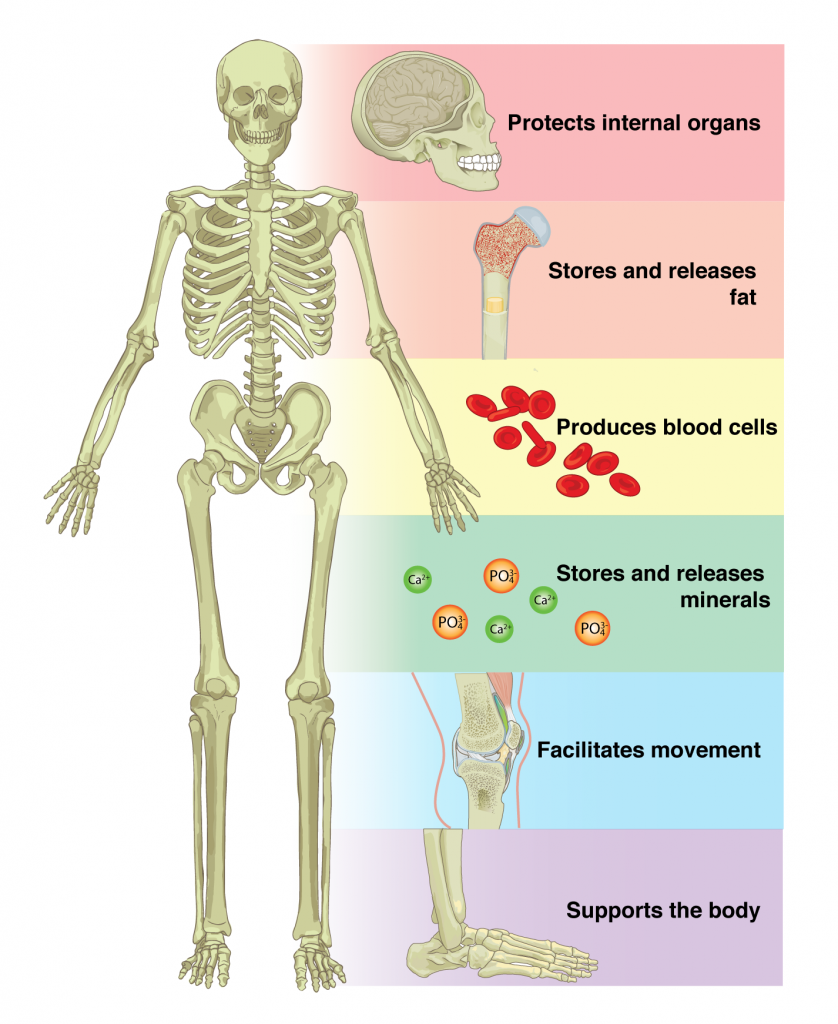
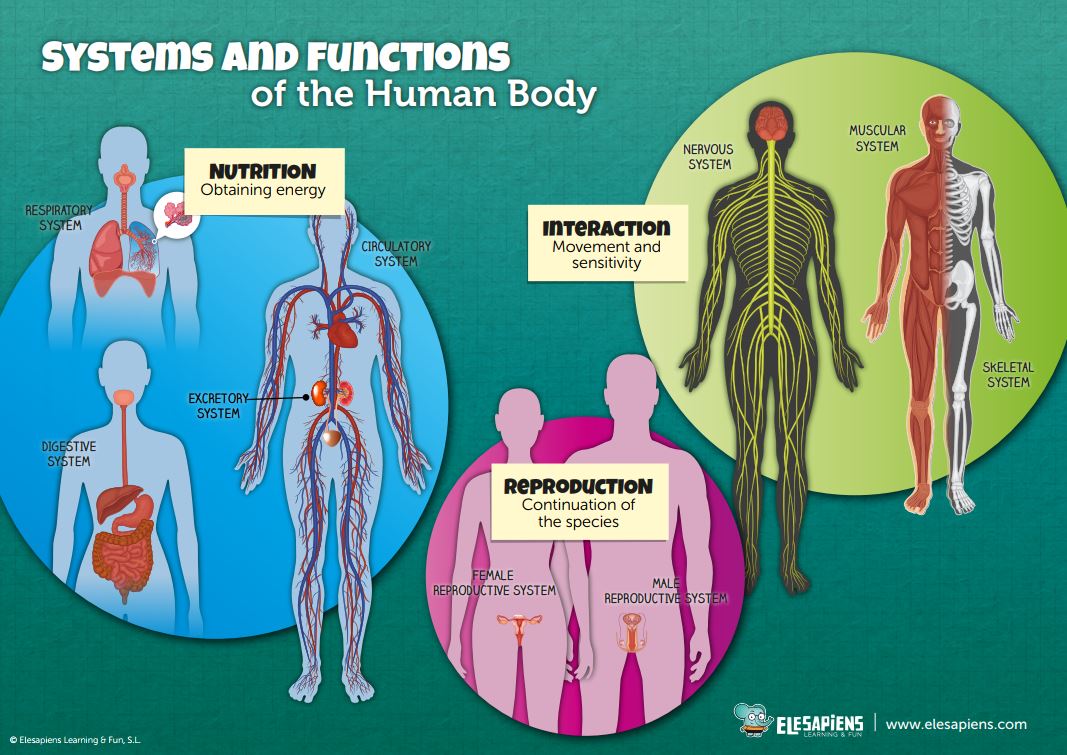
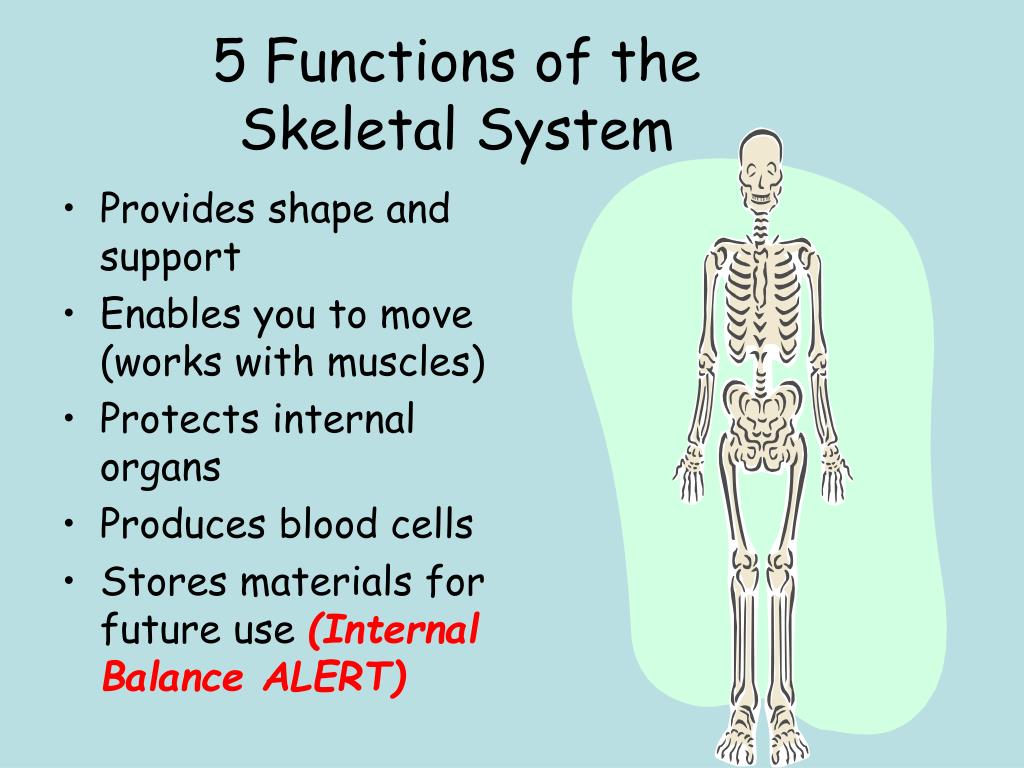
