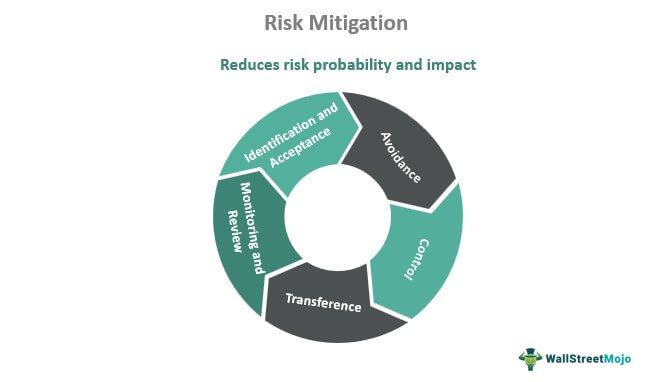
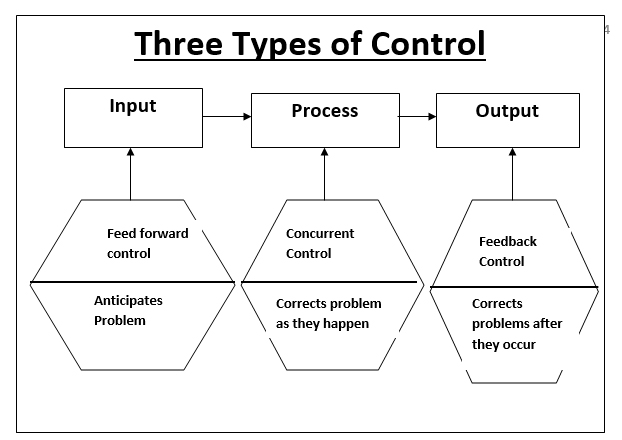
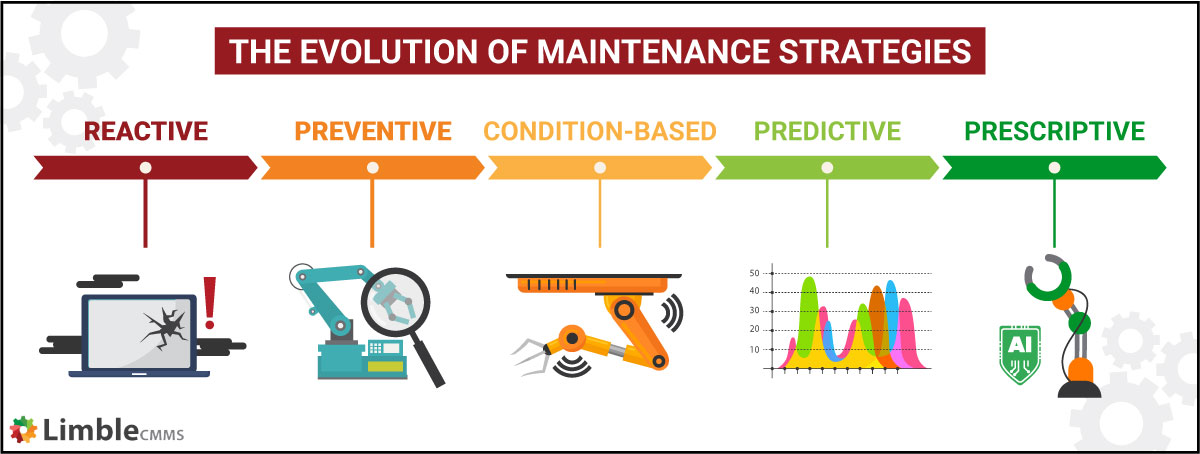
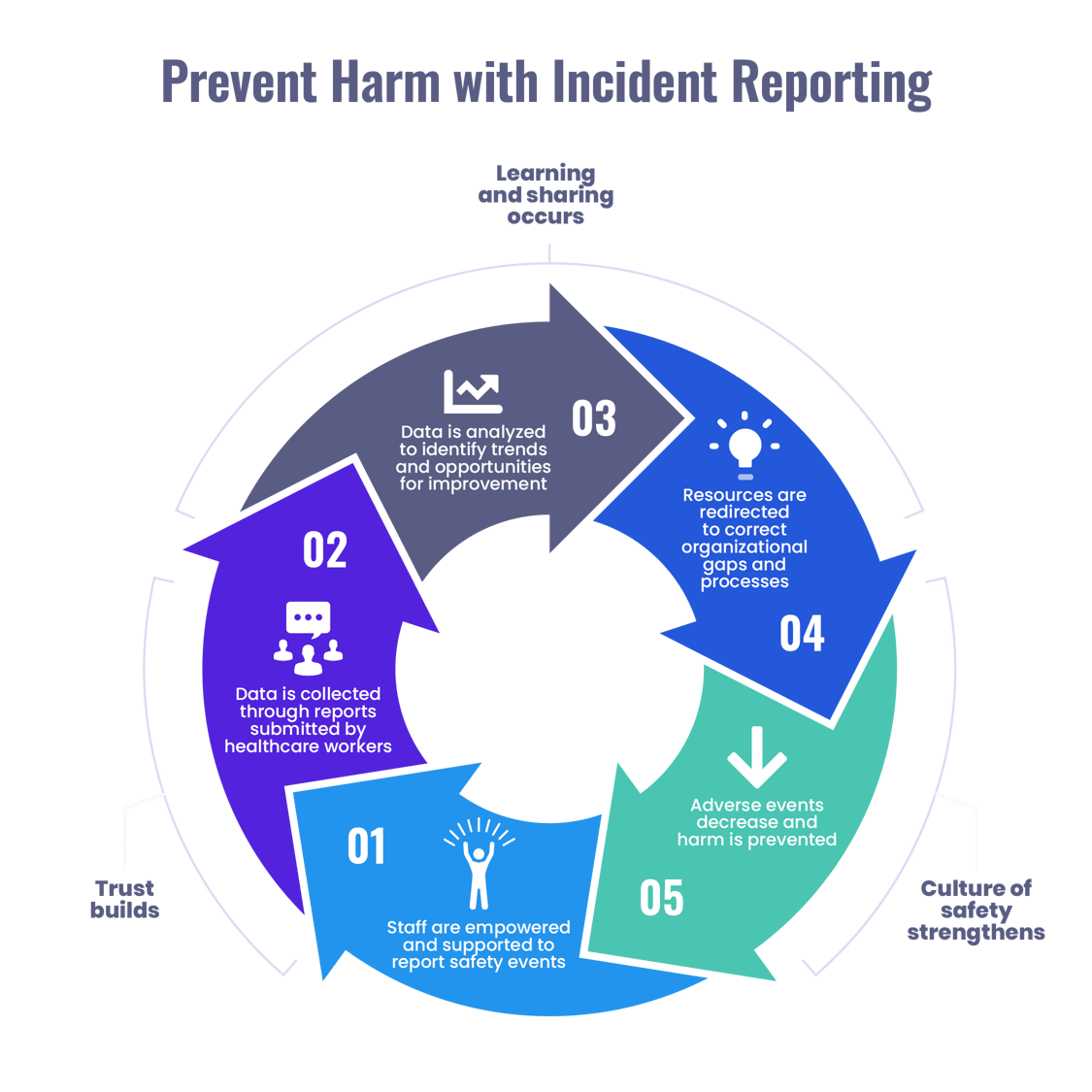
This Type Of Control Focuses On Preventing Potential Future Issues.

Imagine a sprawling garden, lush and vibrant, where the gardener isn't just pulling weeds as they sprout, but actively nurturing the soil, anticipating droughts, and building protective barriers against potential storms. This proactive approach, a foresight that goes beyond immediate problem-solving, is increasingly becoming the defining strategy in various fields, from business to healthcare to environmental management.
