The Rationale Behind Related Diversification Is To

In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and volatile market conditions, companies are constantly seeking strategies to achieve sustainable growth and maintain a competitive edge. One such strategy, related diversification, has become a cornerstone of corporate expansion for many businesses. The decision to diversify, however, is not taken lightly, as it involves significant investment and a complex interplay of strategic considerations.
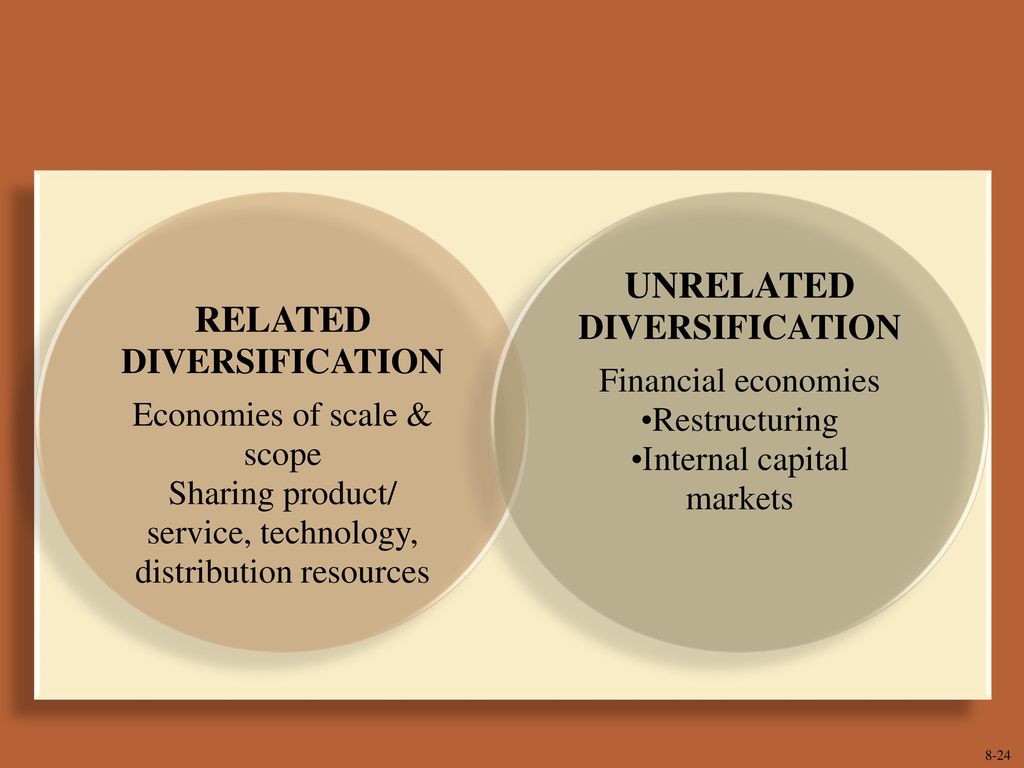
The rationale behind related diversification—expanding into business activities similar to a company's existing operations—rests on the principle of leveraging existing resources and capabilities to gain a competitive advantage in new markets. This article delves into the strategic drivers behind this approach, exploring how companies capitalize on synergies, mitigate risks, and foster innovation through related diversification. It will also analyze the potential pitfalls and complexities that companies must navigate to ensure success.
Core Rationale: Leveraging Synergies
The primary driver behind related diversification is the potential for synergies. These synergies arise from the ability to share resources, capabilities, and expertise across different business units.
For example, a company with strong research and development (R&D) capabilities in pharmaceuticals may diversify into related areas such as medical devices or diagnostics. By leveraging its existing R&D infrastructure and expertise, the company can reduce costs, accelerate innovation, and create a more robust product portfolio.
Another key synergy lies in shared distribution channels and marketing resources. A food manufacturer with a well-established distribution network can easily introduce new, related food products, benefiting from economies of scale and brand recognition.