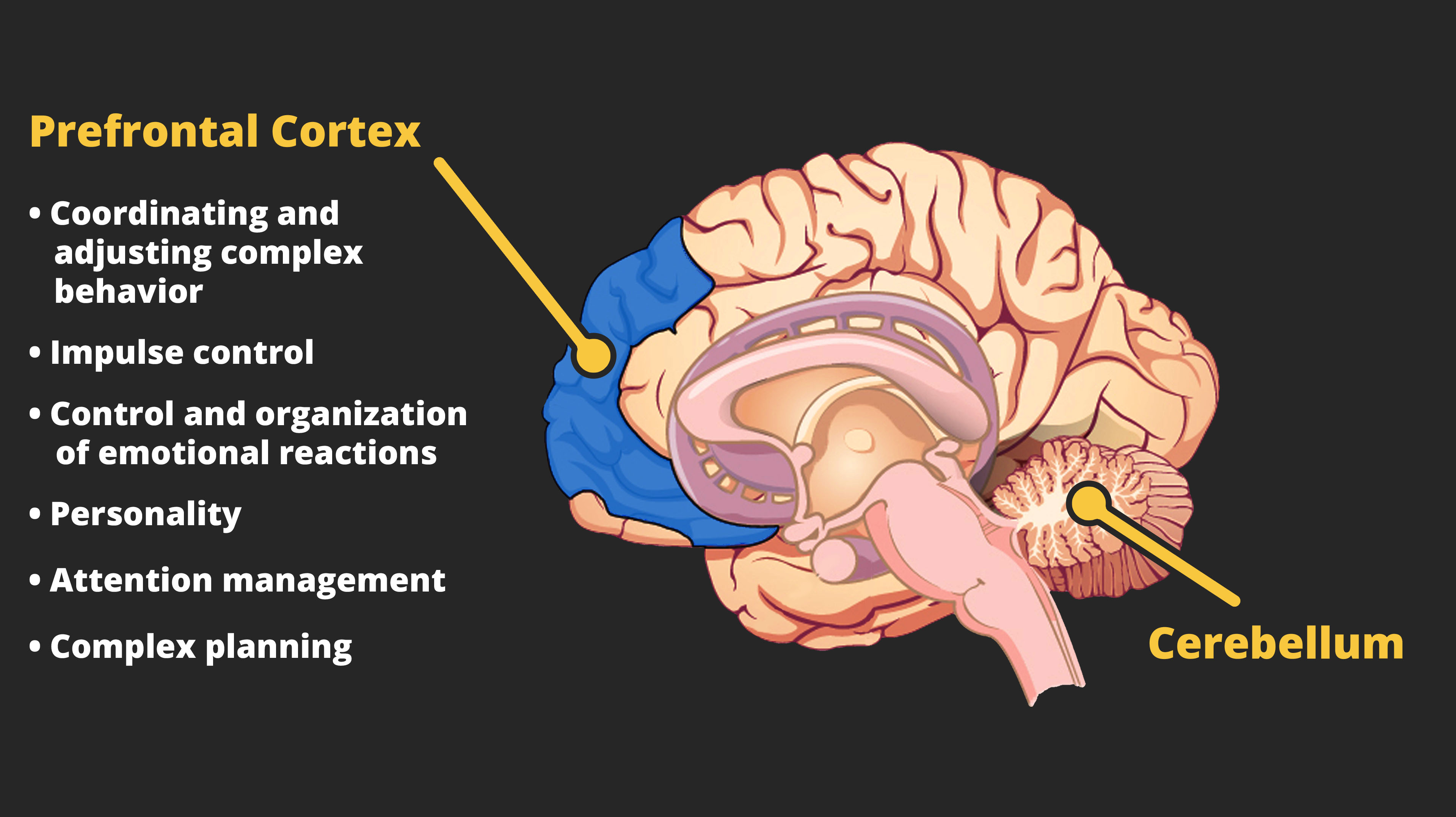
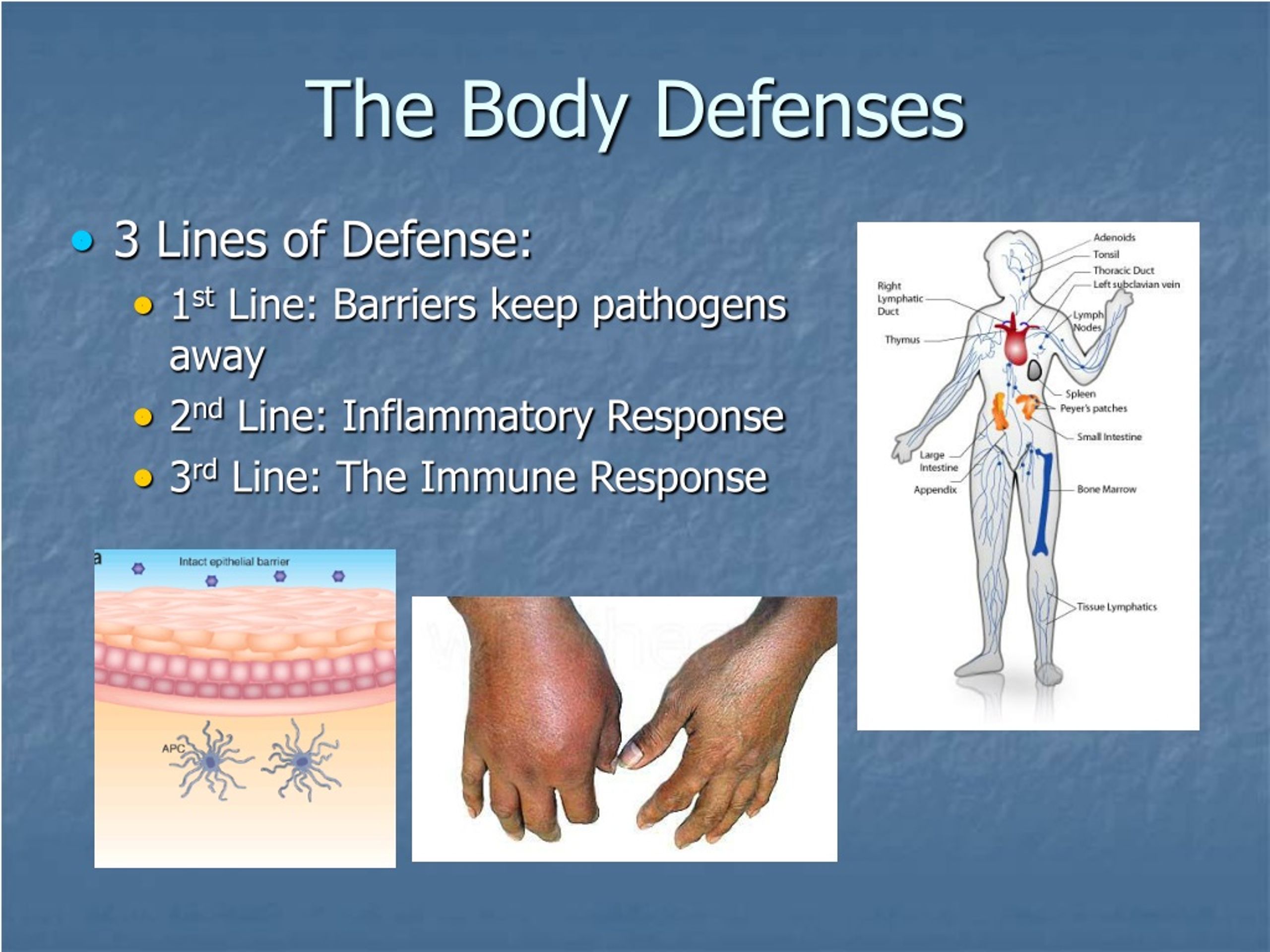
