The Income Statement Measures Performance Over Some Period Of Time.

In an era defined by rapid economic shifts and volatile market conditions, understanding the financial health of businesses is more crucial than ever. Investors, creditors, and managers alike rely on a key financial document to gauge a company's profitability: the income statement. Its interpretation can mean the difference between informed strategic decisions and costly missteps.
This article delves into the significance of the income statement as a performance measure over a specific period, examining its components, limitations, and the critical role it plays in evaluating a company’s financial well-being. We will explore how this financial snapshot informs stakeholders, shapes investment strategies, and ultimately contributes to the overall stability of the economic ecosystem. Understanding the intricacies of the income statement is paramount for anyone navigating the complexities of modern finance.
Deciphering the Income Statement: A Performance Scorecard
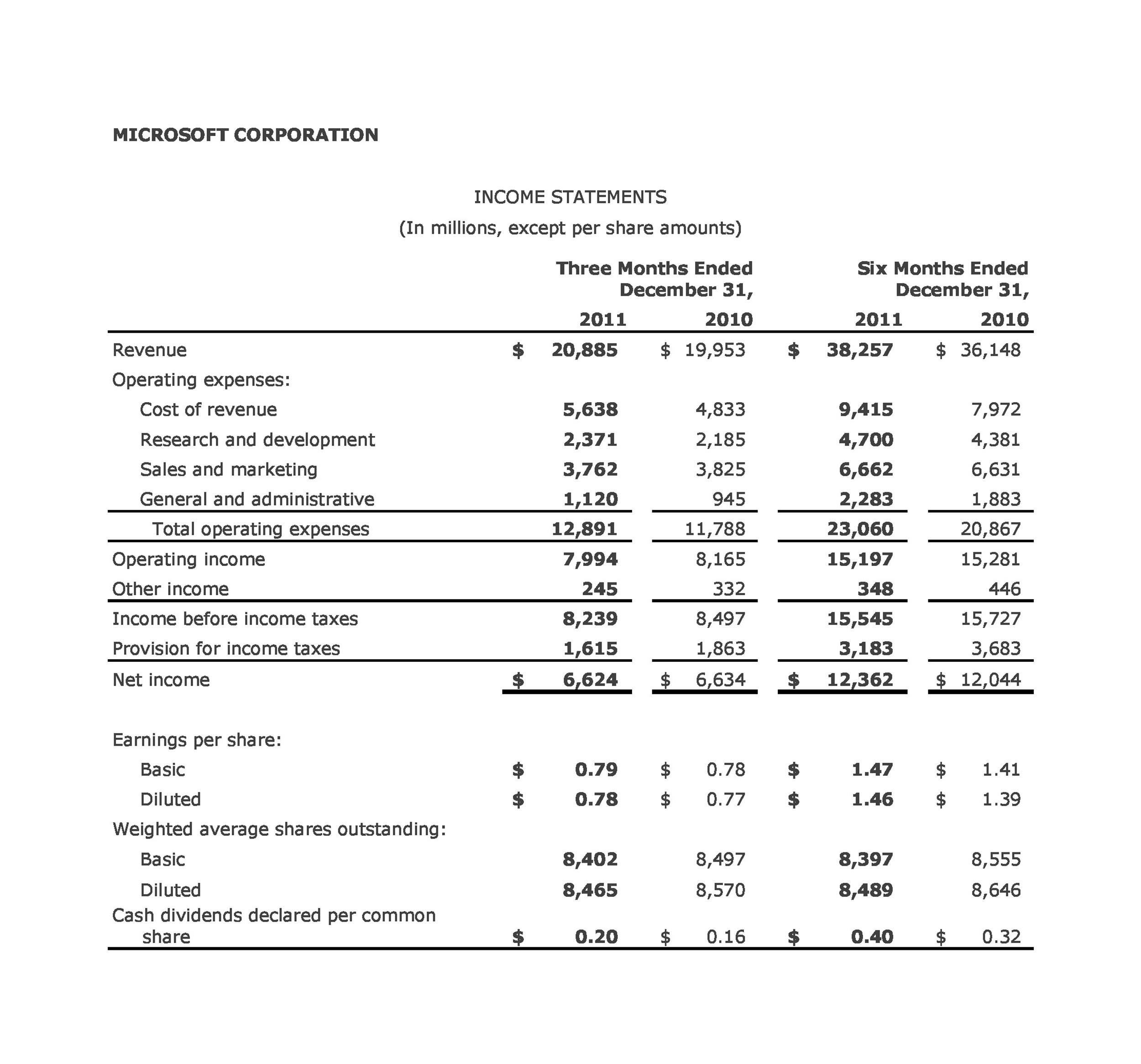
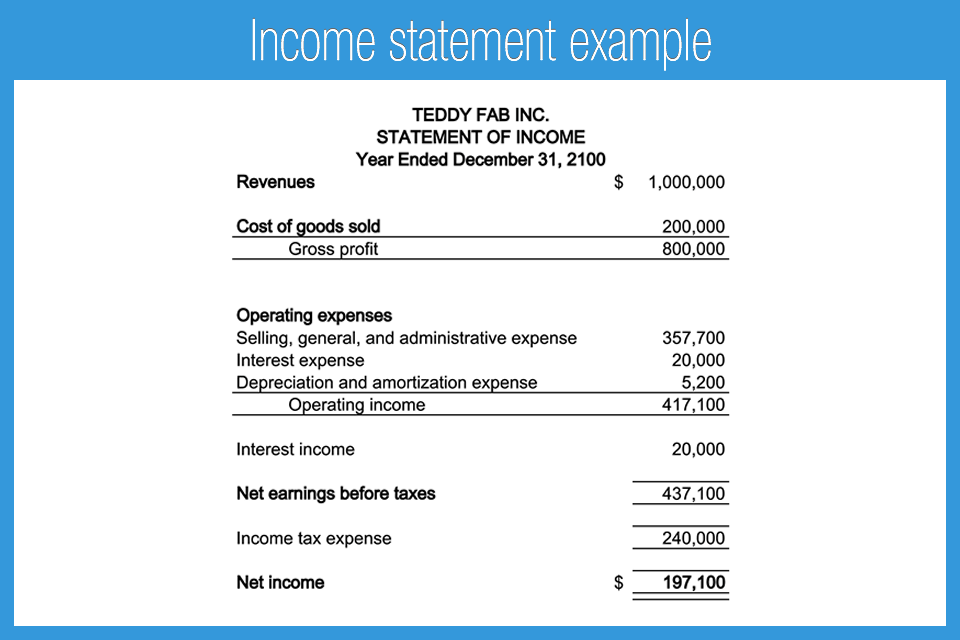
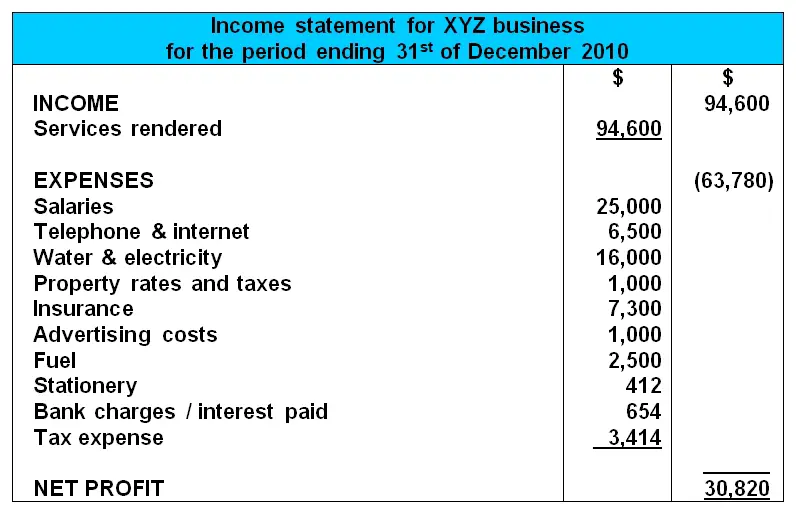
The income statement, often referred to as the profit and loss (P&L) statement, provides a summary of a company's revenues, expenses, and profits over a defined period. This period can be a month, a quarter, or a year, offering a temporal view of financial performance.
The fundamental equation underpinning the income statement is simple: Revenue - Expenses = Net Income. This seemingly straightforward equation provides a wealth of information about a company’s operational efficiency and profitability.
Key Components of the Income Statement
The income statement typically begins with revenue, representing the total amount of money earned from the sale of goods or services. Analyzing revenue trends reveals insights into a company's market position and sales effectiveness.
