changes and adapt their strategies accordingly. In essence, "The Five Competitive Forces That Shape Strategy" offers a lasting legacy: a framework for understanding, adapting, and thriving in a competitive world.