Operational Efficiencies
Related diversification can lead to significant operational efficiencies. Shared services, such as human resources, finance, and IT, can be centralized, reducing overhead costs and improving overall efficiency.
Companies can also benefit from economies of scale in procurement and manufacturing. By consolidating purchasing power and optimizing production processes across multiple business units, they can lower costs and improve profitability.
Procter & Gamble (P&G) is a prime example, leveraging its vast distribution network and marketing expertise across a wide range of consumer products, from detergents to beauty products.
Risk Mitigation Through Diversification
Related diversification also serves as a crucial risk mitigation strategy. By expanding into related markets, companies reduce their dependence on a single product or industry, lessening the impact of economic downturns or industry-specific challenges.
A company operating solely in the automotive industry, for example, may face significant losses during a recession. Diversifying into related areas, such as automotive parts manufacturing or transportation services, can help cushion the blow.
This strategy allows companies to spread their risk across multiple business units, creating a more stable and resilient organization.
Financial Stability
Diversification can improve a company's financial stability by generating multiple revenue streams. This can lead to a more consistent cash flow and reduce the volatility of earnings.
Furthermore, diversification can increase a company's access to capital. Investors often view diversified companies as less risky, making it easier to secure funding for future growth and expansion.
According to a report by Standard & Poor's, companies with diversified revenue streams tend to have higher credit ratings and lower borrowing costs.
Fostering Innovation and Growth
Related diversification can foster innovation and drive growth by exposing companies to new ideas, technologies, and markets. This can lead to the development of new products and services, as well as the improvement of existing ones.
By entering new markets, companies gain access to new customer segments and can learn from their experiences. This knowledge can be used to refine existing products and services, as well as to develop new ones that meet the evolving needs of customers.
Companies can also leverage their existing R&D capabilities to develop new technologies and innovations that can be applied across multiple business units.
Creating New Opportunities
Diversification can create new opportunities for employees, fostering a culture of innovation and learning. Employees can gain new skills and experiences by working in different business units, leading to increased job satisfaction and retention.
Furthermore, diversification can attract talented employees who are seeking opportunities for growth and development. This can help companies build a more skilled and motivated workforce.
Google, for instance, has diversified into various related fields, such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and autonomous vehicles, attracting top talent and fostering a culture of innovation.
Potential Challenges and Pitfalls
While related diversification offers numerous benefits, it also presents significant challenges and pitfalls. One of the biggest challenges is the potential for increased complexity. Managing multiple business units can be difficult, especially if they operate in different industries or geographic regions.
Companies must also be careful not to over-diversify, as this can lead to a loss of focus and a decline in performance. It is important to choose diversification opportunities that are closely related to the company's existing operations and that leverage its core competencies.
Another potential pitfall is the risk of cultural clashes between different business units. Companies must take steps to integrate their cultures and ensure that all employees are aligned with the company's overall goals and values.
The Importance of Strategic Fit
Successful related diversification requires a strong strategic fit between the existing business and the new venture. This means that the two businesses should have complementary resources, capabilities, and strategies.
If there is not a strong strategic fit, the diversification effort is likely to fail. Companies must carefully evaluate potential diversification opportunities to ensure that they align with their overall strategic goals.
A study by McKinsey & Company found that companies with a strong strategic fit between their existing business and their diversification efforts were more likely to achieve superior financial performance.
Conclusion: A Strategic Imperative
The rationale behind related diversification is multifaceted, encompassing the pursuit of synergies, the mitigation of risks, and the fostering of innovation. While challenges exist, the potential rewards are substantial, making it a strategic imperative for companies seeking sustainable growth and long-term competitive advantage.
However, success hinges on careful planning, a thorough understanding of market dynamics, and a commitment to integrating new ventures into the company's overall strategic framework. As markets continue to evolve, related diversification will likely remain a critical tool for companies navigating the complexities of the modern business landscape.
Moving forward, companies must prioritize strategic alignment, cultural integration, and a relentless focus on leveraging synergies to unlock the full potential of related diversification. This approach will enable them to not only survive but thrive in an increasingly competitive global economy.