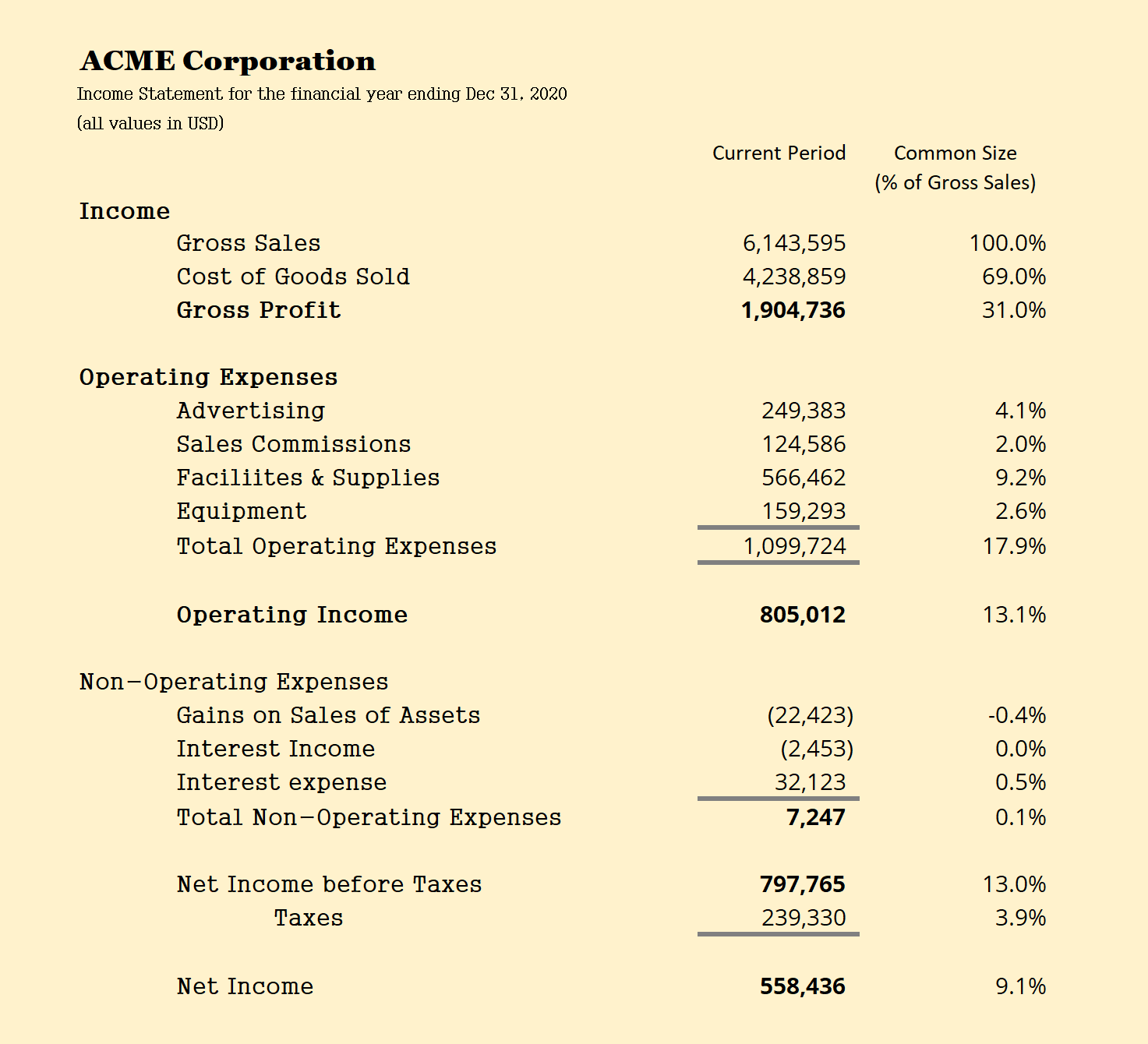
Next, cost of goods sold (COGS), details the direct costs associated with producing goods or delivering services. Subtracting COGS from revenue yields the gross profit, a crucial indicator of production efficiency.
Operating expenses, including selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A), are then deducted to arrive at operating income. Operating income reflects the profitability of a company's core business operations before considering interest and taxes.
Interest expense, representing the cost of borrowing money, and other non-operating items are accounted for next. Finally, income taxes are deducted, resulting in net income, the "bottom line" of the income statement, which represents the company's profit after all expenses and taxes.
The Income Statement as a Performance Indicator
The income statement is not merely a historical record; it's a powerful tool for assessing performance and making informed projections. By analyzing trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability, stakeholders can gain valuable insights into a company's operational efficiency and financial health.
For investors, the income statement provides essential data for evaluating a company's earnings potential and making investment decisions. A consistent track record of increasing revenue and profitability often signals a healthy and well-managed company.
Creditors use the income statement to assess a company's ability to repay its debts. A strong income stream indicates a greater likelihood of meeting financial obligations.
Management utilizes the income statement to monitor performance against budget, identify areas for improvement, and make strategic decisions. Detailed analysis of expense categories can reveal opportunities to cut costs and improve efficiency.
Limitations of the Income Statement
While invaluable, the income statement is not without its limitations. It's crucial to recognize these constraints to avoid drawing misleading conclusions.