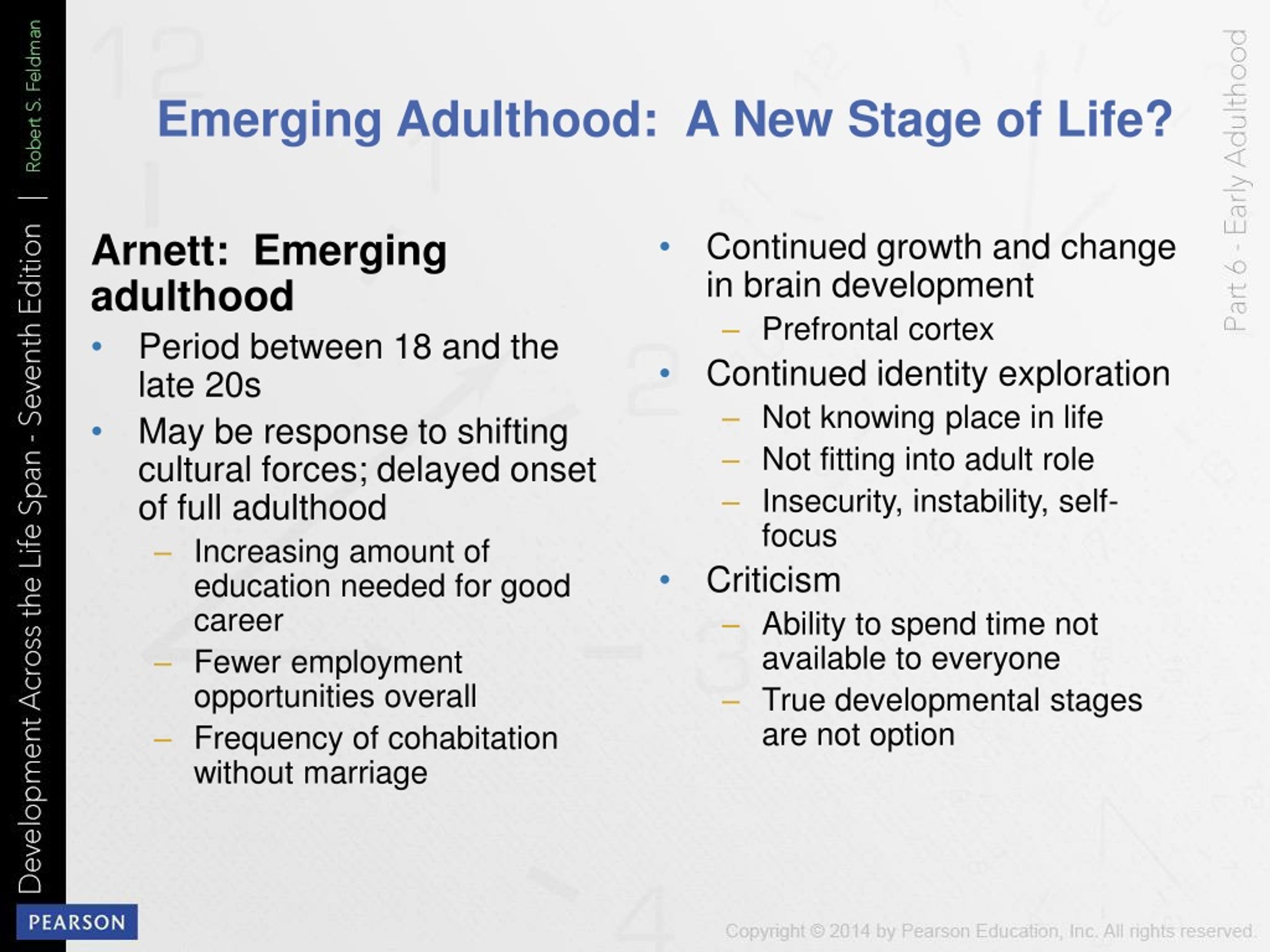
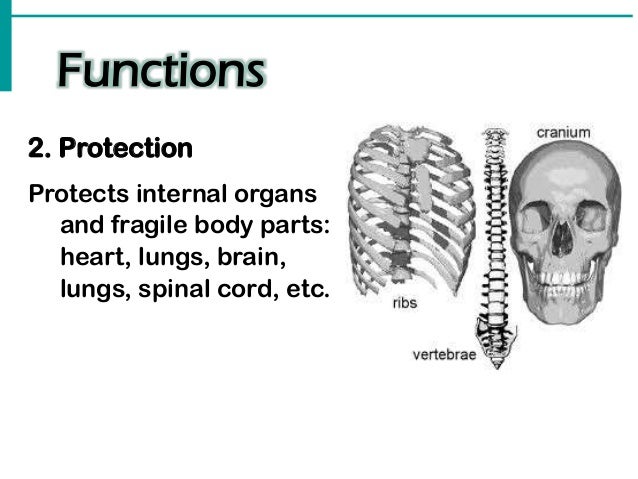
The Three Body Functions That Protect Emerging Adults Are
Emerging adults face unprecedented health risks. Experts identify three critical body functions safeguarding their well-being amidst rising stress and chronic disease threats.
