Troubleshoot My Internet Connection
Frustration with sluggish internet speeds and dropped connections is a ubiquitous experience in the digital age, impacting everything from remote work productivity to streaming entertainment. Understanding the common causes of these issues and how to troubleshoot them is becoming an increasingly vital skill for navigating modern life.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to diagnosing and resolving common internet connection problems. We will explore a range of troubleshooting steps, from simple fixes like restarting equipment to more advanced techniques for identifying network bottlenecks and optimizing wireless performance. The goal is to empower readers to take control of their internet experience and minimize downtime.
Basic Troubleshooting: The First Line of Defense
Before diving into complex diagnostics, start with the fundamentals. The most common, and often surprisingly effective, first step is the "power cycle."
Simply unplug your modem and router from the power outlet, wait about 30 seconds, and then plug the modem back in first. Allow the modem to fully initialize (usually indicated by a stable set of lights) before plugging the router back in. This process often resolves temporary glitches and clears cached data that can interfere with connectivity.
Check all physical connections, ensuring that cables are securely plugged into the correct ports. Look for any signs of damage to cables, such as fraying or kinks. Even a slightly loose or damaged cable can significantly degrade internet performance.
Identifying the Source of the Problem
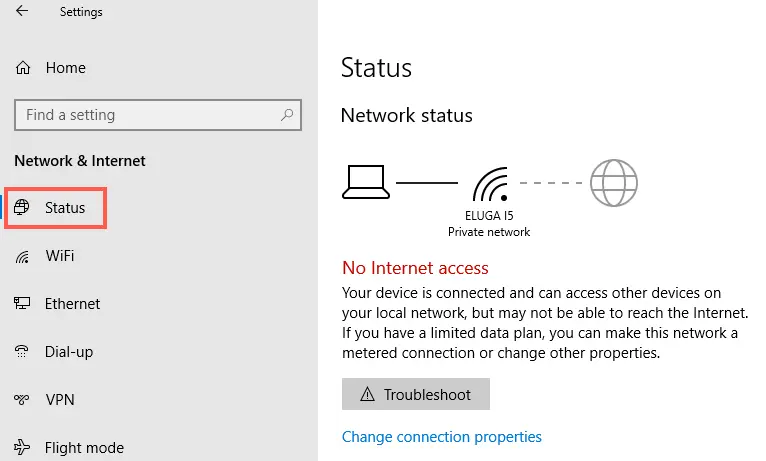
If the power cycle doesn't work, the next step is to pinpoint where the problem lies. Is it with your devices, your home network, or your internet service provider (ISP)?
Connect a device directly to the modem using an Ethernet cable, bypassing the router. If the internet works fine when connected directly to the modem, the issue is likely with your router or wireless network. If the problem persists even with a direct connection, it suggests a problem with your modem or the ISP's service.
Router Configuration and Wireless Interference
Routers can be a source of many internet problems. Ensure your router's firmware is up to date.
Visit the manufacturer's website to download and install the latest firmware. Outdated firmware can contain bugs that affect performance and security.
Wireless interference can significantly impact Wi-Fi speeds. Common sources of interference include microwave ovens, cordless phones, and other electronic devices operating on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. Try switching to the 5 GHz band on your router, which is less prone to interference, if your devices support it.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
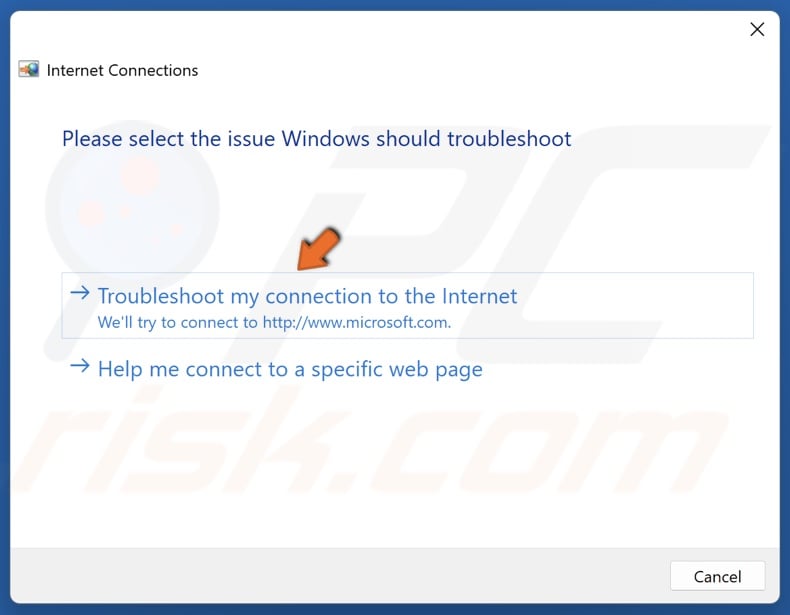
If basic troubleshooting doesn't resolve the issue, consider more advanced techniques. One useful tool is a speed test website, such as Speedtest.net.
These tests measure your download and upload speeds, as well as latency (ping). Compare the results to the speeds you are paying for from your ISP. If the measured speeds are consistently lower than expected, contact your ISP to report the problem.
Analyzing your network traffic can help identify bottlenecks and bandwidth hogs. Many routers have built-in traffic monitoring tools. This feature will help you see which devices are consuming the most bandwidth.
When to Call Your ISP
There are times when the problem is beyond your control and requires professional assistance. If you've tried all the troubleshooting steps and the internet still isn't working, it's time to contact your ISP.
Be prepared to provide them with details about the troubleshooting steps you've already taken. This will help them diagnose the problem more quickly.
According to FCC data, customer satisfaction with ISPs is often linked to the speed and reliability of their internet service. Therefore, ISPs are often responsive to customer complaints about internet performance.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting internet connection issues can be a frustrating experience, but by following these steps, you can often diagnose and resolve the problem yourself. Remember to start with the basics, systematically investigate the source of the problem, and don't hesitate to contact your ISP if necessary. With a little patience and persistence, you can get your internet back up and running smoothly.