This article explores the concept of preventive control, a forward-thinking management strategy focused on identifying and mitigating potential risks before they materialize, fostering long-term stability and success. We will delve into its core principles, explore its applications across different sectors, and examine its growing importance in an increasingly uncertain world.
The Essence of Preventive Control
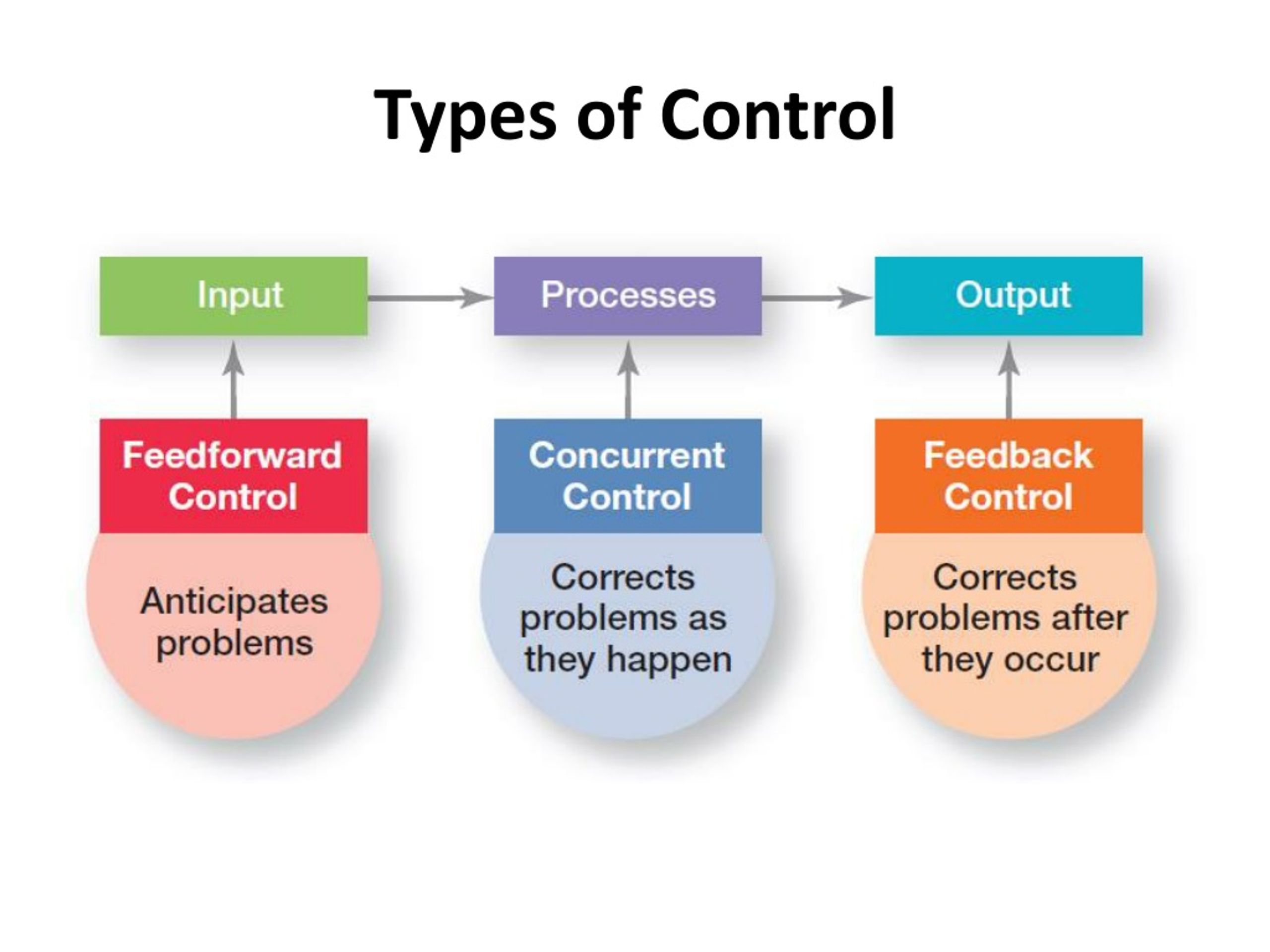
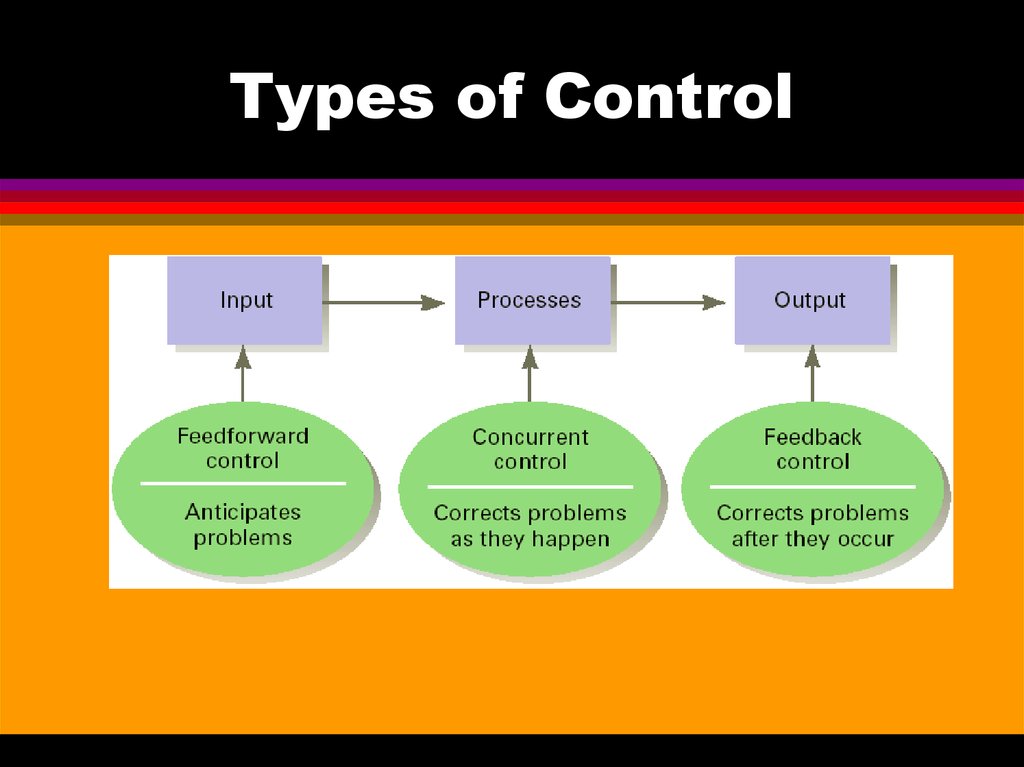
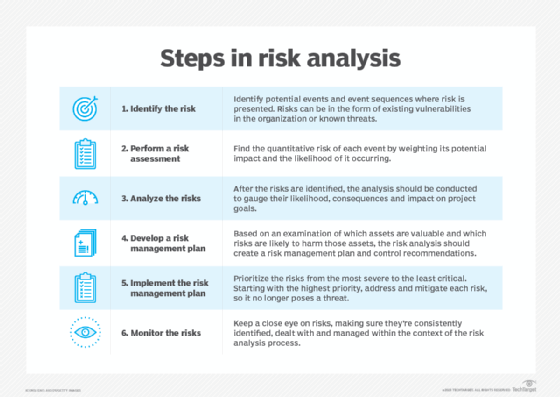
Preventive control is, at its heart, about anticipation. It's about looking beyond the present and envisioning potential future problems, then taking steps to avoid them altogether. Instead of reacting to crises, preventive control aims to create systems and processes that make crises less likely to occur in the first place.
This approach contrasts sharply with reactive control, which addresses issues only after they arise. Think of reactive control as patching a leak in a dam after it's already started gushing; preventive control, on the other hand, involves reinforcing the dam's structure and monitoring water levels to prevent leaks from forming in the first place.