These functions, acting as key defense mechanisms, are crucial for navigating the volatile transition into adulthood, demanding immediate attention and proactive management to mitigate potential long-term health consequences.
The Vital Trio: Core Protective Functions
Researchers at the National Institute of Health (NIH) have pinpointed three primary functions: sleep regulation, stress response, and gut microbiome health.
Each plays a distinct yet interconnected role in preserving the physical and mental equilibrium of emerging adults, aged 18-25.
Sleep Regulation: A Foundation for Resilience
A study published in the Journal of Adolescent Health revealed that over 60% of college students experience chronic sleep deprivation.
Disrupted sleep patterns severely impact cognitive function, mood stability, and immune system efficiency, increasing vulnerability to illness and mental health disorders.
Dr. Anya Sharma, lead researcher, emphasizes that "Prioritizing consistent sleep schedules is paramount for mitigating the pervasive effects of sleep debt in this vulnerable age group."
Stress Response: Calibrating the Body's Alarm System
The chronic activation of the stress response system, driven by academic pressures, financial anxieties, and social uncertainties, poses a significant threat.
Prolonged exposure to stress hormones like cortisol contributes to cardiovascular problems, weakens the immune system, and exacerbates mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
Mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and social support networks are crucial tools for modulating the stress response and promoting resilience, according to a report by the American Psychological Association (APA).
Gut Microbiome Health: The Unsung Hero
The gut microbiome, a complex ecosystem of bacteria residing in the digestive tract, plays a surprisingly critical role in overall health.
Research indicates that a diverse and balanced gut microbiome supports immune function, regulates inflammation, and even influences mood and cognitive function.
Professor David Miller from Stanford University highlights that "Dietary choices, particularly the consumption of processed foods and sugary drinks, can drastically disrupt the gut microbiome, leading to a cascade of negative health consequences."
Interconnectedness and Synergistic Effects
These three functions are not isolated entities but rather interconnected components of a complex system.
For example, sleep deprivation can negatively impact gut microbiome diversity, leading to increased inflammation and heightened stress responses.
Conversely, a healthy gut microbiome can improve sleep quality and enhance stress resilience, creating a positive feedback loop.
Data and Statistics Highlighting the Risks
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that emerging adults experience higher rates of mental health disorders than any other age group.
Studies also show a significant increase in chronic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes among this population, linked to poor lifestyle choices and disrupted physiological functions.
A recent survey by the National College Health Assessment found that over 85% of college students reported feeling overwhelmed by their responsibilities.
Call to Action: Prioritizing Emerging Adult Health
Addressing the health challenges faced by emerging adults requires a multi-faceted approach involving individuals, families, educational institutions, and healthcare providers.
Promoting healthy sleep habits, stress management techniques, and nutritious dietary choices is essential for safeguarding their well-being.
Furthermore, increased awareness and access to mental health services are crucial for addressing the growing mental health crisis among this vulnerable population.
Next Steps and Ongoing Research
The NIH is funding ongoing research to further investigate the intricate relationships between these three critical functions and their impact on emerging adult health.
Future studies will focus on developing targeted interventions and preventative strategies to promote optimal health and well-being during this crucial developmental period.
Public health campaigns aimed at raising awareness and promoting healthy lifestyle choices are also underway to empower emerging adults to take control of their health.