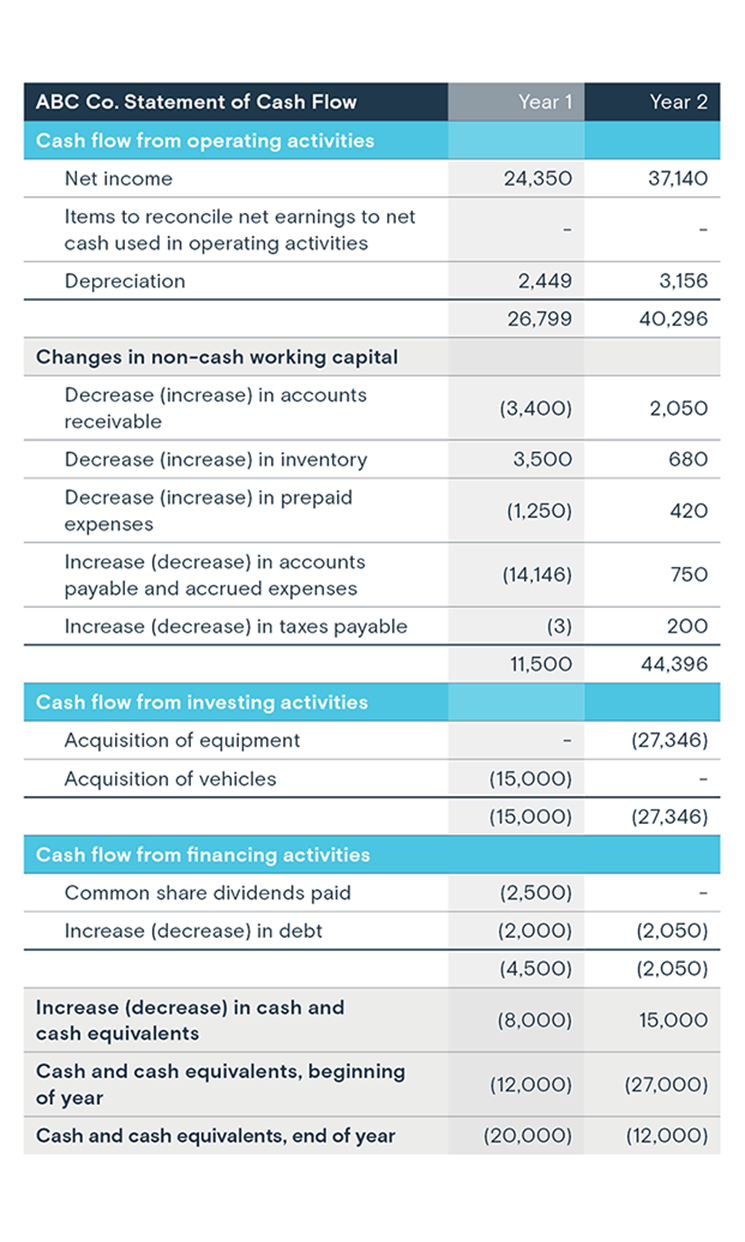
The income statement relies on accrual accounting, which recognizes revenue and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of when cash changes hands. This can sometimes create a disconnect between reported profits and actual cash flow.
Furthermore, the income statement is susceptible to accounting manipulation. Companies may use aggressive accounting practices to inflate earnings or conceal losses, making it essential to critically evaluate the numbers presented.
The income statement only provides a snapshot of performance over a specific period, neglecting long-term trends and future prospects. A single year's income statement provides limited insights into a company’s sustainability.
"The income statement, while crucial, should be analyzed in conjunction with other financial statements, such as the balance sheet and cash flow statement, for a comprehensive understanding of a company's financial health," – Dr. Anya Sharma, Professor of Finance, University of California, Berkeley.
The Future of Income Statement Analysis
As technology advances and the business landscape evolves, so too does the analysis of income statements. Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly being used to extract deeper insights from income statement data and identify potential risks and opportunities.
Sophisticated financial modeling techniques enable analysts to forecast future earnings based on historical income statement data and macroeconomic trends. This helps investors and managers make more informed decisions.
Furthermore, the increasing focus on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors is prompting companies to include non-financial metrics in their reporting, offering a more holistic view of performance. The income statement, while traditionally focused on financial metrics, is gradually being supplemented with ESG data to provide a more comprehensive assessment of a company's value.
Ultimately, the income statement remains a cornerstone of financial analysis. By understanding its components, limitations, and evolving role, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of the business world and make sound financial decisions. Its continued relevance in the age of big data and sophisticated analytical tools underscores its fundamental importance to the global economy. The ability to effectively interpret an income statement is a crucial skill for any individual seeking to understand and participate in the financial markets.









:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Income_Statement_Aug_2020-01-6b926d415b674b13b56bede987b7a2fb.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ScreenShot2022-04-26at10.39.54AM-4a117e7e494c422ca6480746c97612a8.png)