A Historical Perspective
The roots of preventive control can be traced back to various disciplines. In public health, for instance, vaccination programs represent a classic example of preventive control, aiming to build immunity against diseases before exposure occurs.
Similarly, in engineering, preventative maintenance schedules for machinery aim to avoid breakdowns and extend the equipment's lifespan. The concept gained significant traction in the business world during the Total Quality Management (TQM) movement of the late 20th century, which emphasized continuous improvement and proactive risk management.
Preventive Control in Action: Examples Across Sectors
Preventive control isn't just a theoretical concept; it's a practical strategy being implemented in diverse sectors with tangible results.
Business and Finance
In the corporate world, preventive control manifests in various ways. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures to prevent data breaches is a prime example of preventive action.
Financial institutions use predictive modeling to identify and mitigate risks associated with lending and investment, preventing potential financial losses. Supply chain diversification is another key preventative measure, reducing dependence on single suppliers and mitigating disruptions caused by geopolitical events or natural disasters.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector has long embraced preventive control as a cornerstone of public health. Regular check-ups, screenings for diseases like cancer, and promoting healthy lifestyles are all examples of preventive measures aimed at reducing the incidence and severity of illnesses.
Hospitals implement strict infection control protocols to prevent the spread of healthcare-associated infections. The current emphasis on mental wellness programs within workplaces and communities also represents a shift towards preventative care, aimed at reducing stress and improving emotional wellbeing before crises arise.
Environmental Management
Environmental management increasingly relies on preventive control strategies to address pressing global challenges. Implementing regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote renewable energy sources is a key example of preventing future climate change impacts.
Sustainable agriculture practices that minimize soil erosion and water pollution are also preventive measures. Reforestation efforts aim to prevent deforestation and its associated ecological consequences, preserving biodiversity and mitigating climate change effects.
The Benefits and Challenges of Preventive Control
The advantages of adopting a preventive control approach are manifold. By anticipating and mitigating potential risks, organizations can reduce costs associated with crises, such as repairs, lawsuits, or lost productivity.
Preventive control enhances operational efficiency by streamlining processes and avoiding disruptions. Most importantly, it strengthens an organization's resilience, enabling it to weather unforeseen challenges and emerge stronger.
However, implementing preventive control also presents challenges. It requires a significant investment in resources, including time, money, and expertise. Resistance to change from employees accustomed to reactive problem-solving can also hinder implementation.
Accurately assessing future risks and predicting their potential impact is inherently difficult. It can be challenging to measure the effectiveness of preventive measures, as the absence of a crisis doesn't necessarily prove their success. This is sometimes known as the "prevention paradox" - when preventative measures are so successful, people forget the original threat.
The Role of Technology
Technological advancements are playing a crucial role in enhancing preventive control capabilities. Data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are enabling organizations to identify patterns and predict potential risks more accurately.
The Internet of Things (IoT) allows for real-time monitoring of equipment and environmental conditions, enabling early detection of anomalies that could lead to problems. Cloud-based platforms facilitate collaboration and information sharing, improving coordination of preventive efforts across different departments and organizations.
For example, in manufacturing, AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors on machinery to predict equipment failures and schedule preventative maintenance, minimizing downtime and increasing productivity.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Preventive Control
As the world becomes increasingly complex and interconnected, the importance of preventive control will only grow. Organizations will need to become more proactive in identifying and mitigating potential risks to thrive in an uncertain environment.
This will require a shift in mindset, from reacting to problems to anticipating them. Investments in technology, training, and organizational culture will be crucial to building preventive control capabilities.
Collaboration and information sharing will also be essential, as many risks transcend organizational boundaries. From combating climate change to preventing pandemics, the future of many of the world's biggest challenges depend on our ability to anticipate issues and act proactively.
Ultimately, the adoption of preventive control isn't just about avoiding problems; it's about building a more resilient, sustainable, and prosperous future for all.